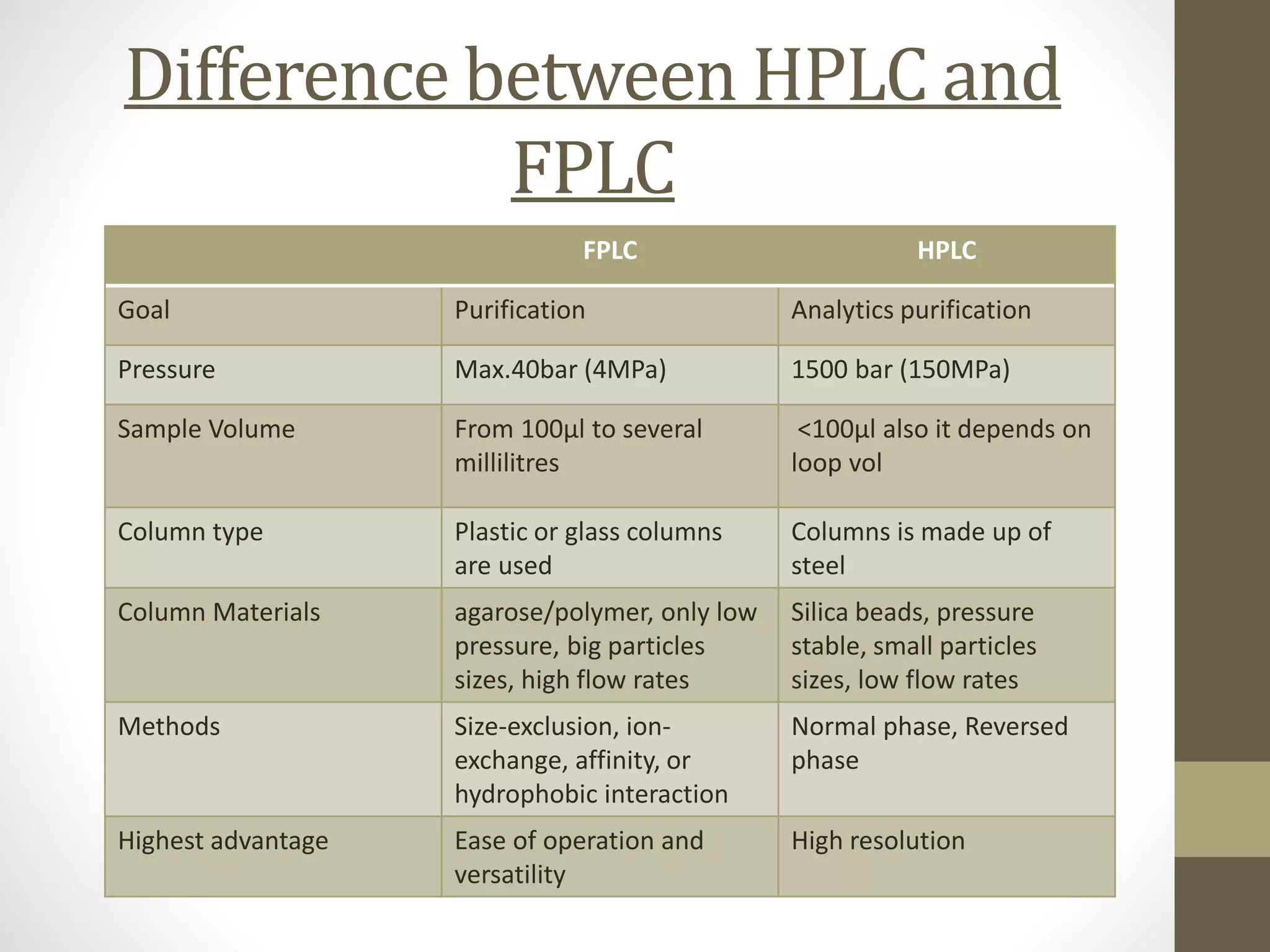
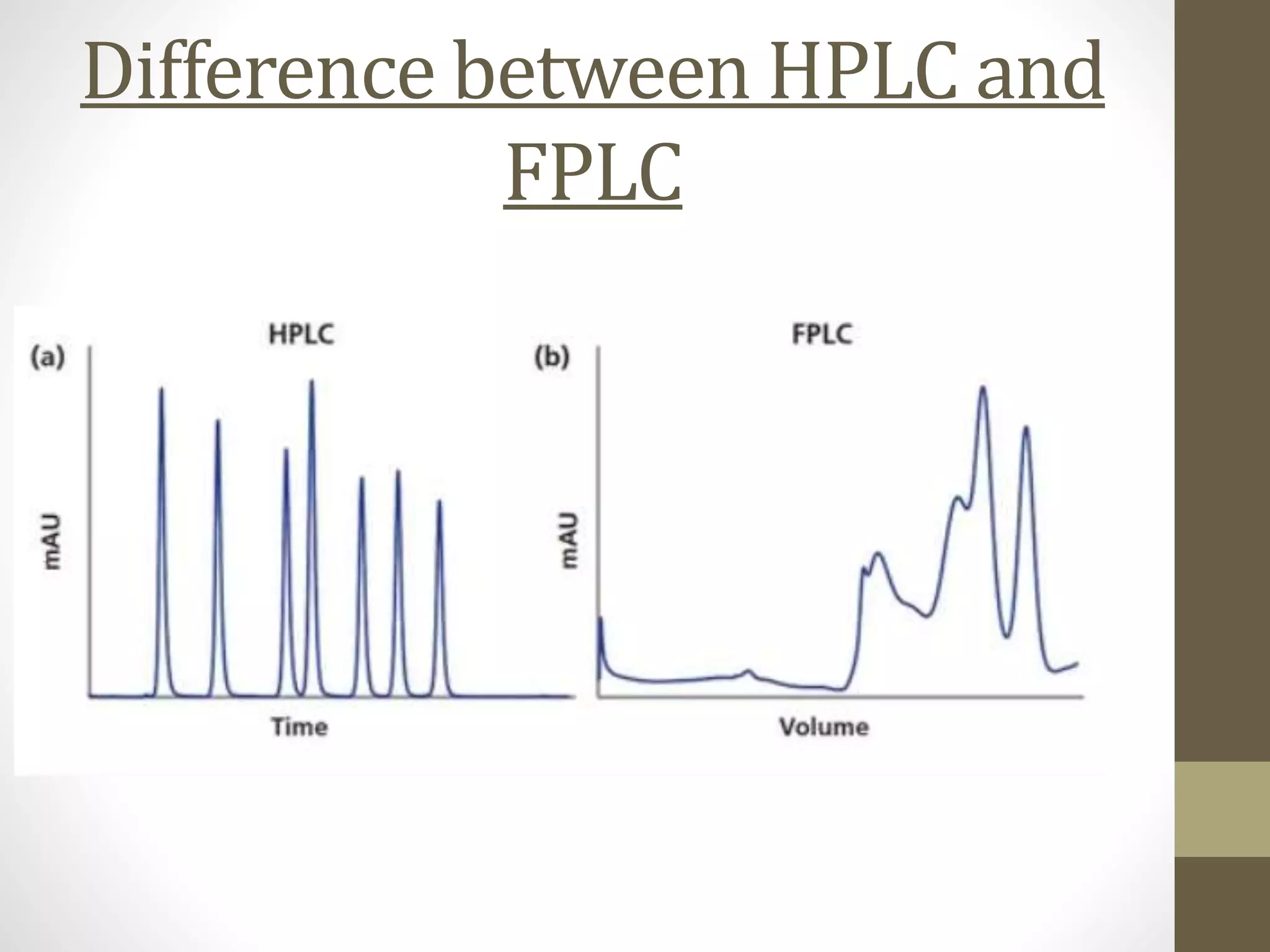
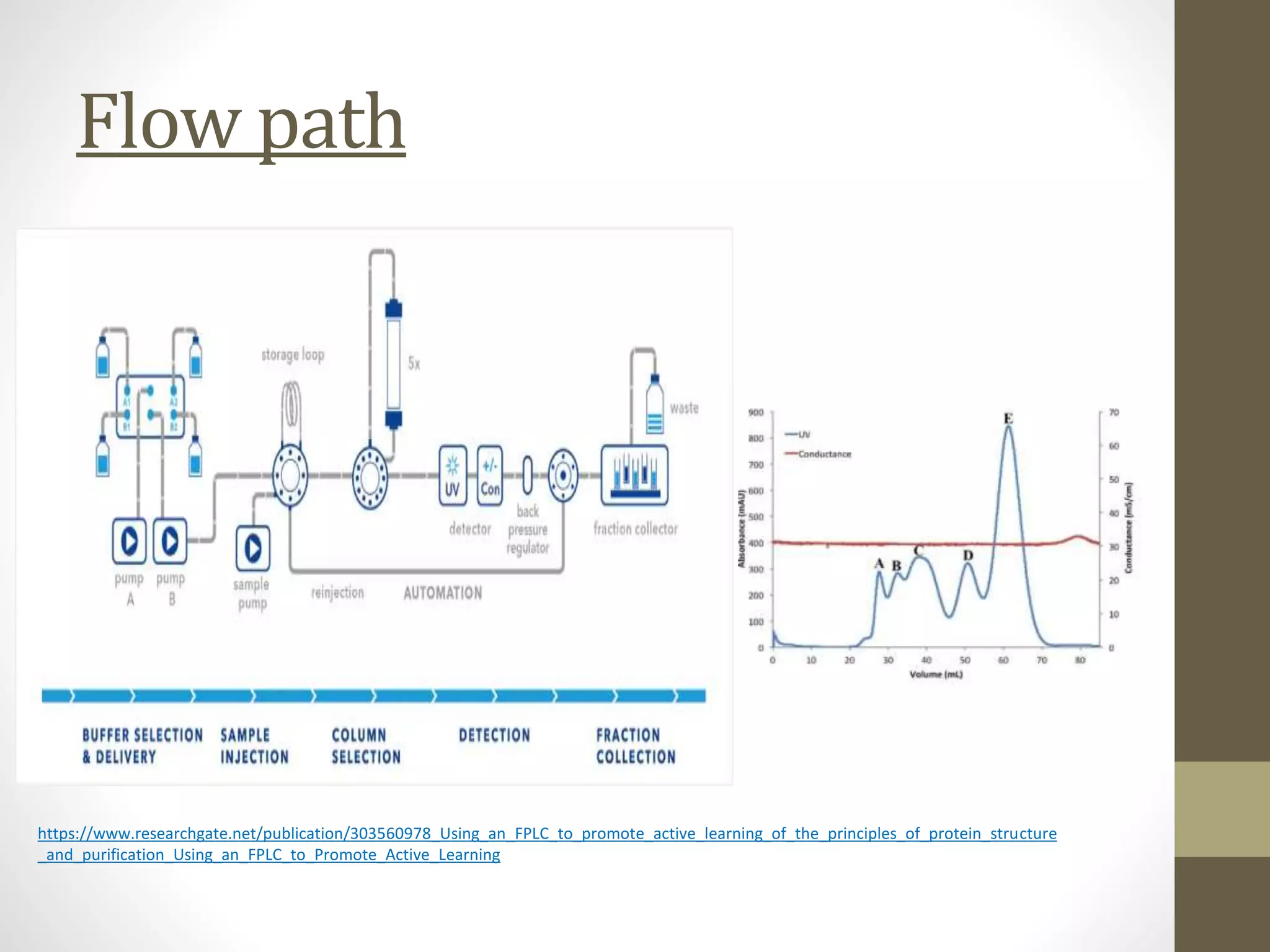
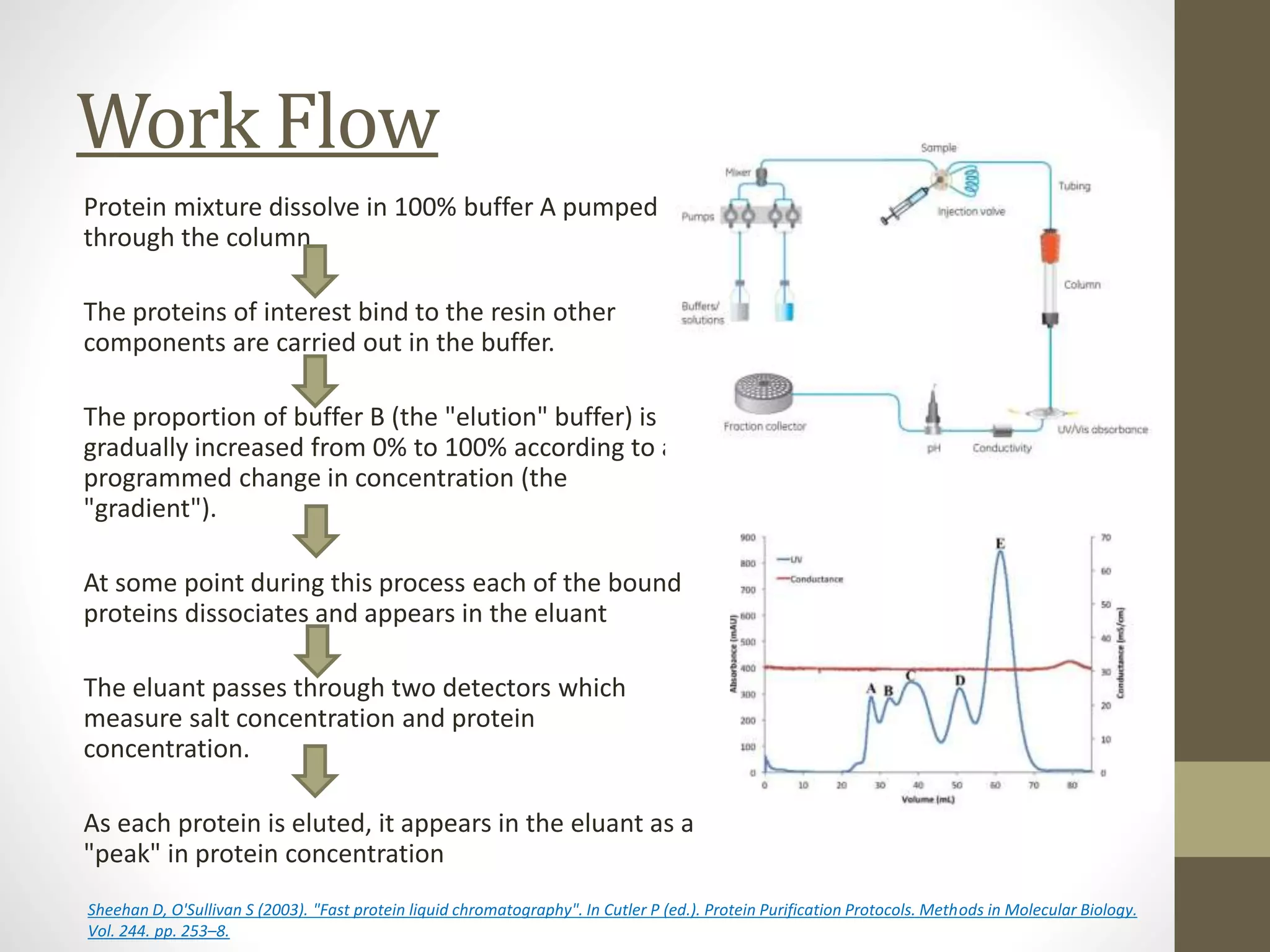
Fast Protein Liquid Chromatography (FPLC) is a technique used to separate and purify proteins based on their interactions with a stationary phase and a mobile phase. FPLC operates at lower pressures compared to High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) and utilizes a range of methods including affinity, size-exclusion, and ion-exchange chromatography. The process involves binding proteins to a resin, followed by elution using a gradient of buffers, and is supported by various instrumentation for monitoring and collecting samples.