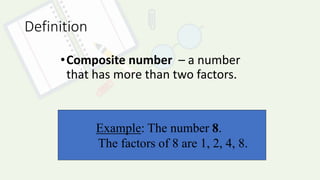
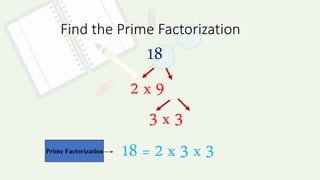
The document defines prime and composite numbers and provides examples of each. A prime number is only divisible by 1 and itself, while a composite number has more than two factors. Methods for determining if a number is prime or composite are presented, as well as two approaches for finding the prime factorization of composite numbers by breaking them down into products of prime numbers.