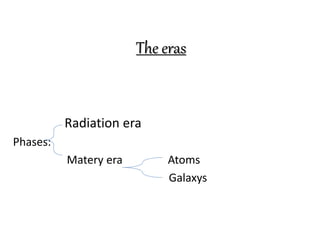
The document discusses the evolution of the universe from the Big Bang theory. It describes the Big Bang theory as the most accepted explanation for the origin and early development of the universe. It states that before the Big Bang, there was nothing - no time, no matter. After the Big Bang, the universe began rapidly expanding from an extremely dense and hot state. As it expanded, the early universe progressed through different eras from radiation to the formation of atoms, galaxies, and stars. The expansion of the universe continues today.