This document introduces the version control system Git. It discusses:
- The creator of Git, Linus Torvalds, who developed it to enable collaboration on open source projects.
- What Git is used for, including managing code versions, group collaboration, and reverting to old versions.
- How to download and set up Git on different operating systems.
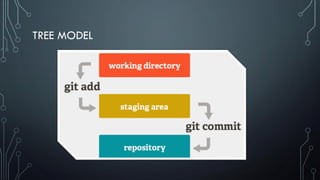
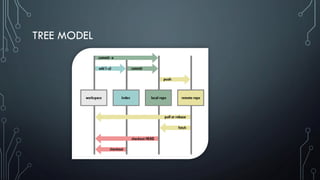
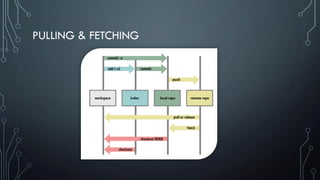
- Important Git commands for adding, committing, pushing, pulling changes and resolving conflicts when merging branches.
- Alternatives to the command line interface for Git including graphical user interfaces and GitHub.