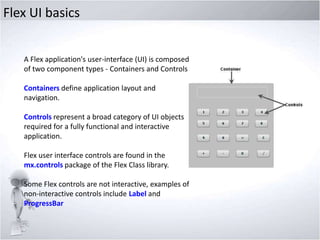
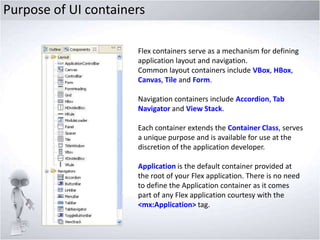
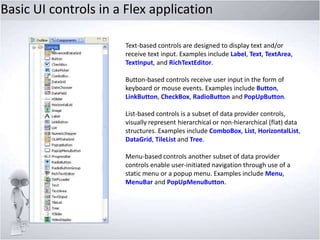
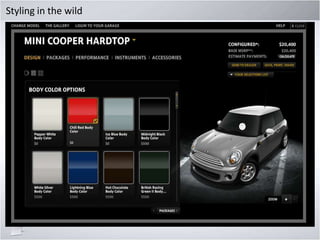
This document provides an overview of exploring Adobe Flex, including:
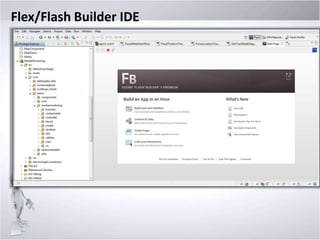
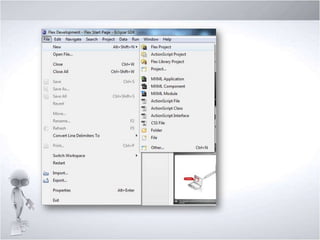
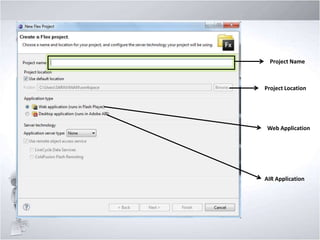
1. Discussing Flex/Flash Builder IDE, naming conventions, and organizing Flex projects.
2. Covering key Flex features like CSS support, states management, layouts, controls, charts, and data binding.
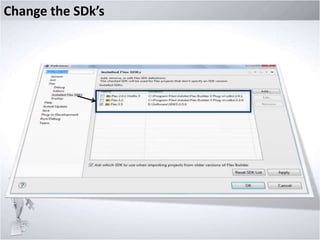
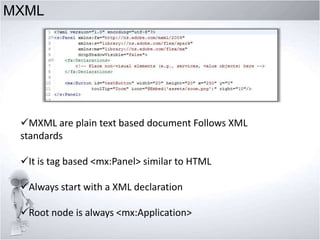
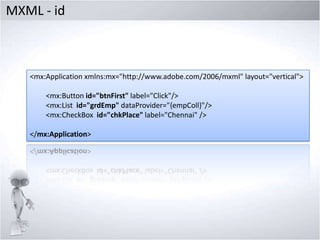
3. Comparing MXML and ActionScript, how the MXMLC compiler works, using MXML components and properties.
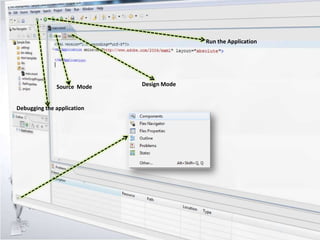
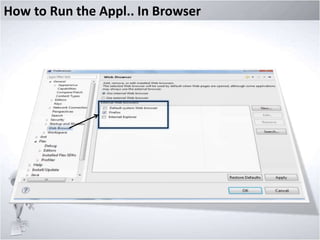
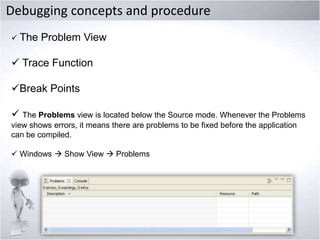
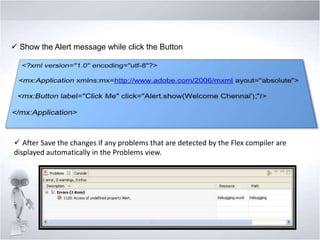
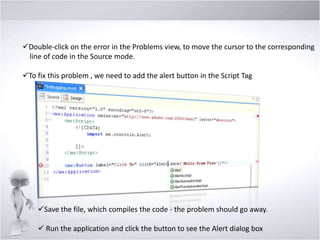
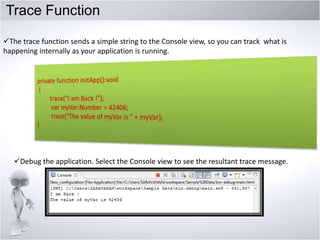
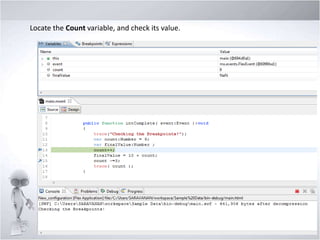
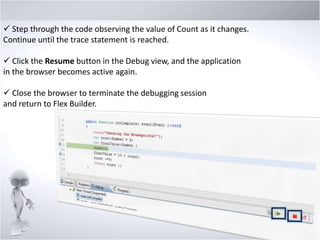
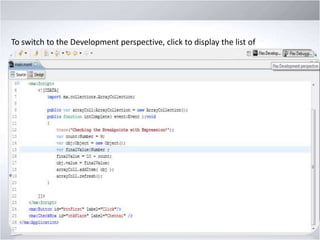
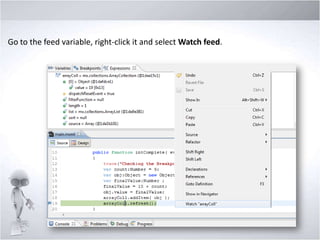
4. Explaining debugging concepts like the problems view, trace function, and breakpoints in Flex.