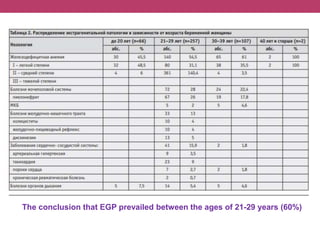
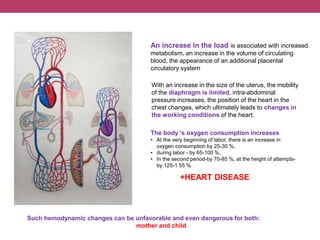
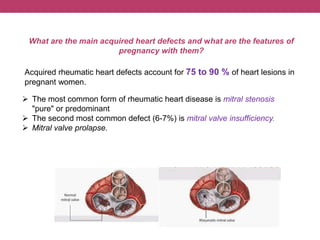
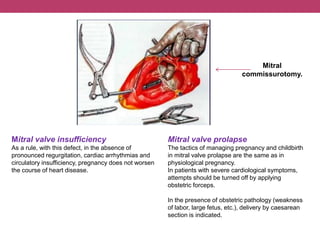
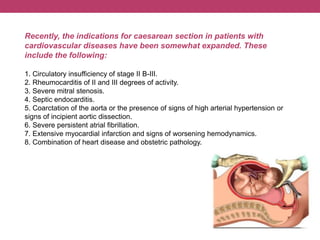
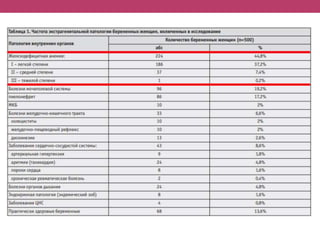
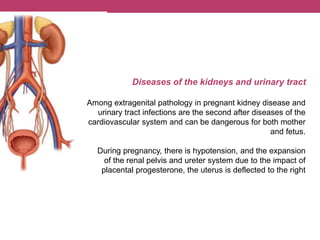
This document discusses features of pregnancy and childbirth management in women with extragenital pathology. It notes that only 20% of pregnancies proceed without complications, while 30-40% involve extragenital pathology (EGP) such as cardiovascular, kidney, or blood diseases. Pregnancy termination risks are 12% and can affect fetal development. The most common EGP in women ages 21-29 is cardiovascular disease, observed in 7% of cases. Management of pregnancy involves frequent hospitalizations and selecting delivery methods based on the severity of the woman's condition.