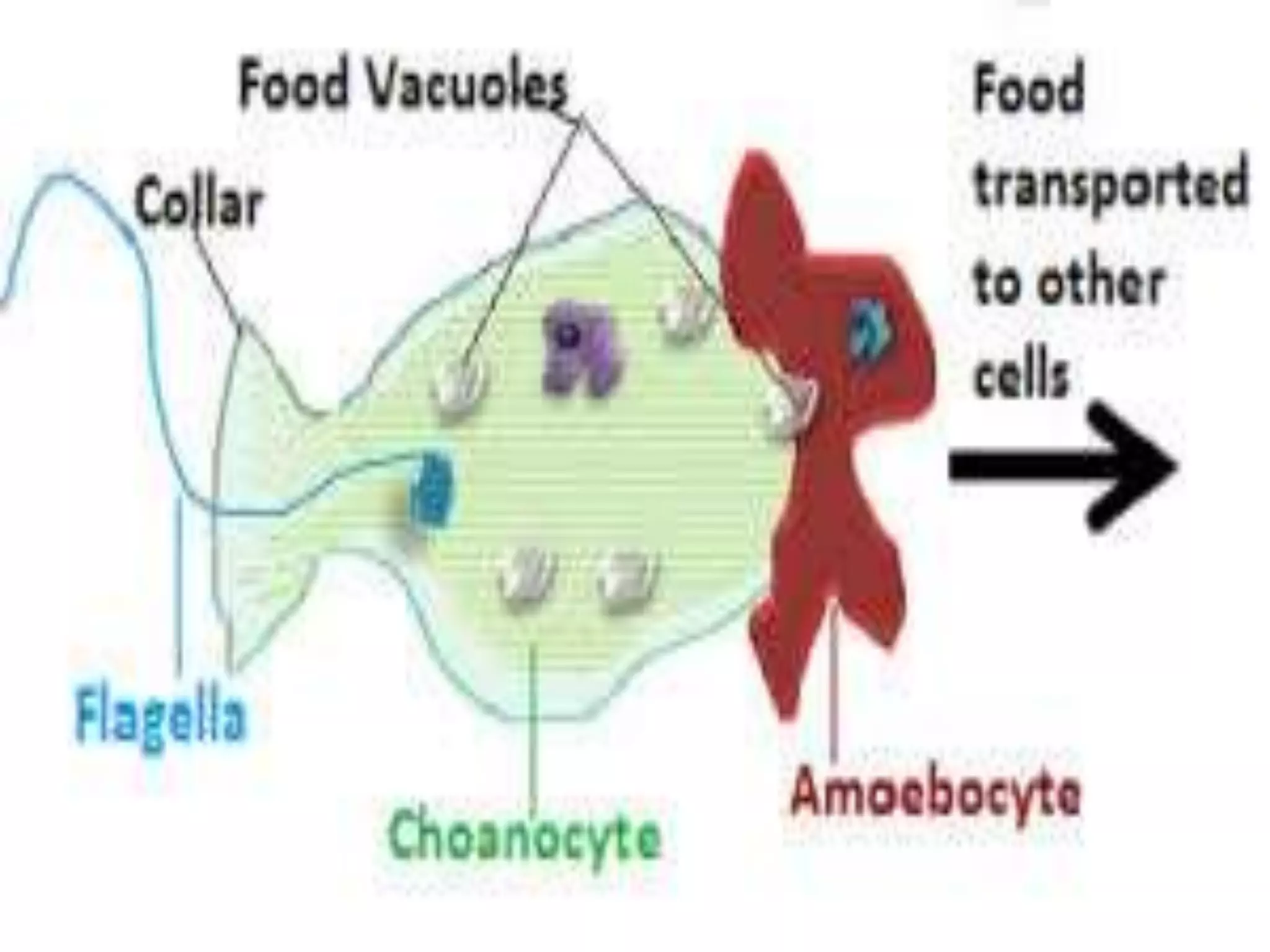
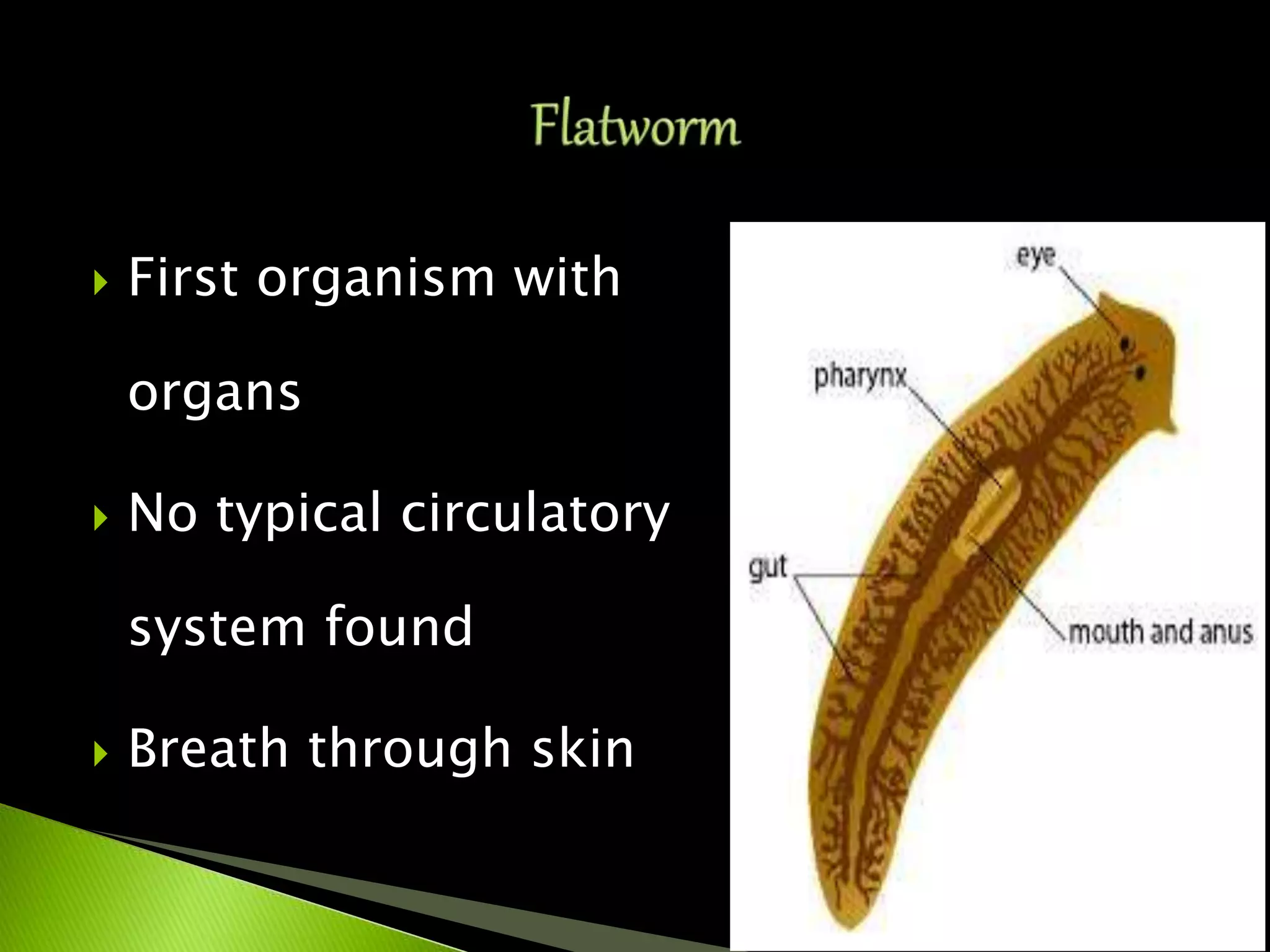
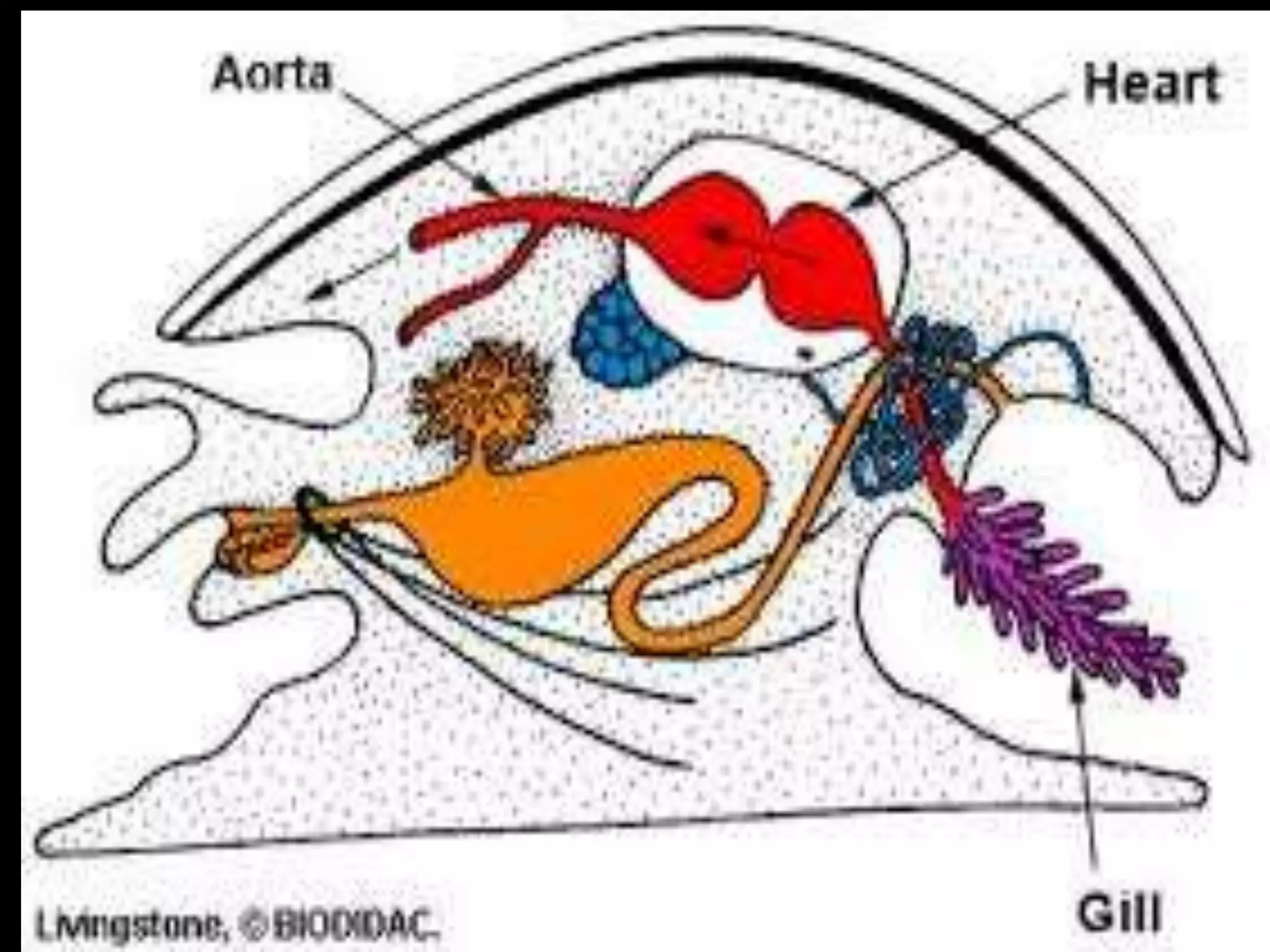
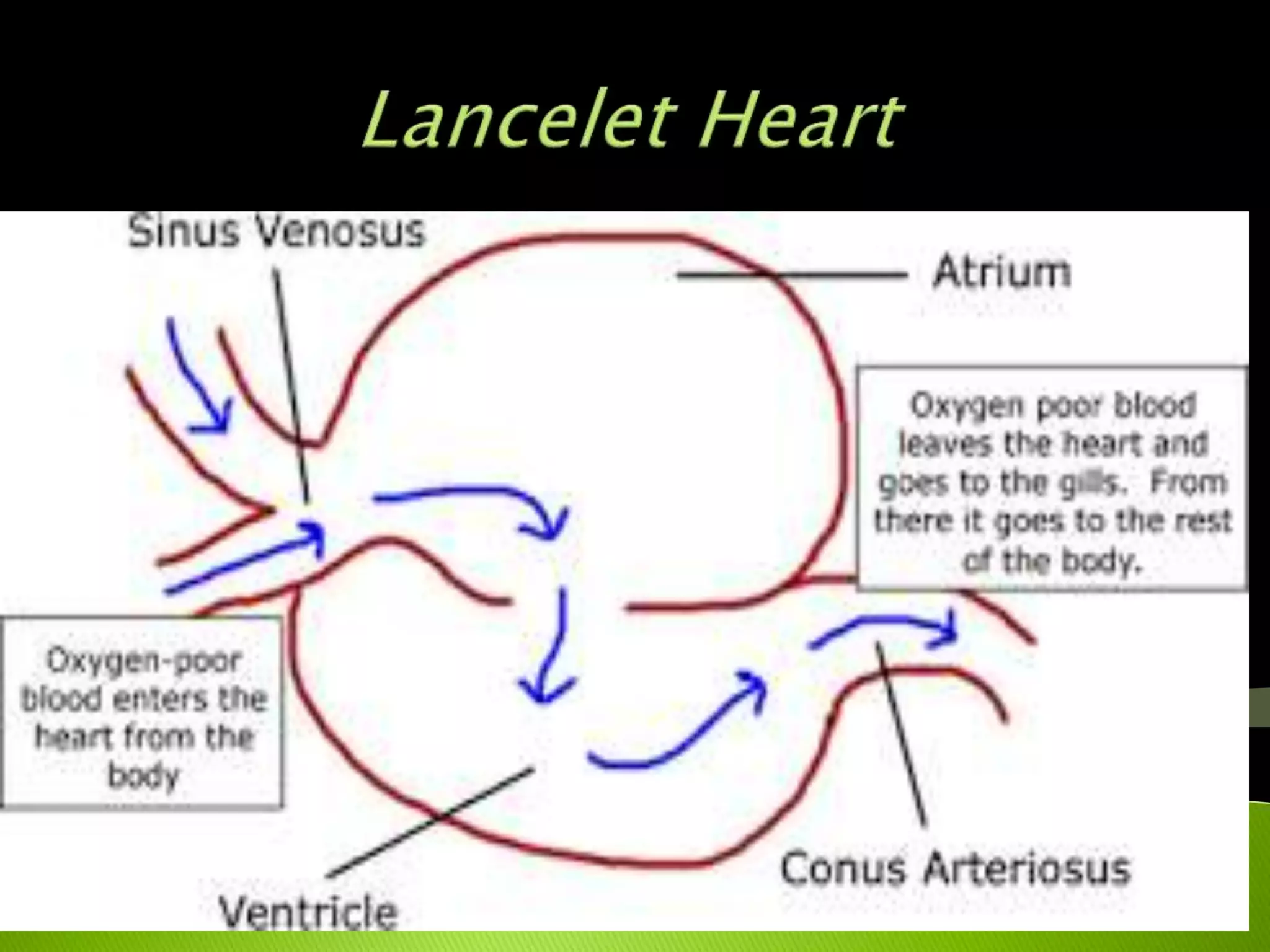
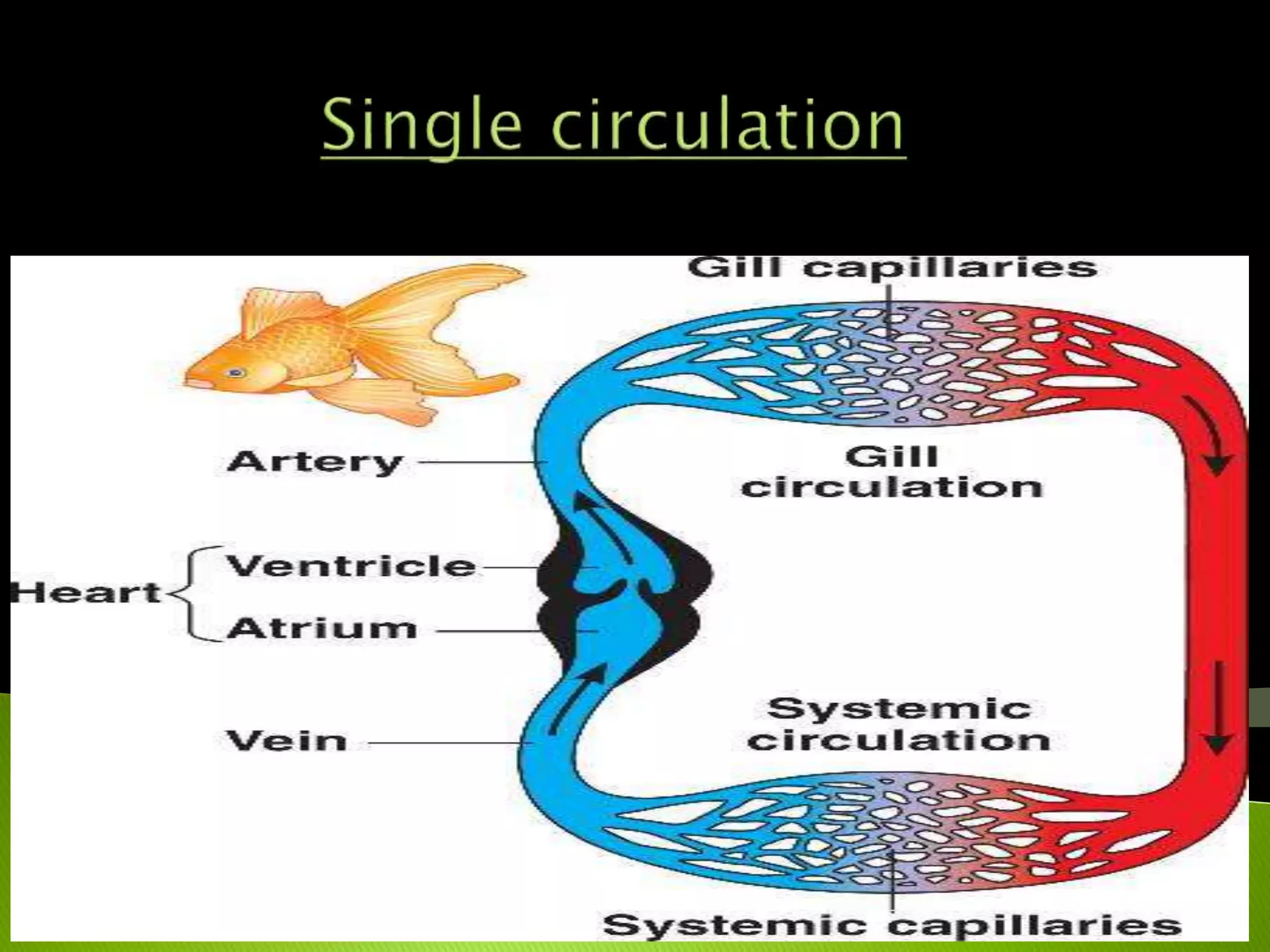
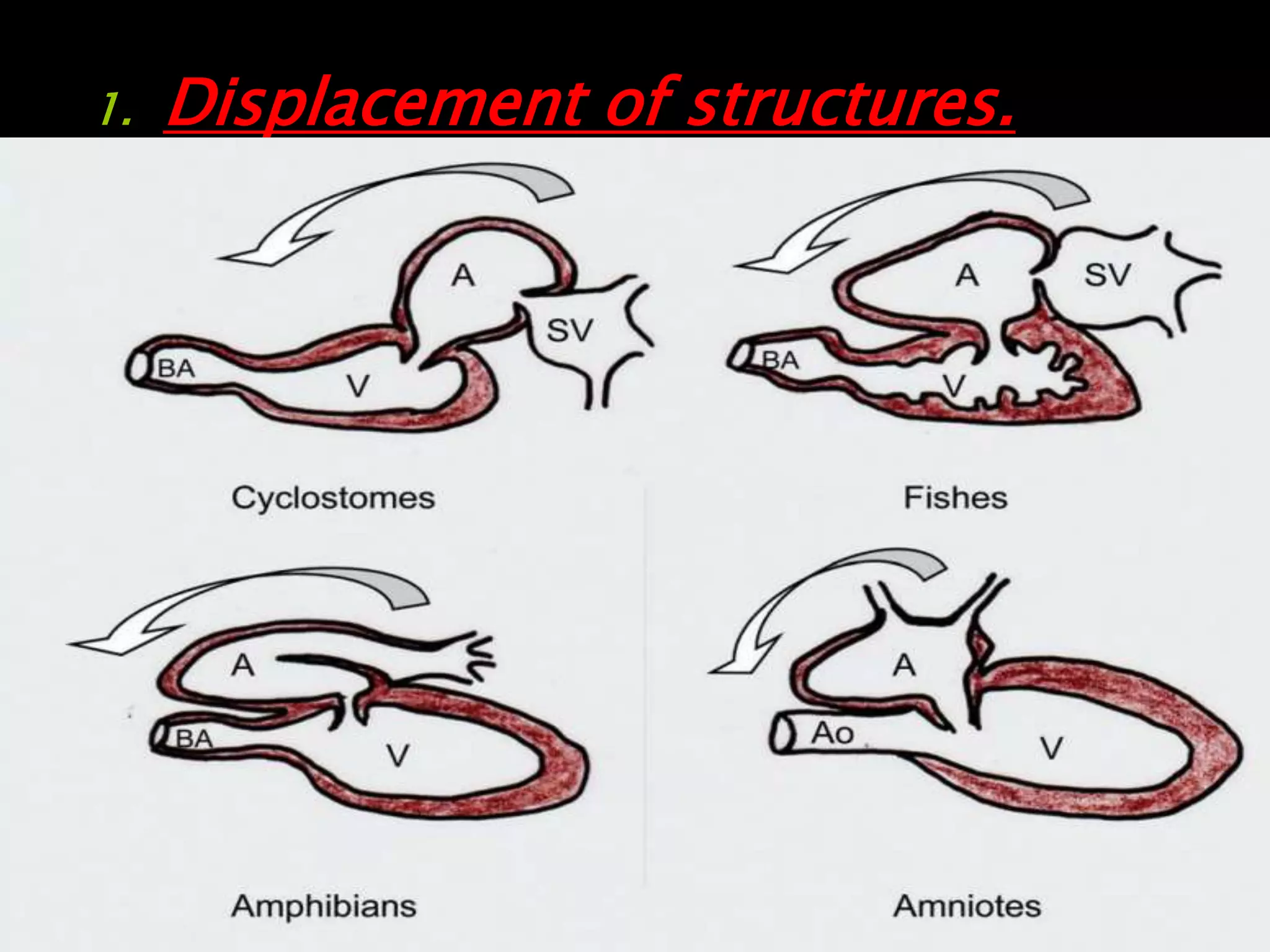
The document traces the evolution of the heart from simple to complex organisms. It begins with unicellular and simple multicellular organisms that lacked specialized cells, tissues, and organs. More complex invertebrates first developed specialized cells and muscular pumping in structures like sponges and jellyfish, representing early precursors to cardiac muscle cells. Vertebrates evolved with the first two-chambered hearts in fish and amphibians. Reptiles developed three-chambered hearts with two atria and one ventricle. Birds and mammals further evolved four-chambered hearts with two atria and two ventricles allowing for double circulation.