This document elaborates on the skill of explaining in microteaching, highlighting its importance in making complex concepts understandable to students. It discusses various forms of explanation, positive and negative components of skill, and provides examples of effective teaching techniques including lesson plans. Additionally, it addresses common pitfalls teachers may encounter while explaining, such as irrelevant statements and inappropriate vocabulary.





















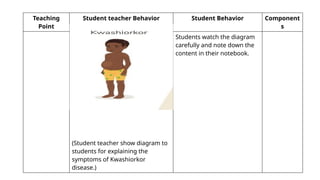
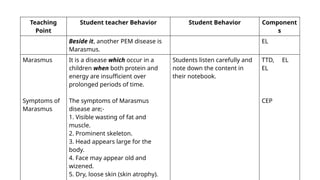

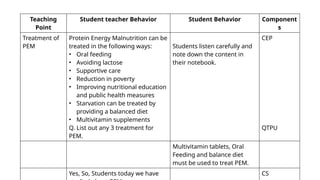

![References
Passi, B. K. and Et.al. (). Introduction to microteaching. [ (P.78-85), (P .117-120) ].
Stanford Center For Health Education, (September 30, 2023). What is Malnutrition
[Video File]. You tube. https://youtu.be/jEd91r___5Y?si=kcbbVvwXHk-w-GAT
https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/23296-marasmus
https://www.msdmanuals.com/en-in/professional/nutritional-disorders/undernutrition
/protein-energy-undernutrition-peu
https://www.careinsurance.com/blog/health-insurance-articles/let-s-decode-protein-en
ergy-malnutrition
https://byjus.com/biology/pem/](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/explainingskill-240912100926-0b3540a2/85/Explaining-skill-An-art-of-expressing-knowledge-pptx-31-320.jpg)
