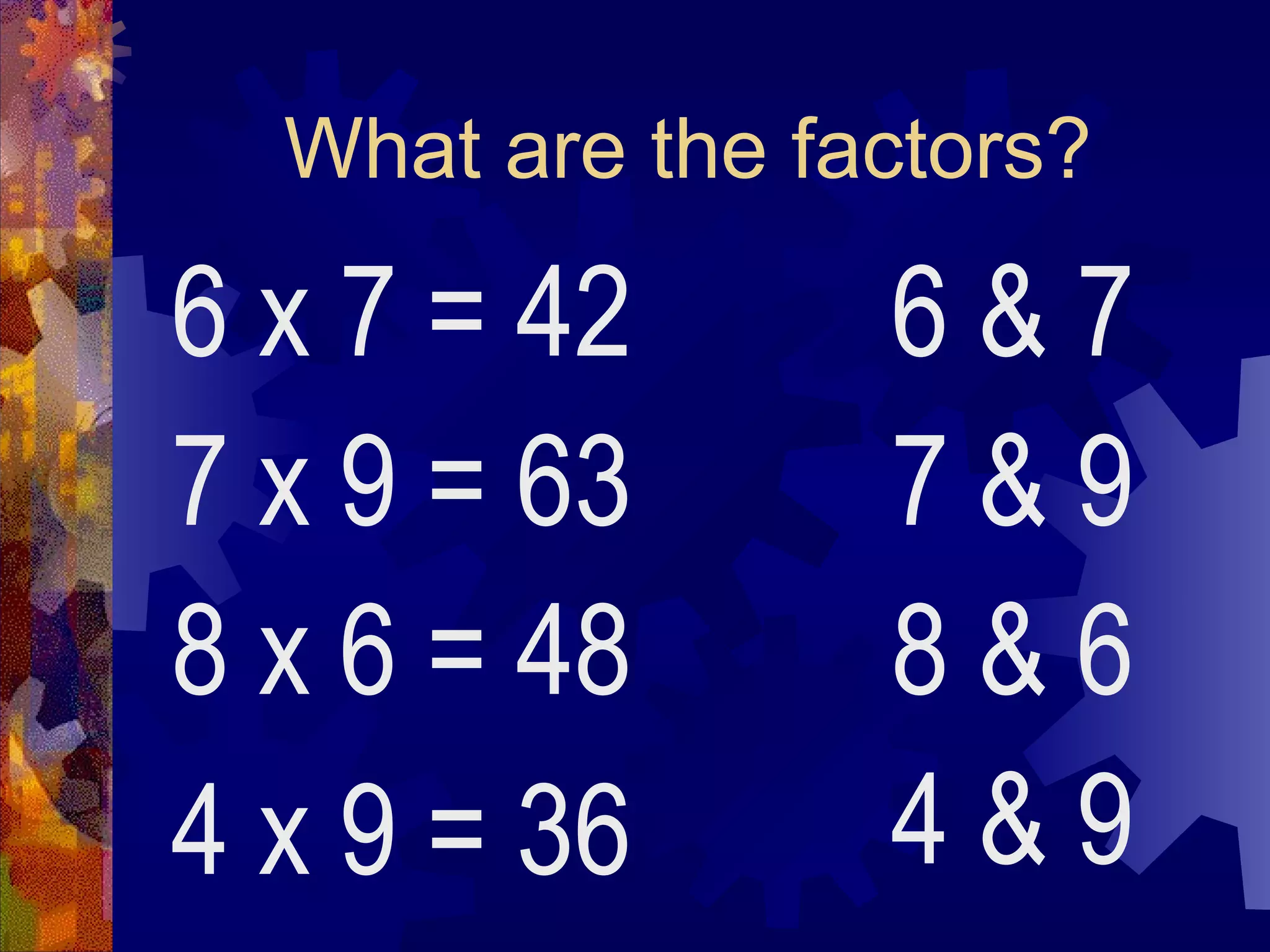This document defines key terms related to prime and composite numbers including: product, factor, prime number, composite number, and prime factorization. A prime number has exactly two factors - itself and 1. A composite number has more than two factors. Prime factorization is writing a composite number as the product of its prime factors. The document provides examples of prime and composite numbers and demonstrates how to perform prime factorization using a factor tree method.