Management of Extravasations of Chemotherapy
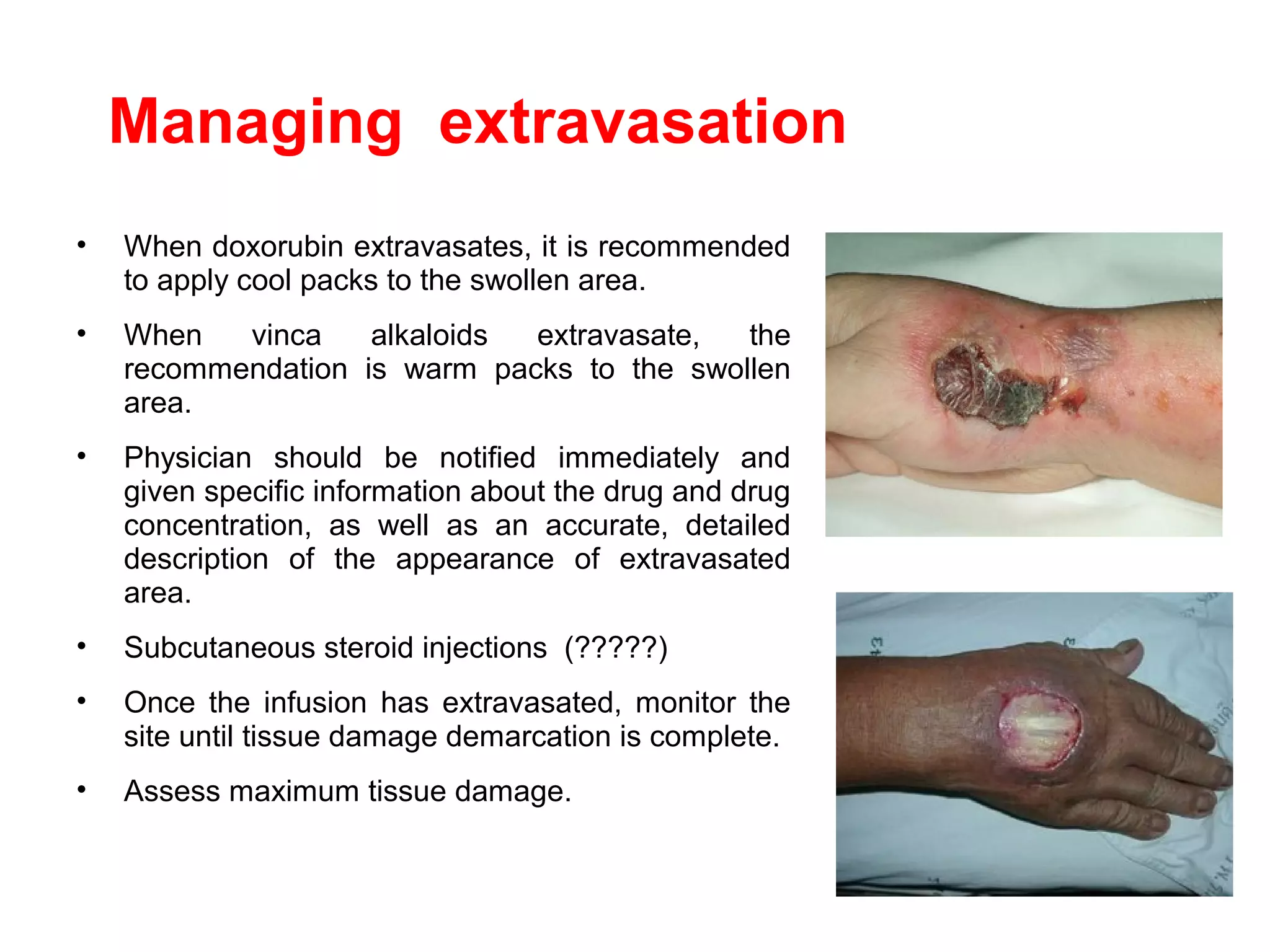
1) Extravasation occurs when chemotherapy drugs leak into the surrounding tissues rather than entering the vein, and can cause damage ranging from mild skin reactions to severe tissue necrosis, depending on the drug.
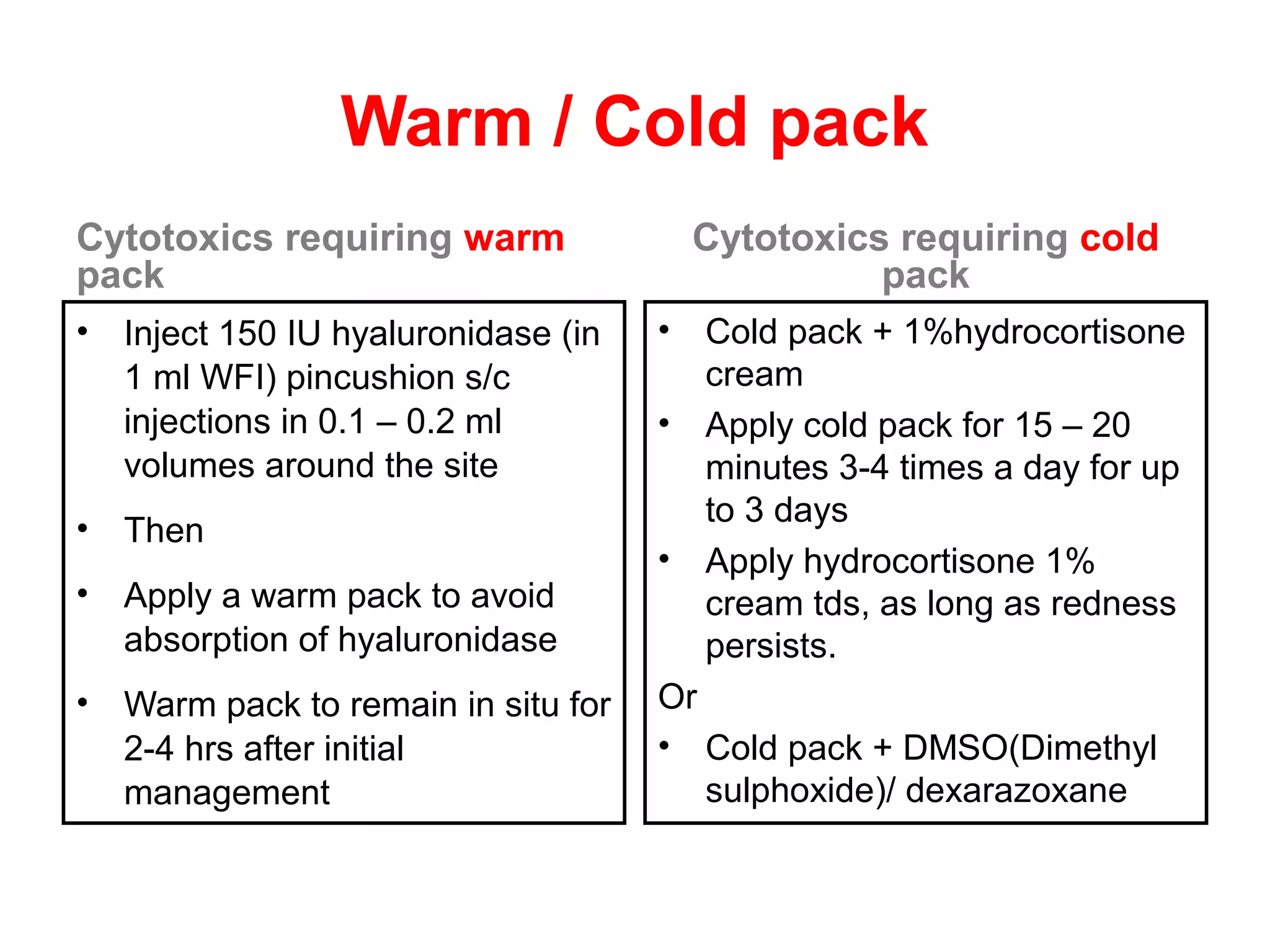
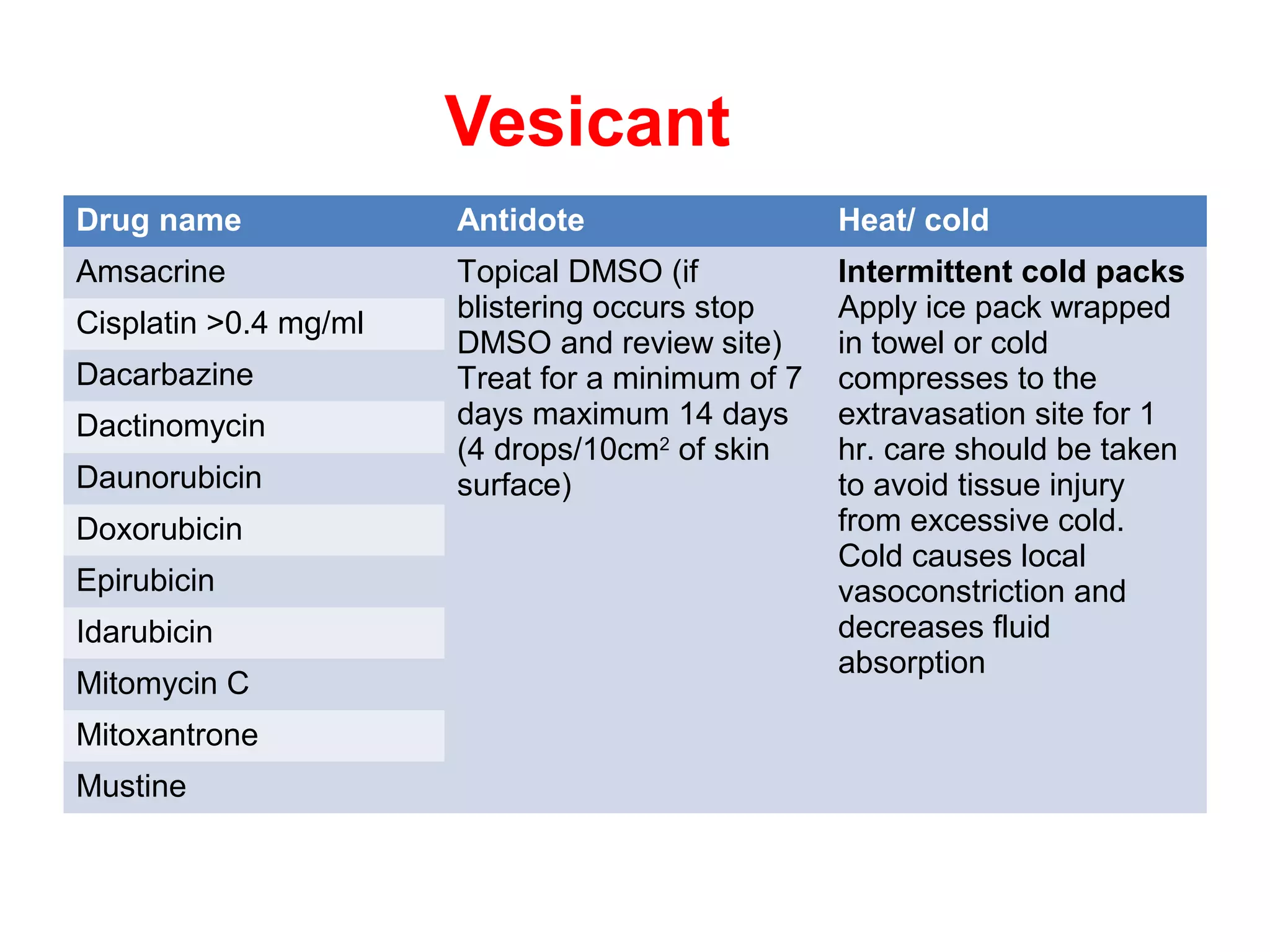
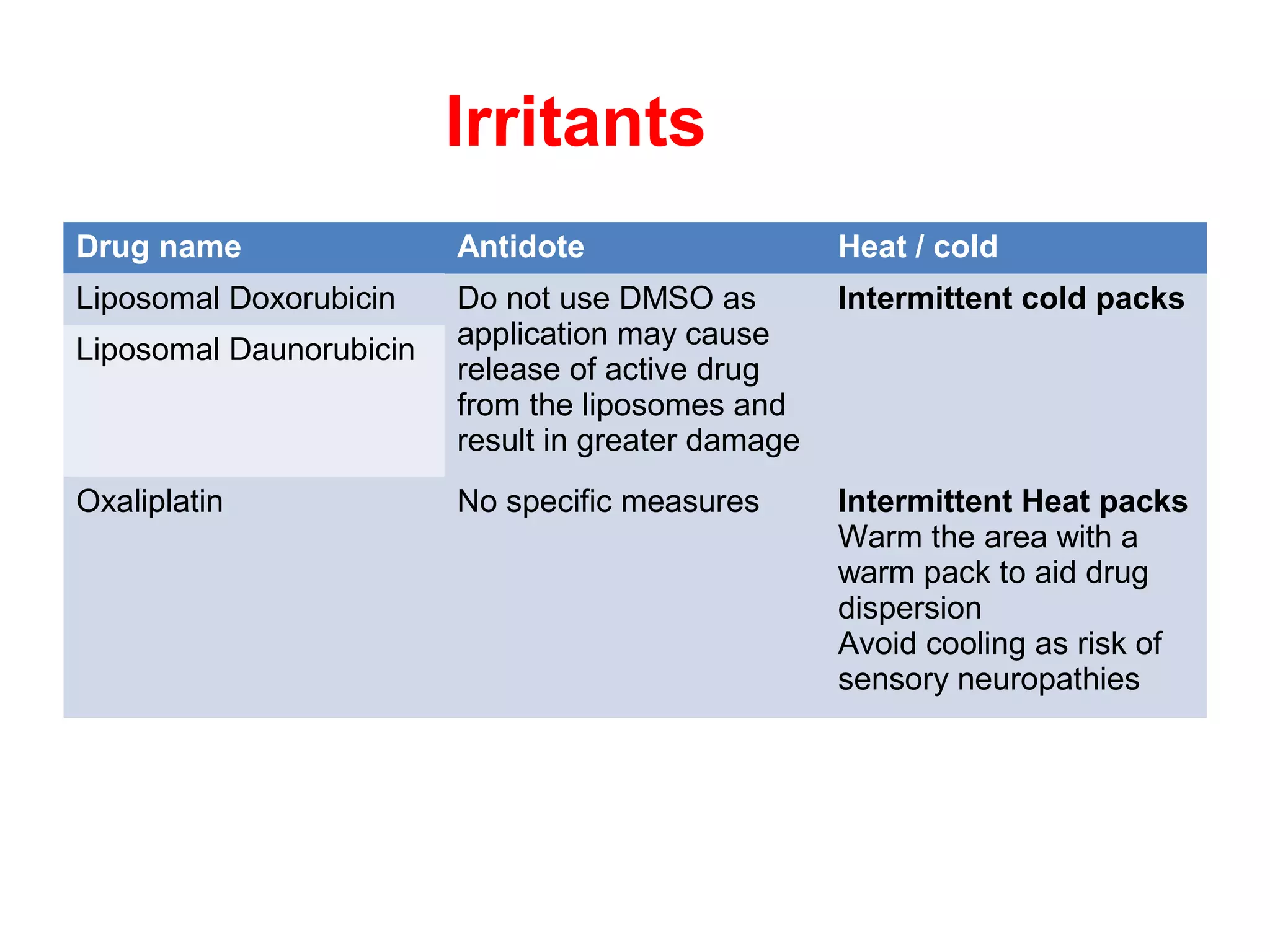
2) Drugs are classified as vesicants, irritants, inflammitants, or neutrals based on their propensity to cause tissue damage. Vesicants like doxorubicin are most likely to cause damage.
3) Risk of extravasation is higher for fragile veins, elderly or ill patients, and irritating/vesicant drugs. Signs include pain, swelling, discoloration at the injection site.
4)