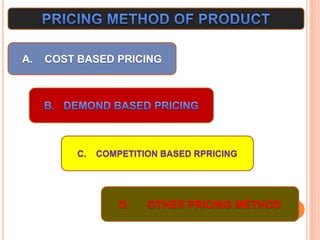
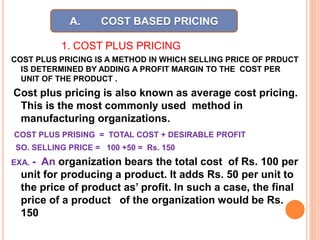
This document discusses various factors that affect pricing of products and different pricing methods. It outlines internal factors like product costs, quality and external factors like competition, demand. Pricing methods covered include cost-based pricing using cost-plus or mark-up approaches, competition-based pricing by considering competitors' prices, and other methods like value, target return, going rate and transfer pricing. The key factors and various pricing strategies are compared and explained with examples.