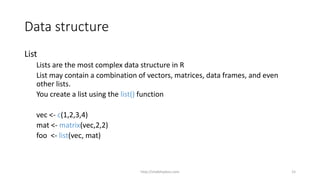
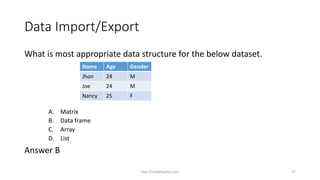
This document discusses various data structures in R programming including vectors, matrices, arrays, data frames, lists, and factors. It provides examples of how to create each structure and access elements within them. Various methods for importing and exporting data in different file formats like Excel, CSV, and text files are also covered.

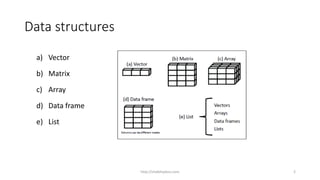
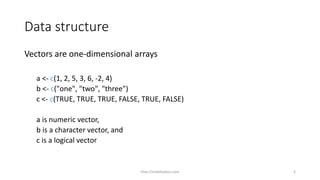

![Data structure
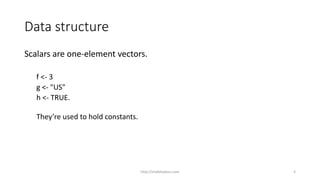
Vector
You can refer to elements of a vector using a numeric vector of positions within
brackets.
Example
vec <- c(“a”, “b”, “c”, “d”, “e”, ”f”)
vec[1] # will return the first element in the vector
vec[c(2,4)] # will return the 2nd and 4th element in the vector.
http://shakthydoss.com 6](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-r-tutorial-data-structure-151030161143-lva1-app6892/85/3-R-Tutorial-Data-Structure-6-320.jpg)
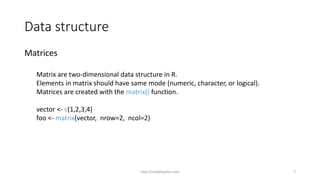

![Data structure
Matrix element can be accessed by subscript and brackets
Example
mat <- matrix(c(1:4), nrow=2,ncol = 2)
mat[1,] # returns first row in the matrix.
mat[2,] # returns second row in the matrix.
mat[,1] # returns first column in the matrix.
mat[,2] # returns second column in the matrix.
mat[1,2] # return element at first row of second column.
http://shakthydoss.com 9](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-r-tutorial-data-structure-151030161143-lva1-app6892/85/3-R-Tutorial-Data-Structure-9-320.jpg)
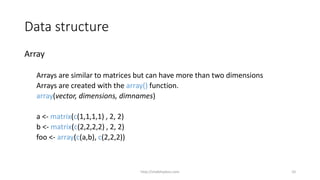
![Data structure
Array
array elements can be accessed in the same way a matrices.
foo[1,,] # returns all elements in first dimension
foo[2,,] # returns all element in second dimension
foo[2,1,] # returns only first row element in second dimension
http://shakthydoss.com 11](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-r-tutorial-data-structure-151030161143-lva1-app6892/85/3-R-Tutorial-Data-Structure-11-320.jpg)

![Data structure
Data frame
Accessing data frame elements can be straight forward. Element can be
accessed by column names.
Example
foo$name # retruns name vector in the data frame
foo$age # retuns age vector in the data frame
foo$age[2] # retuns second element of age vector in the data frame
http://shakthydoss.com 13](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-r-tutorial-data-structure-151030161143-lva1-app6892/85/3-R-Tutorial-Data-Structure-13-320.jpg)