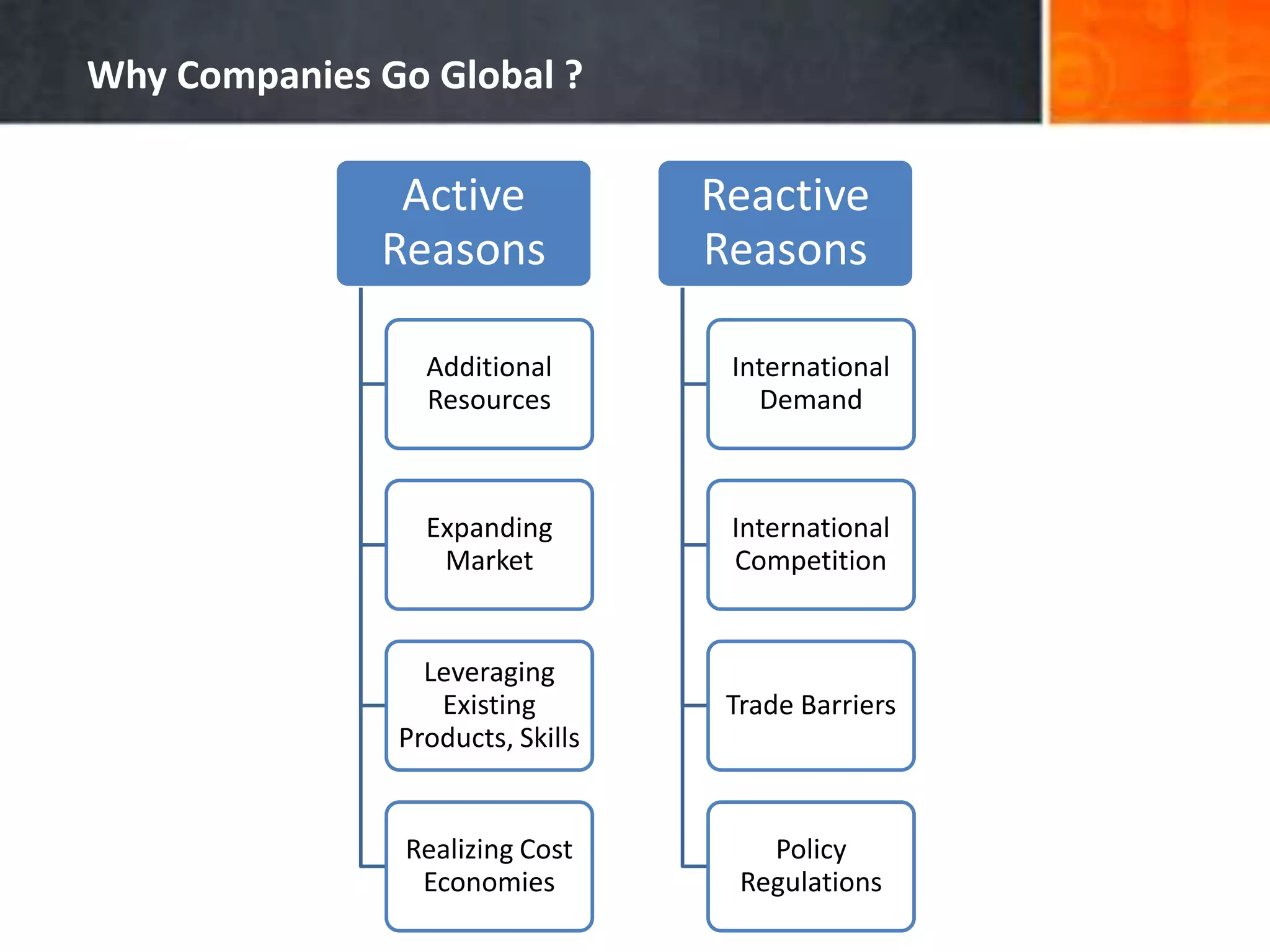
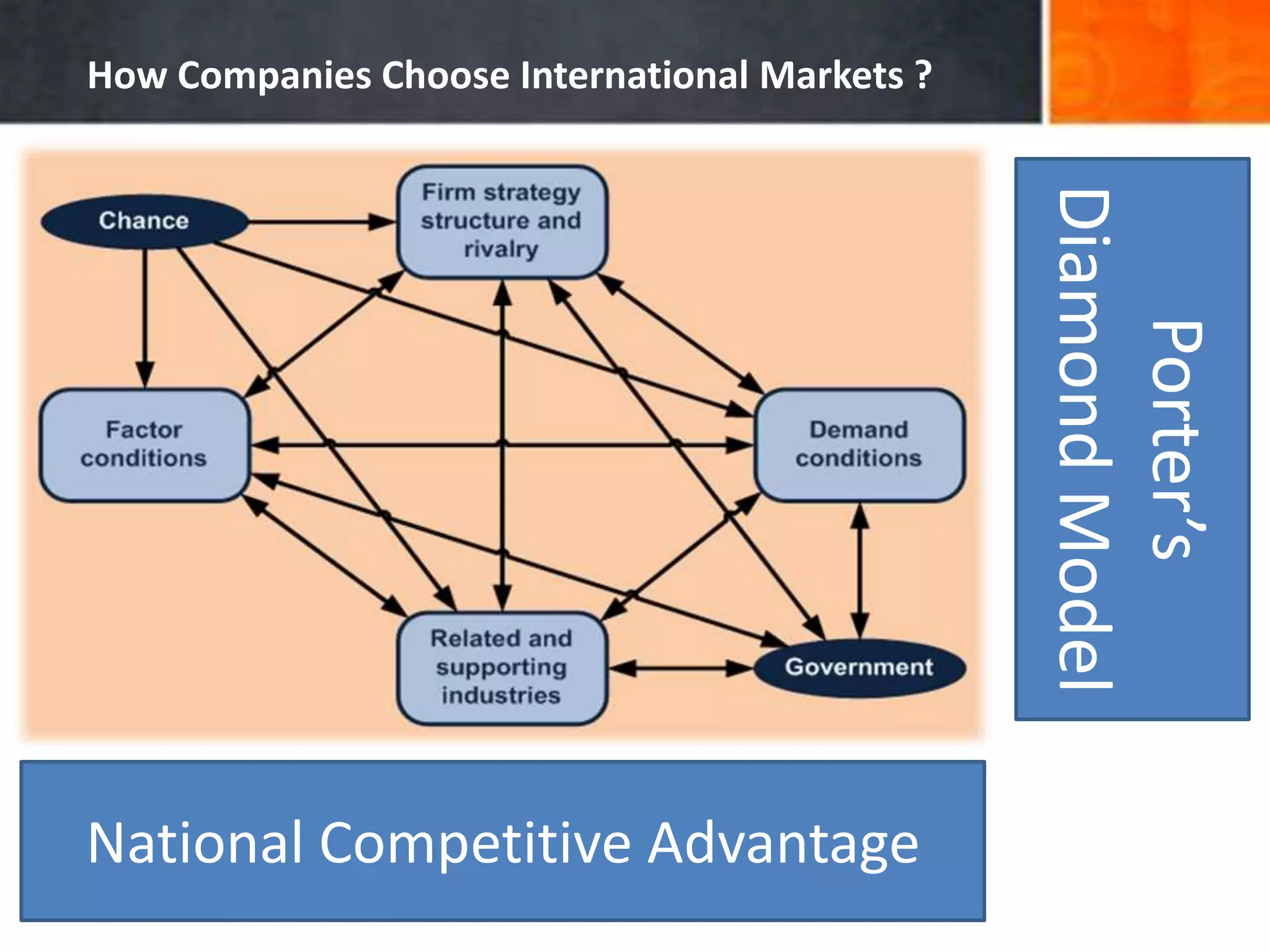
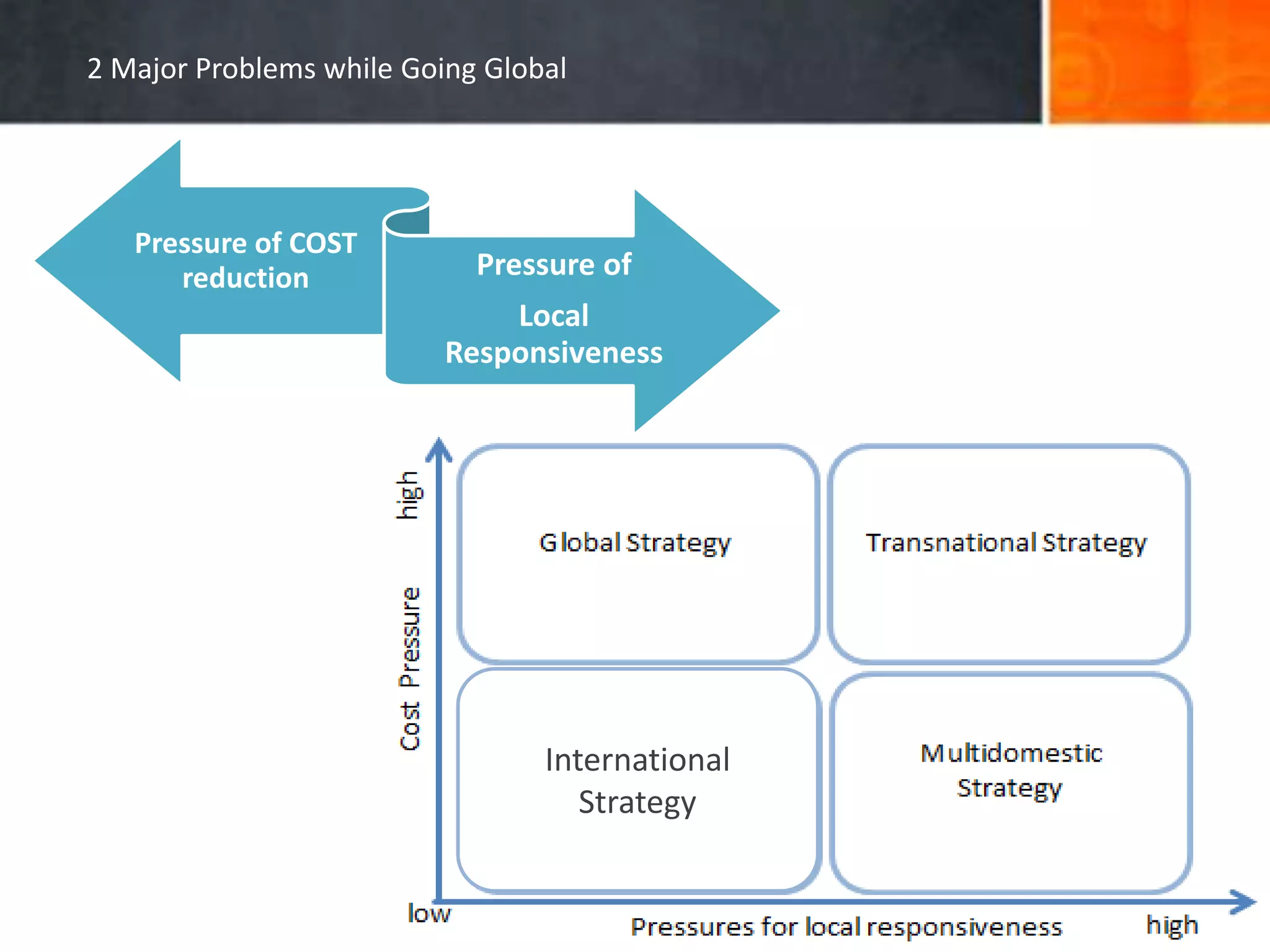
The document discusses the advantages and disadvantages of global expansion for companies, highlighting that entering the international marketplace can lead to faster growth and fewer failures. It presents Porter’s Diamond Model as a framework for selecting international markets based on national competitive advantages and identifies key factors influencing companies to go global. Additionally, it outlines major challenges such as cost reduction and local responsiveness that firms face while operating internationally.