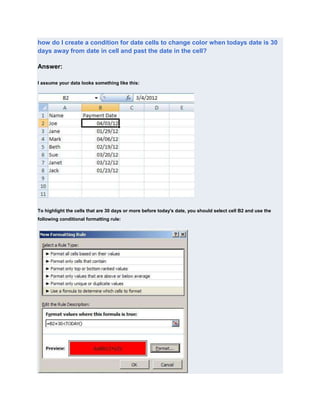
Here are a few ways to find the highest, second highest, etc. values in a column in Excel:
1. Use the LARGE function:
- To find the highest value: =LARGE(A1:A10,1)
- To find the second highest value: =LARGE(A1:A10,2)
- And so on, increasing the second argument by 1 each time
2. Use the SMALL function (opposite of LARGE):
- To find the second highest value: =SMALL(A1:A10,2)
- To find the third highest value: =SMALL(A1:A10,3)
3. Sort