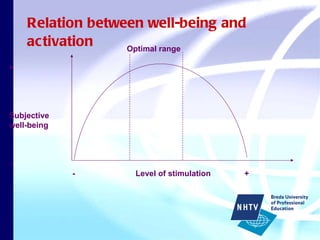
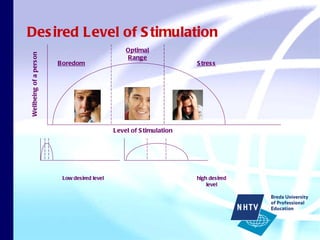
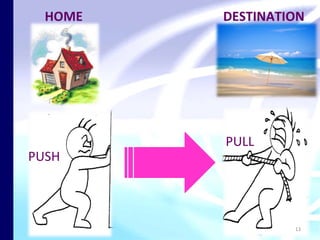
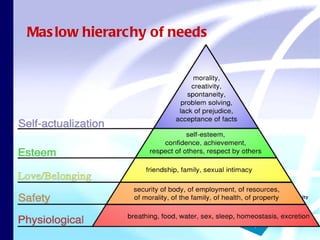
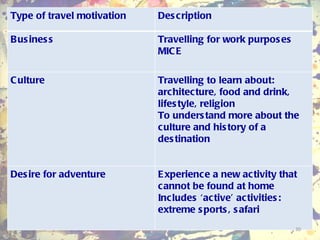
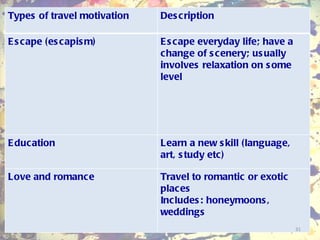
The document discusses theories of leisure motivation and the relationship between needs, expectations, and satisfaction from leisure experiences. It describes how needs drive motivation and behavior, and how the quality of an experience depends on meeting needs and expectations. Satisfaction results when expectations are met or exceeded by the actual experience. However, experiences are also culturally shaped by the time and environment in which they take place.