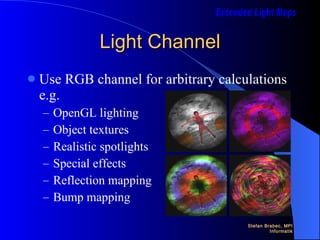
Extended light maps store pre-computed illumination in light maps to improve rendering efficiency. The light map contains two channels - a light channel that stores values like diffuse lighting, and a shadow channel that stores depth values to determine lit pixels. This approach better utilizes hardware and reduces rendering passes. It allows effects like bump mapping and reflections to be pre-computed and applied during rendering. However, the light channel can only affect lit pixels, and high-resolution textures are needed for accurate shadows. Future work includes improving shadow quality and adding more applications of the light channel.


![Motivation Our Shadow Mapping Approach [Brabec/Heidrich `00] Render scene as seen by light source Encode depth values in alpha channel Project this texture into the final scene Subtract depth values to determine lit pixels](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/talkgameon00-120204031143-phpapp01/85/Extended-Light-Maps-3-320.jpg)