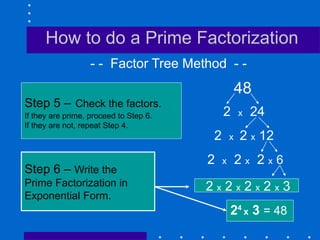
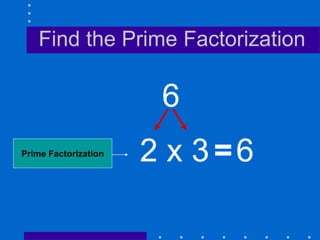
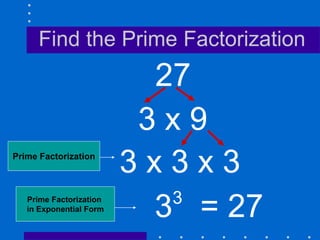
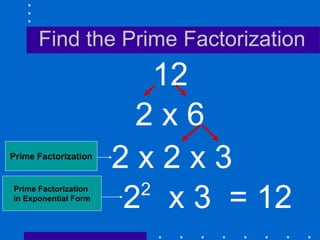
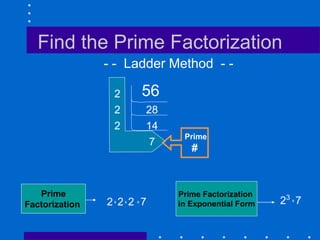
Factors, prime numbers, and composite numbers are defined. A prime number has exactly two factors, 1 and itself. A composite number has more than two factors and can be written as a product of prime numbers through prime factorization. Prime factorization involves repeatedly dividing a composite number by prime numbers and writing the results in exponential form.