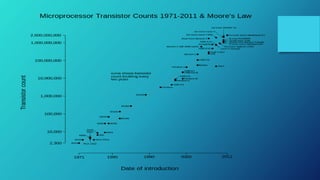
The document outlines the evolution of computers from early origins around 2400 B.C. to the fifth generation since 1980, highlighting advancements in technology, from vacuum tubes and transistors to integrated circuits and artificial intelligence. It also discusses significant milestones in game AI, particularly the challenges faced in mastering complex games like chess and Go, illustrating the progress towards achieving general artificial intelligence. Key developments include the advent of qubit technology in quantum computing and breakthroughs in learning algorithms, exemplified by the success of AlphaGo.