This document provides details about a lecture on extension teaching methods, including:
- Extension teaching methods are devices used to create communication between extension workers and rural communities. They include individual methods like farm visits and demonstrations, group methods like meetings and exhibits, and mass methods like radio and newspapers.
- For methods to be effective there must be clear learning objectives, experiences, and a variety of approaches to accommodate different learning styles.
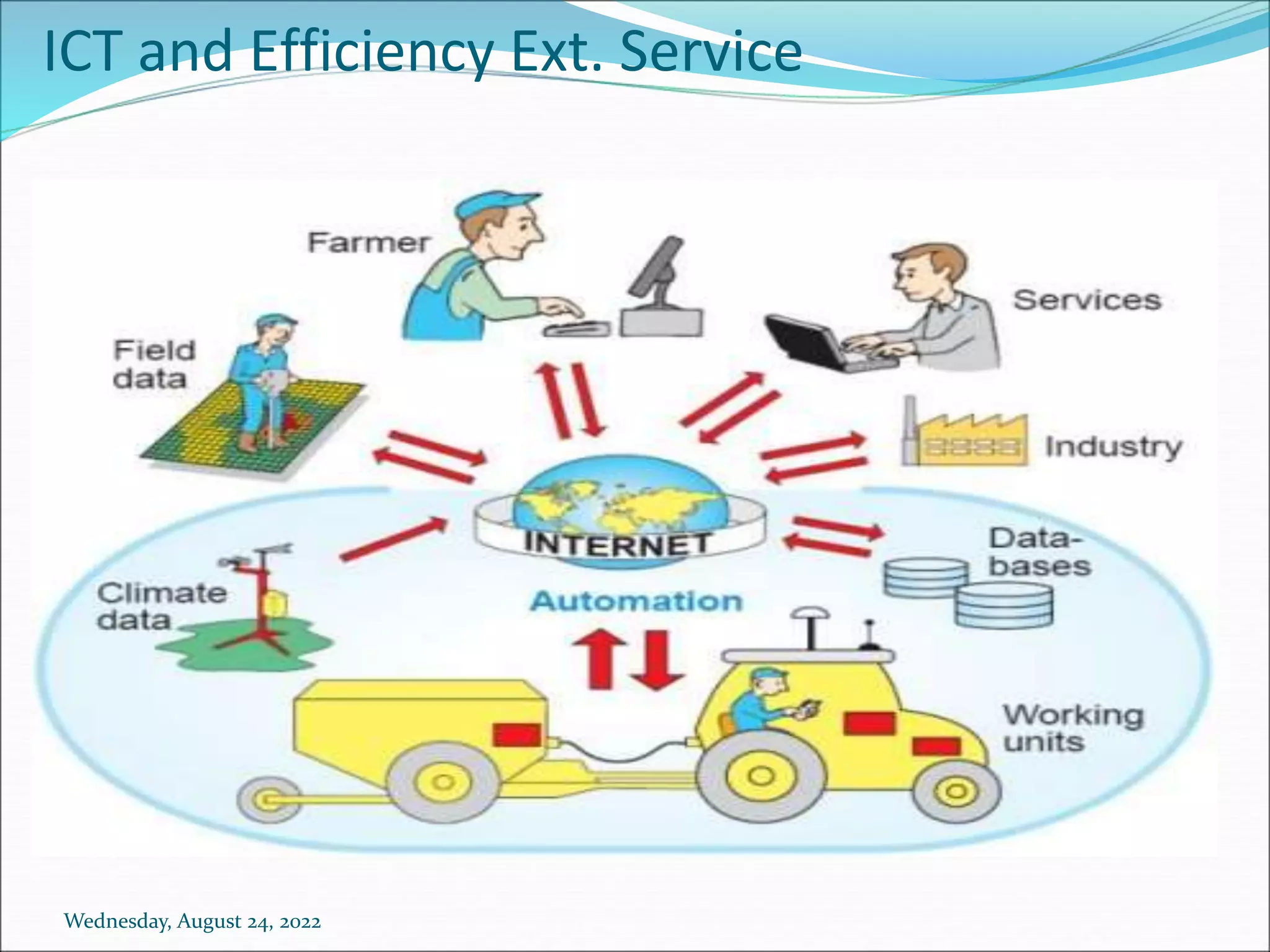
- Methods are classified by their scale (individual, group, mass), format (written, spoken, audiovisual), and emerging technologies are opening new information dissemination options for extension services.