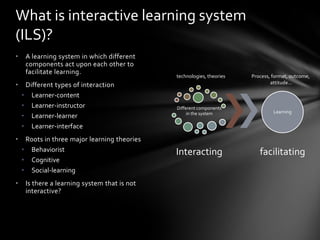
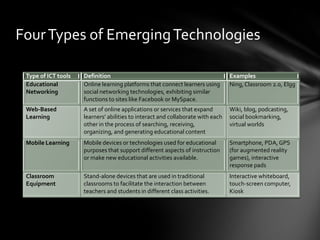
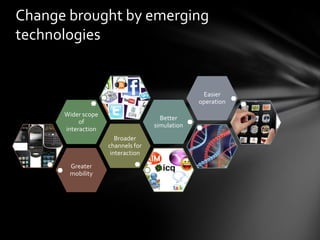
This document discusses interactive learning systems (ILS) and emerging technologies that can be integrated into ILS based on learning theories. It defines ILS and identifies four types of emerging technologies: educational networking, web-based learning, mobile learning, and classroom equipment. Examples are provided of how each technology has been used in ILS along with the learning theory integrated. The shifting focus in educational technology research from a problem-centric to design-based approach is also summarized.