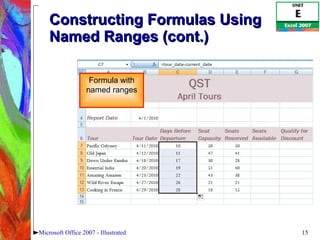
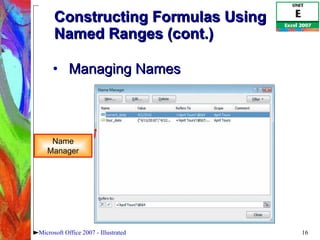
This document discusses various formulas and functions in Microsoft Excel, including:
1) Using text functions to format data, SUMIF to sum a range based on conditions, and CONCATENATE to join strings.
2) Consolidating data using 3D references and formulas.
3) Checking for errors using IFERROR and identifying circular references.
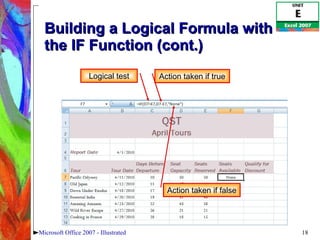
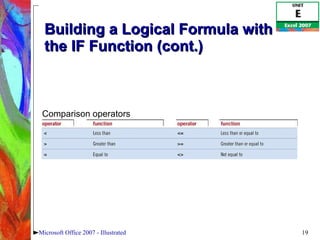
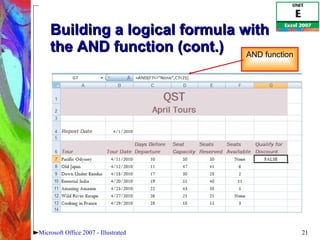
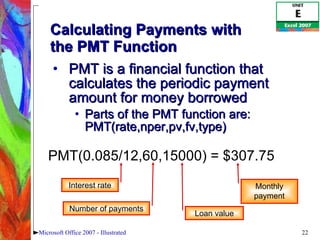
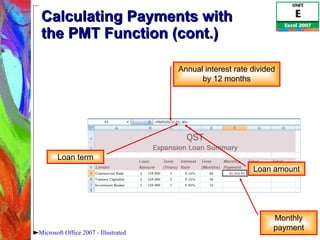
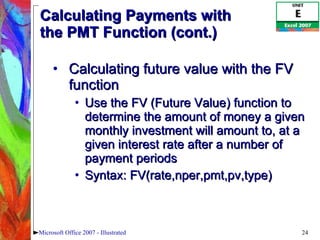
4) Constructing logical formulas using IF, AND, and comparison operators and calculating payments with PMT.




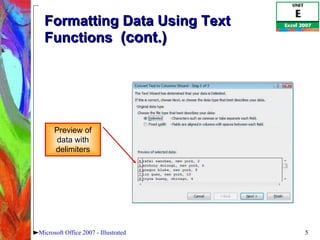

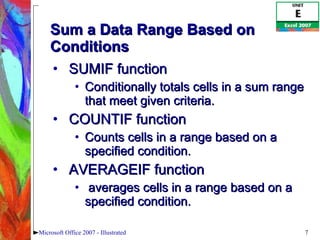
![Sum a Data Range Based on Conditions (cont.) SUMIF(range, criteria, [sum_range]) Microsoft Office 2007 - Illustrated The range where the cells that meet the condition will be totaled The condition that must be satisfied in the range The range the function searches Format of SUMIF Function](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/excel2007unite-090910001627-phpapp02/85/Excel-2007-Unit-E-8-320.jpg)