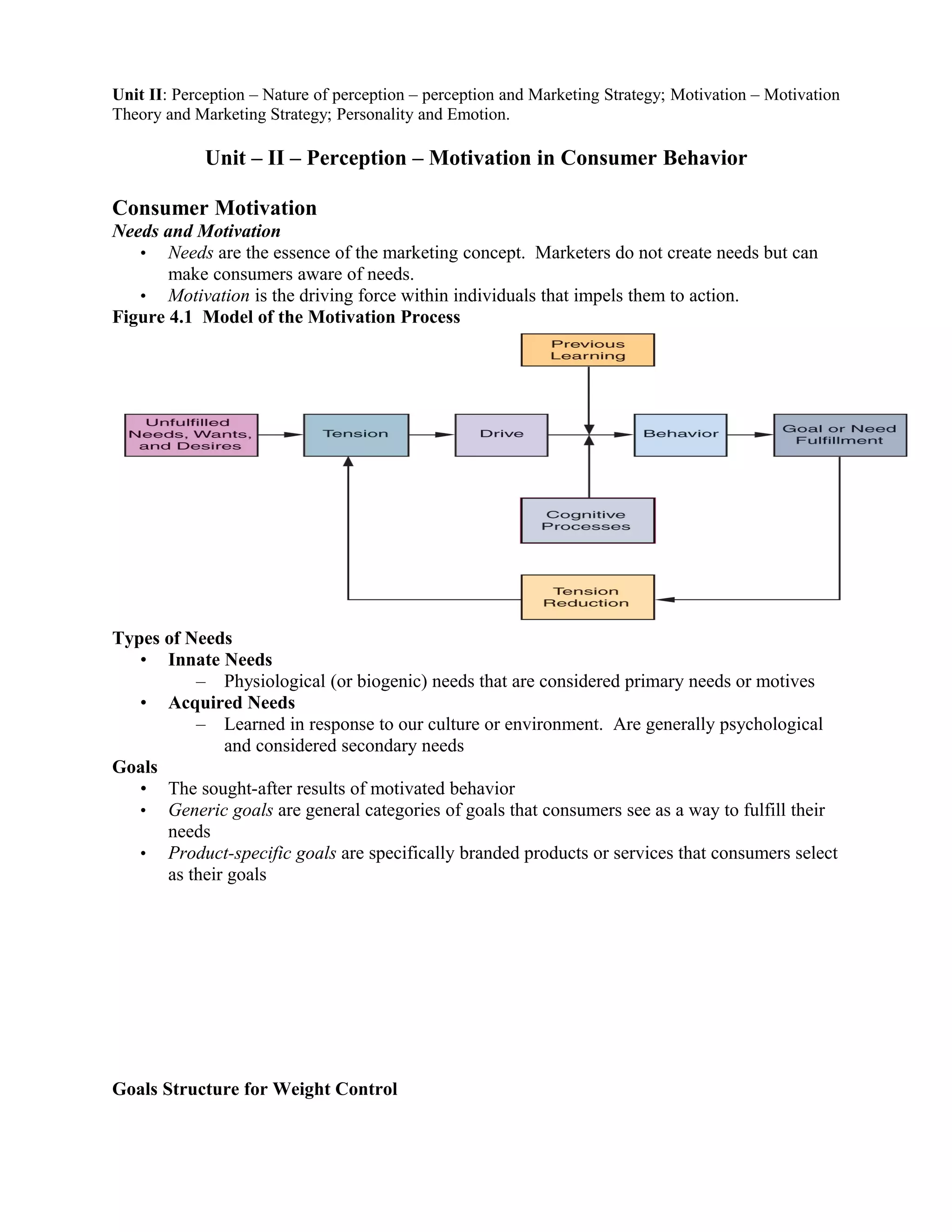
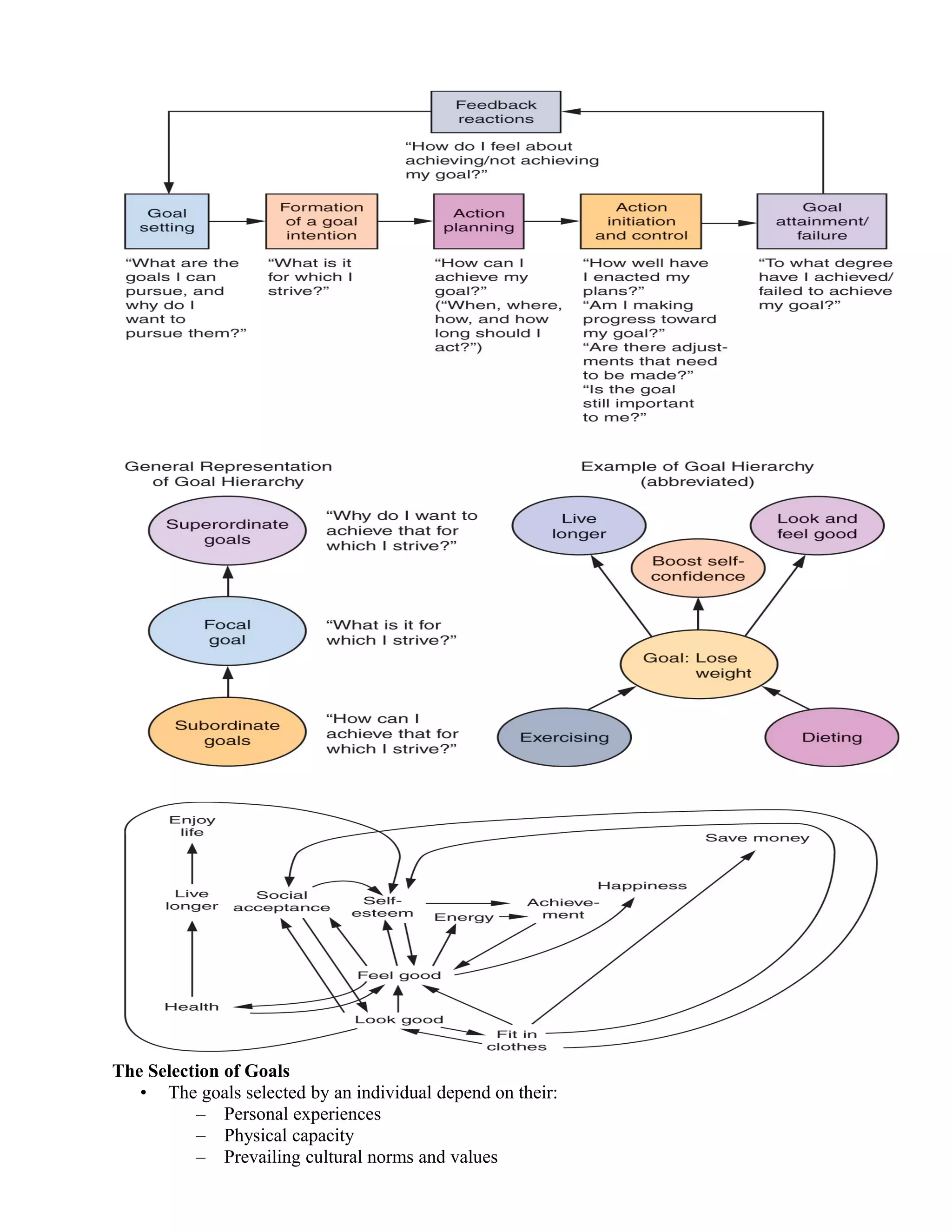
1. The document discusses consumer motivation and personality in marketing. It covers motivation theories including needs, goals, and defense mechanisms.
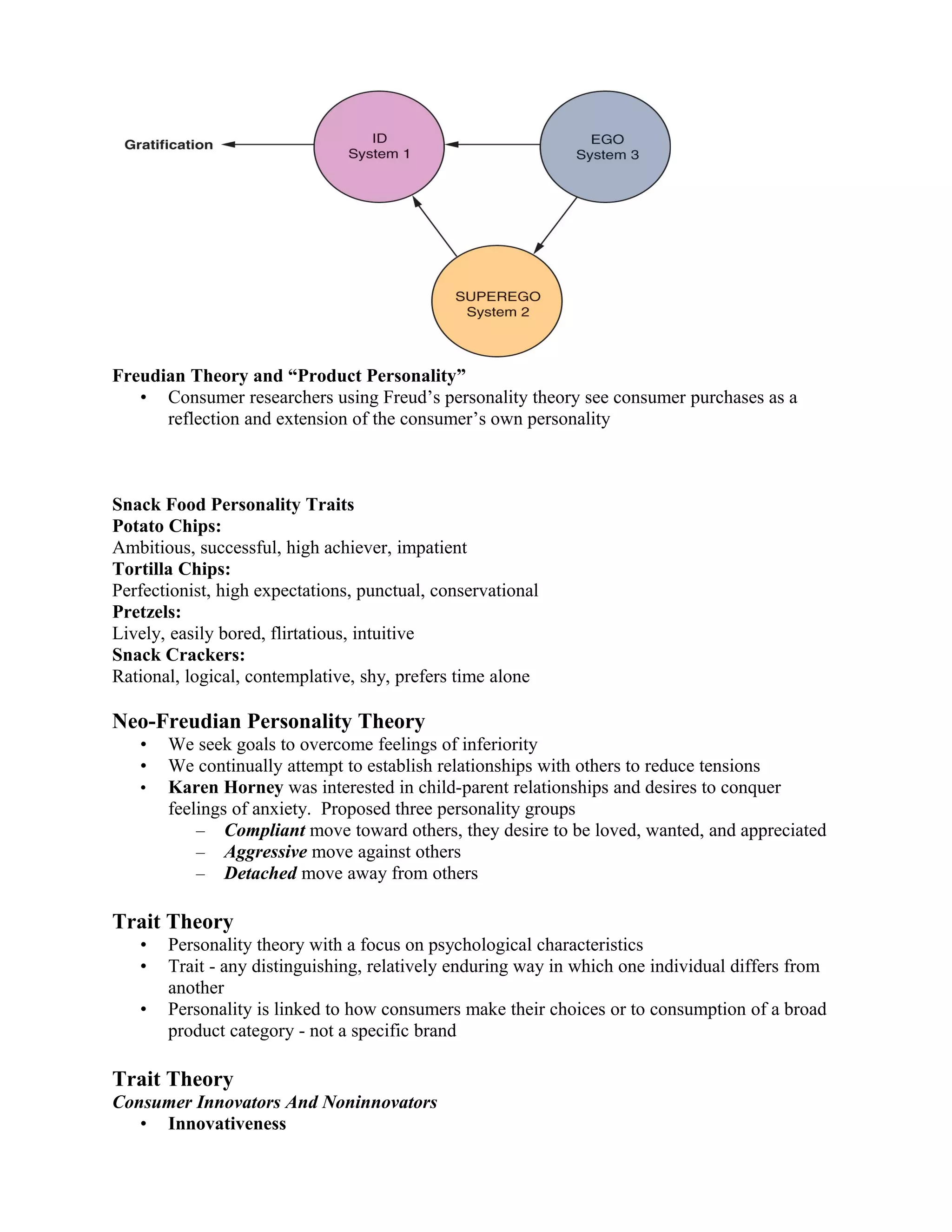
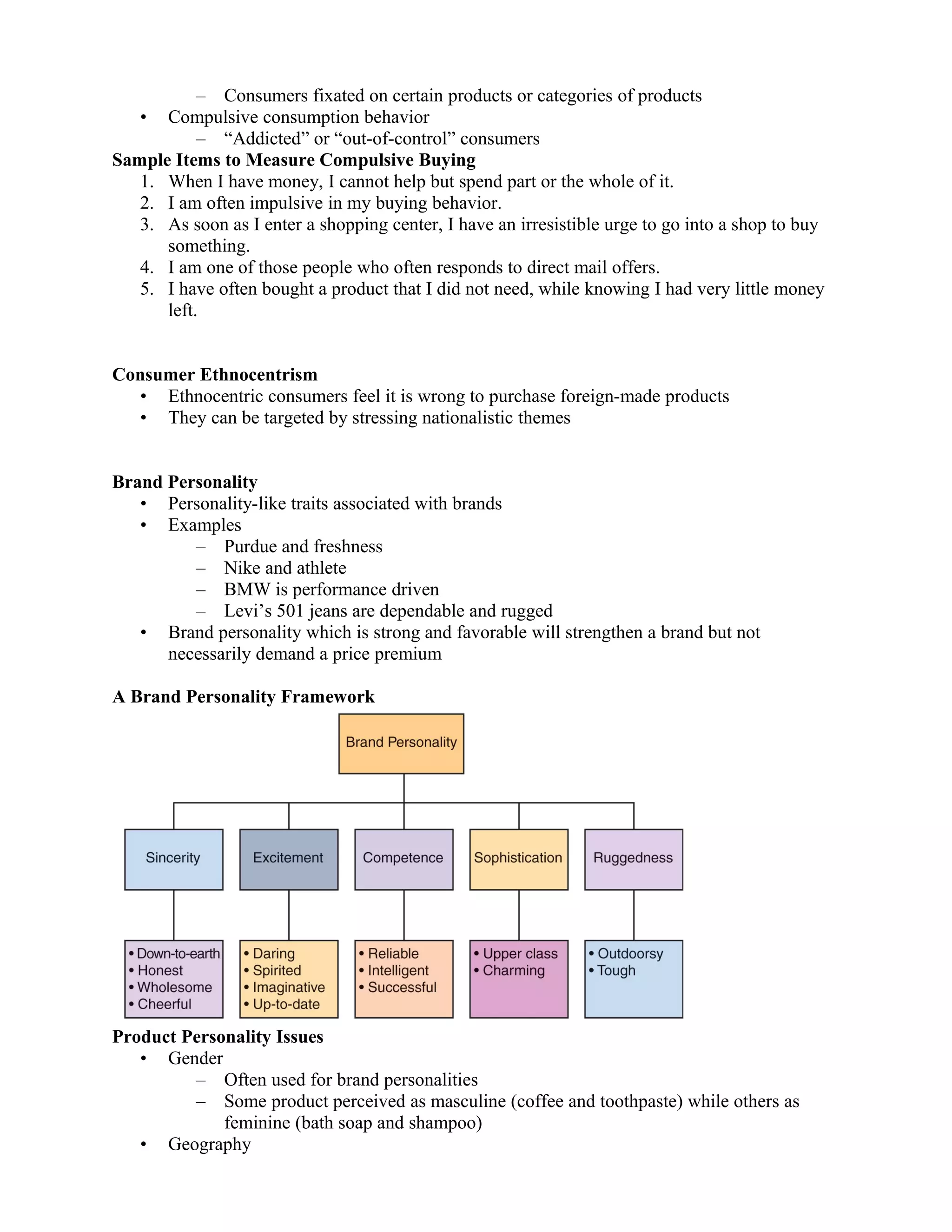
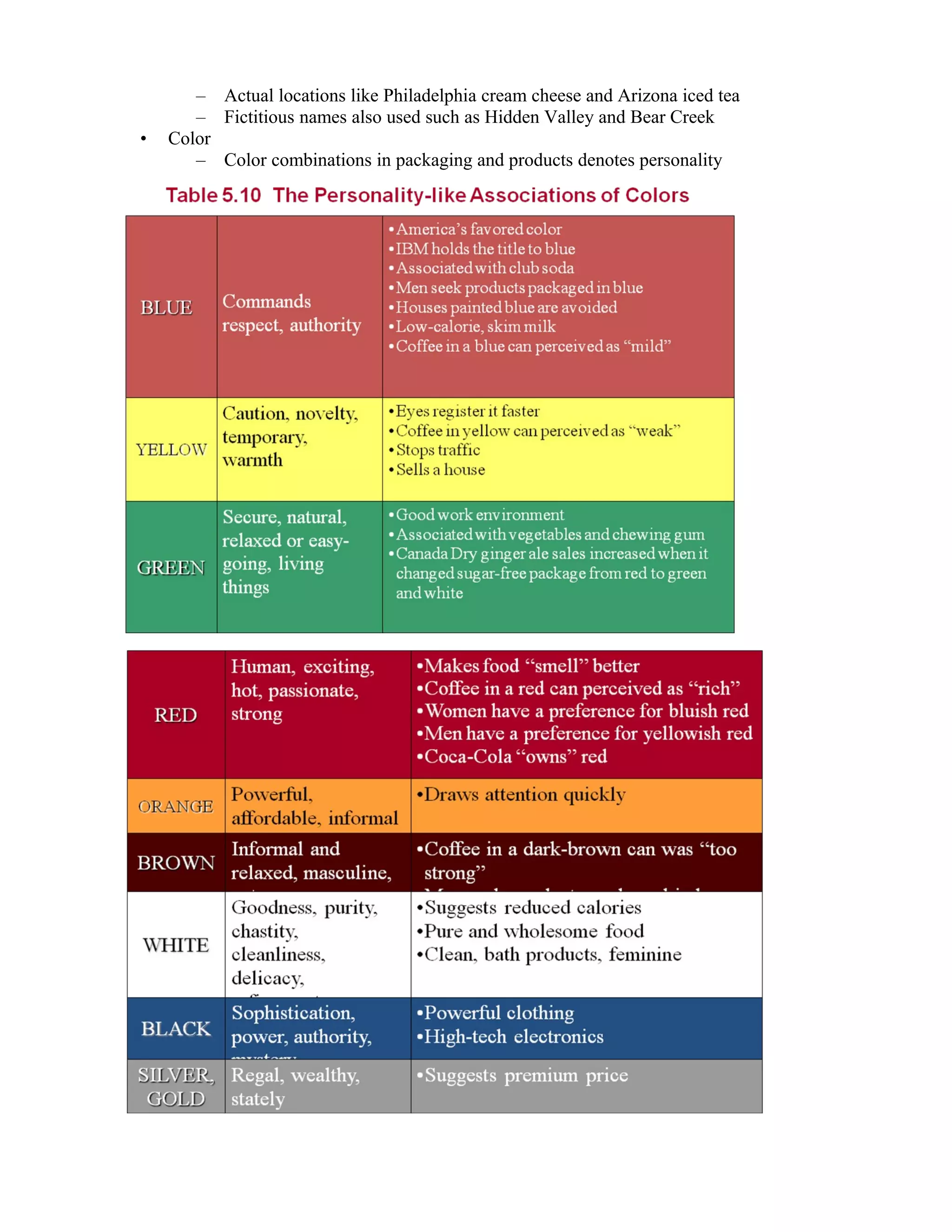
2. Personality theories like Freudian, trait, and self theories are examined in relation to how consumers develop personalities and self-images. Brands can take on personalities that consumers may identify with.
3. Both motivation and personality influence consumer decision making and how consumers relate to products, brands and advertising. Marketers must understand these psychological factors to effectively target consumers.