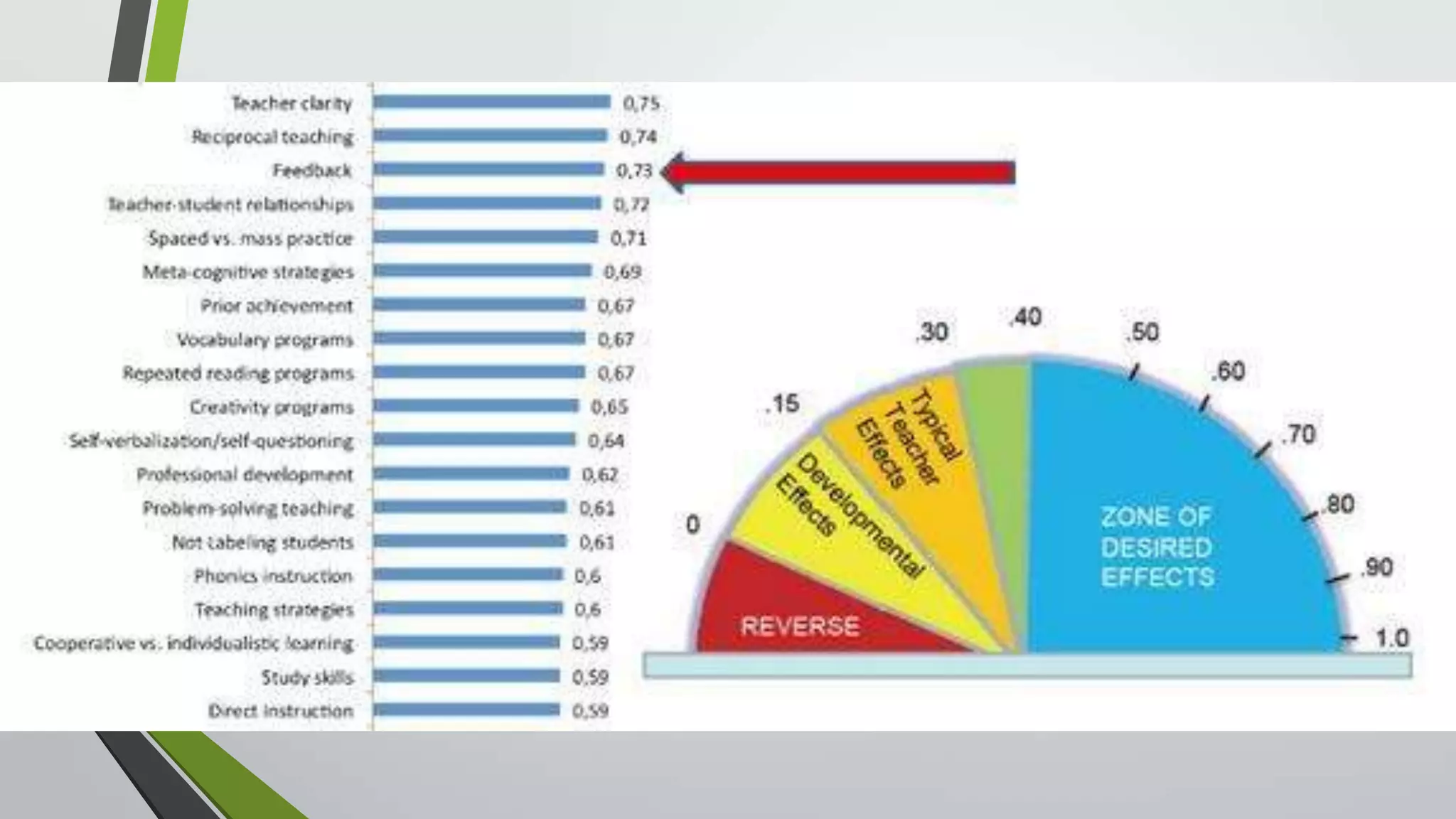
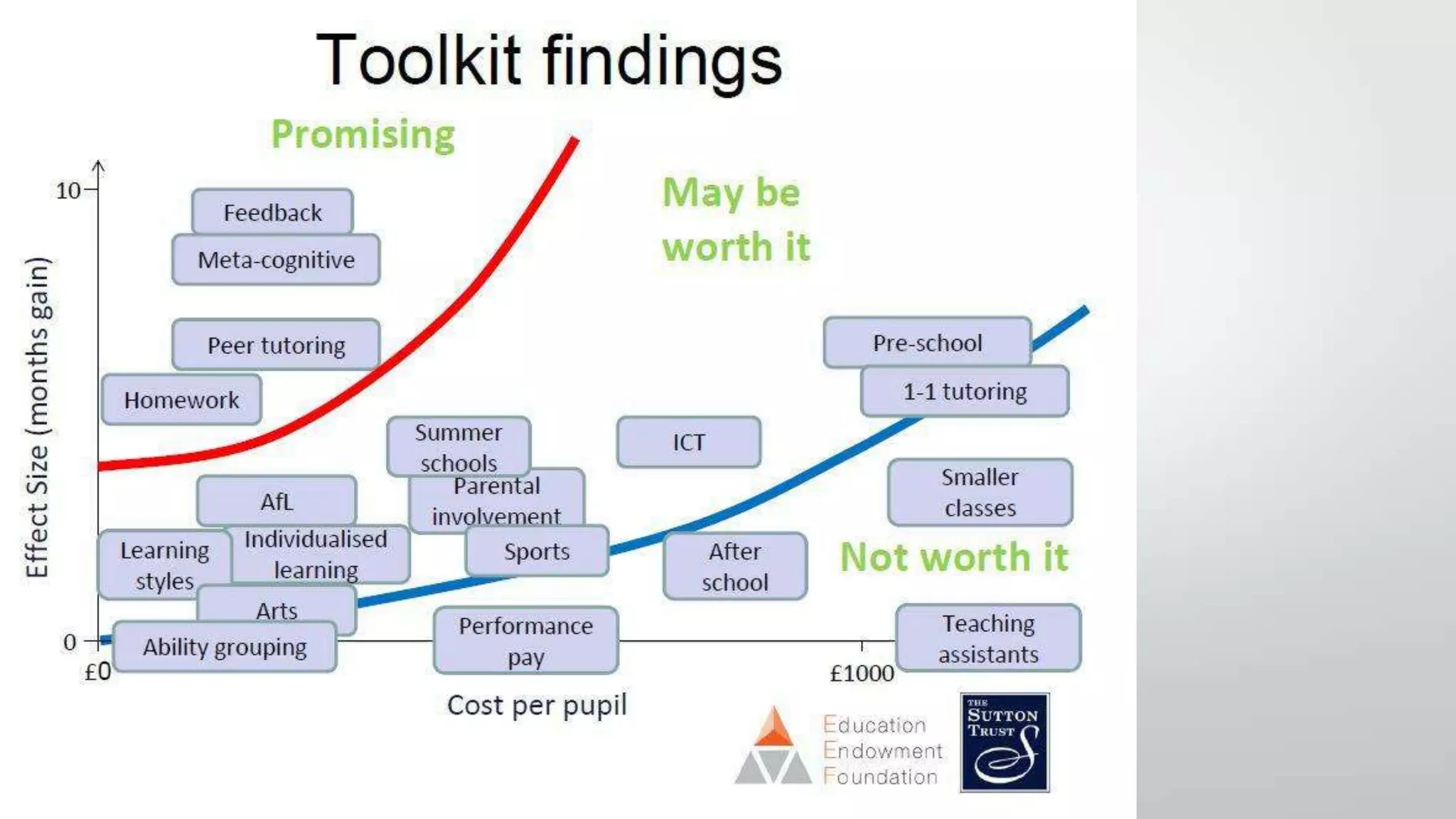
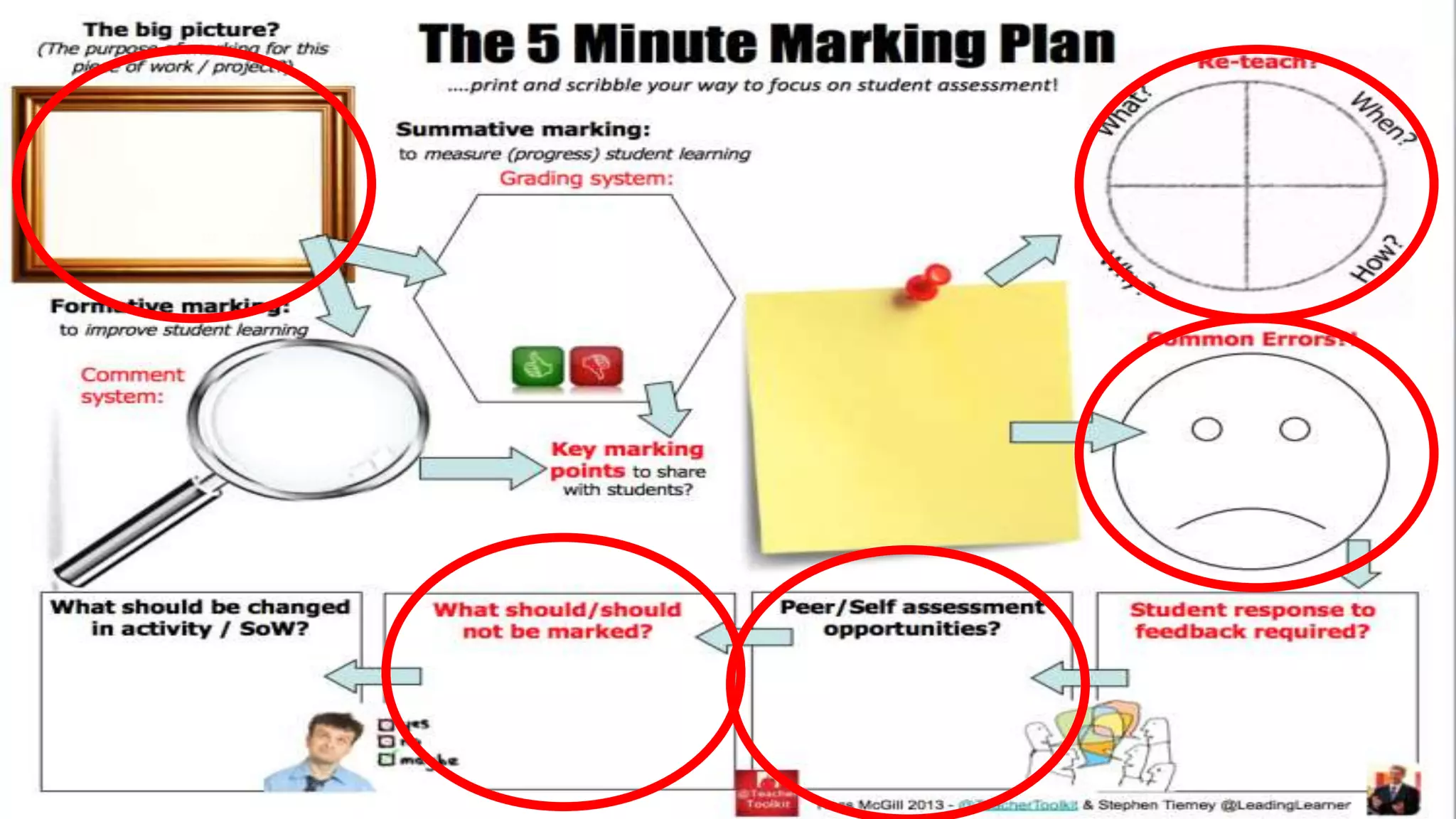
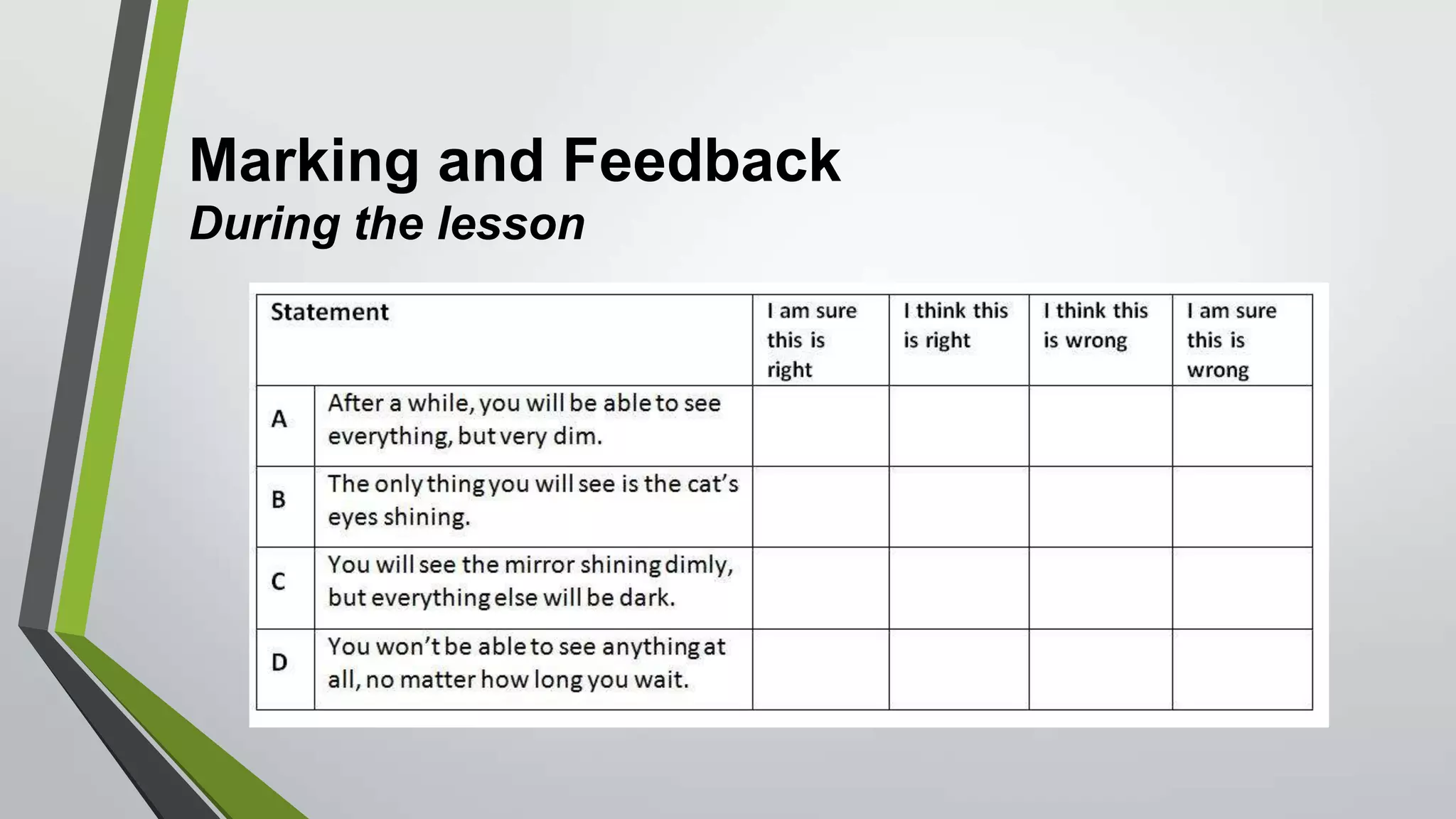
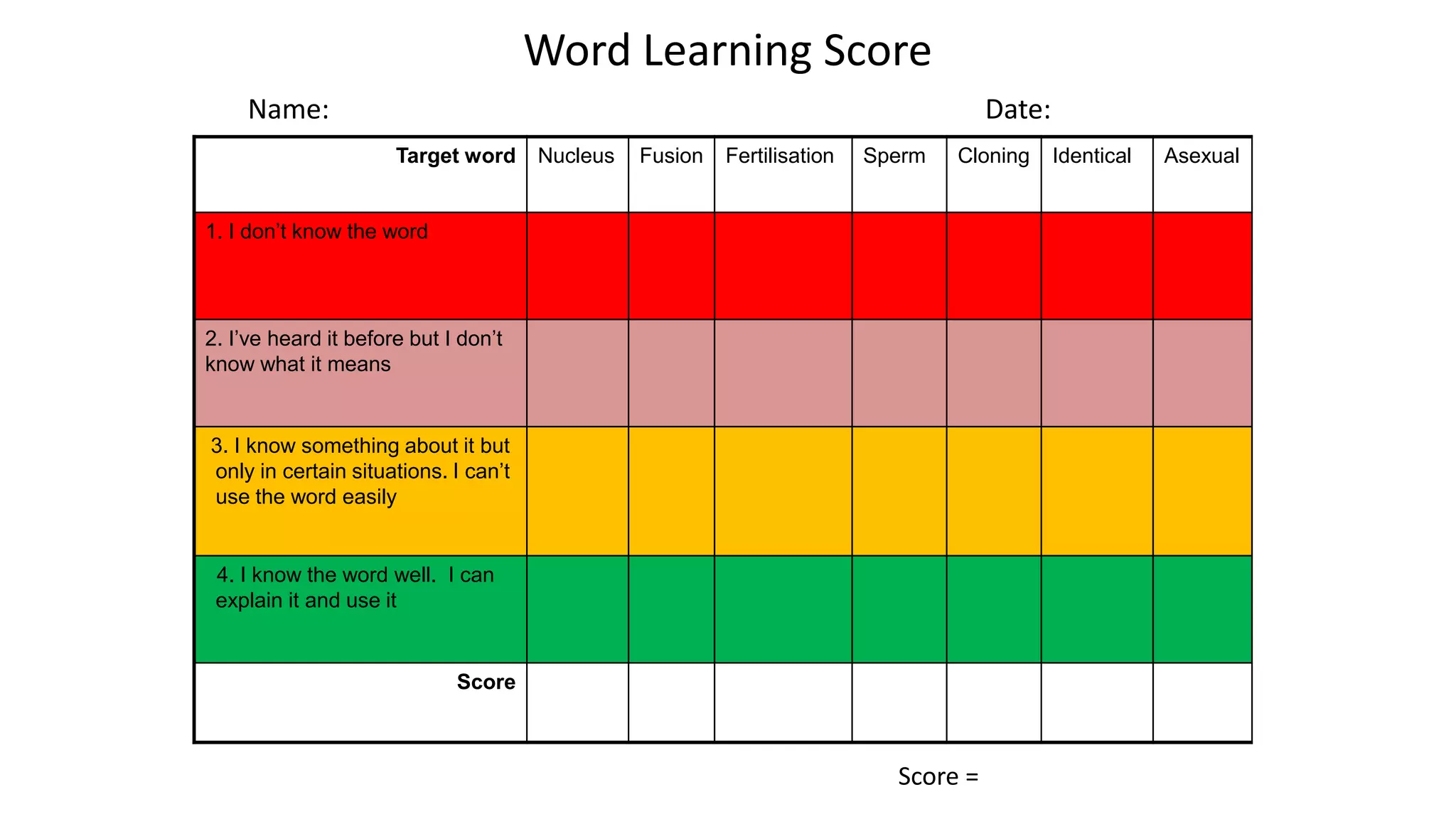
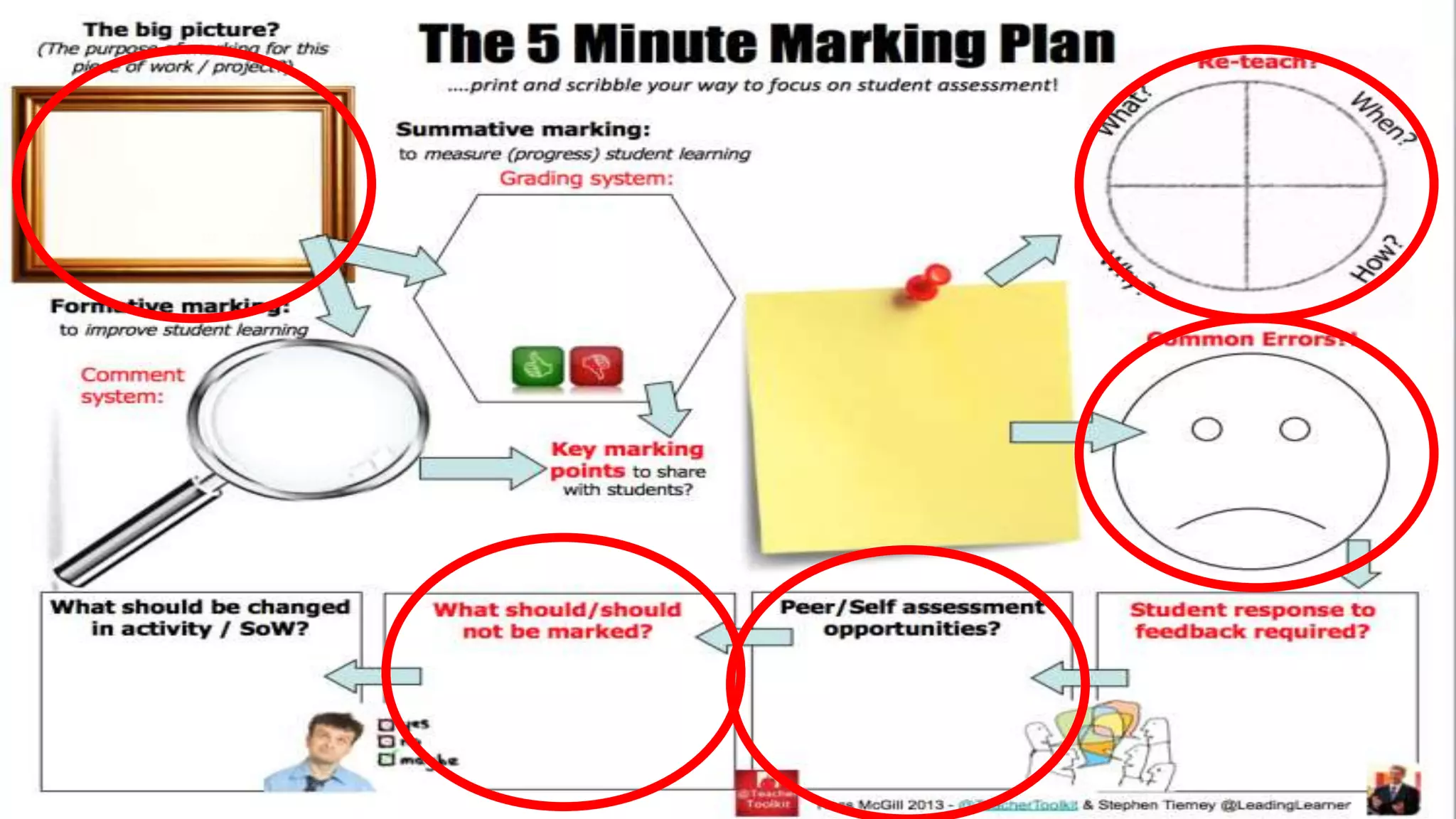
This document discusses feedback and marking in the science classroom. It summarizes research showing that feedback is most effective when it reduces the gap between where students are and where they need to be. Feedback should provide clear next steps for students and cause them to think and monitor their own learning. The most useful feedback is focused on learning goals, prompts future action, and makes students do more work than the teacher. The document also discusses providing feedback before, during, and after lessons through techniques like pre-assessments, self-scoring quizzes, and dedicated reflection time.