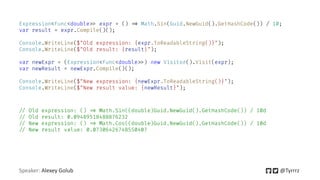
This document discusses expression trees in C#. It begins with an introduction to expression trees, which describe the structure of an expression. It then discusses how expression trees are represented in .NET using types deriving from System.Linq.Expressions.Expression. It provides examples of constructing expression trees manually using factory methods, and how lambda expression trees can be converted into delegates. The document also discusses optimizing reflection-heavy code using expression trees, implementing generic operators with expression trees, parsing DSLs into expression trees, obtaining expression trees from lambdas, and identifying type members using expression trees.














![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
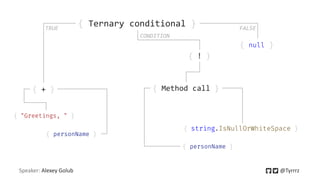
We need to call string.Concat() directly
var concatMethod = typeof(string)
.GetMethod(nameof(string.Concat), new[] {typeof(string), typeof(string)});
var trueClause = Expression.Call(
concatMethod,
Expression.Constant("Greetings, "),
personNameParameter);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-16-320.jpg)





![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
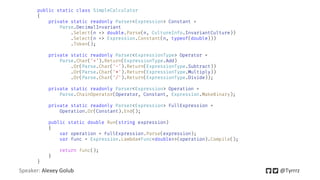
public class Benchmarks
{
[Benchmark(Description = "Reflection", Baseline = true)]
public int Reflection() => (int) typeof(Command)
.GetMethod("Execute", BindingFlags.NonPublic | BindingFlags.Instance)
.Invoke(new Command(), null);
[Benchmark(Description = "Reflection (cached)")]
public int Cached() => ReflectionCached.CallExecute(new Command());
[Benchmark(Description = "Reflection (delegate)")]
public int Delegate() => ReflectionDelegate.CallExecute(new Command());
[Benchmark(Description = "Expressions")]
public int Expressions() => ExpressionTrees.CallExecute(new Command());
public static void Main() => BenchmarkRunner.Run<Benchmarks>();
}
| Method | Mean | Error | StdDev | Ratio |
|---------------------- |-----------:|----------:|----------:|------:|
| Reflection | 192.975 ns | 1.6802 ns | 1.4895 ns | 1.00 |
| Reflection (cached) | 123.762 ns | 1.1063 ns | 1.0349 ns | 0.64 |
| Reflection (delegate) | 6.419 ns | 0.0646 ns | 0.0605 ns | 0.03 |
| Expressions | 5.383 ns | 0.0433 ns | 0.0383 ns | 0.03 |](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-22-320.jpg)





![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
public class Benchmarks
{
[Benchmark(Description = "Static", Baseline = true)]
[Arguments(13.37)]
public double Static(double x) => 3 * x / 4;
[Benchmark(Description = "Expressions")]
[Arguments(13.37)]
public double Expressions(double x) => ThreeFourths.Of(x);
[Benchmark(Description = "Dynamic")]
[Arguments(13.37)]
public dynamic Dynamic(dynamic x) => 3 * x / 4;
public static void Main() => BenchmarkRunner.Run<Benchmarks>();
}
| Method | x | Mean | Error | StdDev | Ratio | RatioSD |
|------------ |------ |-----------:|----------:|----------:|------:|--------:|
| Static | 13.37 | 0.6077 ns | 0.0176 ns | 0.0147 ns | 1.00 | 0.00 |
| Expressions | 13.37 | 1.9510 ns | 0.0163 ns | 0.0145 ns | 3.21 | 0.08 |
| Dynamic | 13.37 | 19.3267 ns | 0.1512 ns | 0.1340 ns | 31.82 | 0.78 |](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-28-320.jpg)



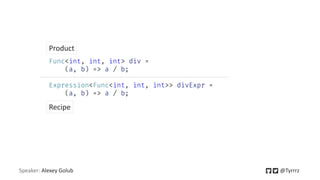
![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
Func<int, int, int> div =
(a, b) => a / b;
Expression<Func<int, int, int>> divExpr =
(a, b) => a / b;
Same value, different type
Console.WriteLine(divExpr.Type);
=/ System.Func`3[System.Int32,System.Int32,System.Int32]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-33-320.jpg)




![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
Limitations
• Null-coalescing operator (obj?.Prop)
• Dynamic variables (dynamic)
• Asynchronous code (async/await)
• Default or named parameters (func(a, b: 5), func(a))
• Parameters passed by reference (int.TryParse("123", out var i))
• Multi-dimensional array initializers (new int[2, 2] { { 1, 2 }, { 3, 4 } })
• Assignment operations (a = 5)
• Increment and decrement (a++, a--, --a, ++a)
• Base type access (base.Prop)
• Dictionary initialization (new Dictionary<string, int> { ["foo"] = 100 })
• Unsafe code (via unsafe)
• Throw expressions (throw new Exception())
• Tuple literals ((5, x))
Can’t use any of the following:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-39-320.jpg)





![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
[Test]
public void IntTryParse_Test()
{
// Arrange
const string s = "123";
// Act
var result = int.TryParse(s, out var value);
// Assert
Assert.That(result, Is.True, "Parsing was unsuccessful");
Assert.That(value, Is.EqualTo(124), "Parsed value is incorrect");
}
X IntTryParse_Test [60ms]
Error Message:
Parsed value is incorrect
Expected: 124
But was: 123](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-46-320.jpg)

![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
X IntTryParse_Test [60ms]
Error Message:
Assert.That(value, Is.EqualTo(124))
Expected: 124
But was: 123
[Test]
public void IntTryParse_Test()
{
// Arrange
const string s = "123";
// Act
var result = int.TryParse(s, out var value);
// Assert
AssertEx.Express(() => Assert.That(result, Is.True));
AssertEx.Express(() => Assert.That(value, Is.EqualTo(124)));
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-48-320.jpg)








![Speaker: Alexey Golub @Tyrrrz
protected override Expression VisitLambda<T>(Expression<T> node)
{
_buffer.Append("fun (");
_buffer.AppendJoin(", ", node.Parameters.Select(p => p.Name));
_buffer.Append(") ->");
return base.VisitLambda(node);
}
protected override Expression VisitMethodCall(MethodCallExpression node)
{
if (node.Method.DeclaringType == typeof(Console) &&
node.Method.Name == nameof(Console.WriteLine))
{
_buffer.Append("printfn ");
if (node.Arguments.Count > 1)
{
var format = (string) ((ConstantExpression) node.Arguments[0]).Value;
var formatValues = node.Arguments.Skip(1).ToArray();
_buffer.Append(""").Append(Regex.Replace(format, @"{d+}", "%O")).Append("" ");
_buffer.AppendJoin(" ", formatValues.Select(v => $"({v.ToReadableString()})"));
}
}
return base.VisitMethodCall(node);
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/expressiontreesinc-201016113323/85/Expression-trees-in-C-58-320.jpg)




