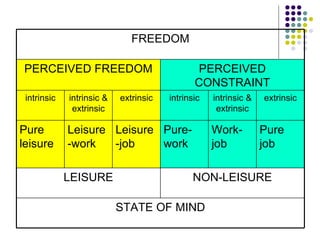
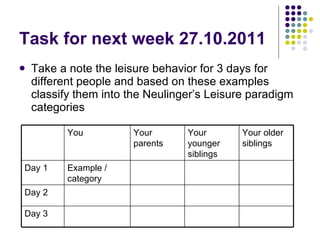
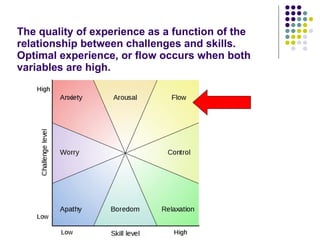
This document discusses theories of emotion and optimal experience in the context of leisure activities. It describes Csikszentmihalyi's theory of "flow" as an optimal experience that occurs when challenges match skills. It also outlines Neulinger's paradigm that classifies leisure and non-leisure activities based on perceived freedom of choice versus constraints and intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation. Examples are given of different types of activities according to this paradigm.