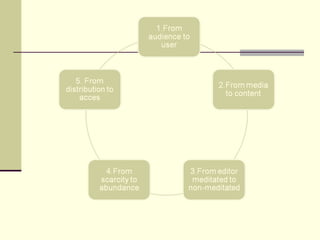
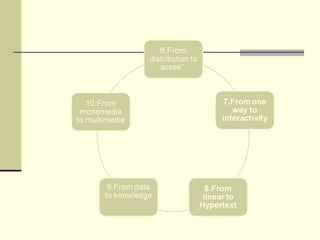
The document outlines 10 paradigms that have shifted from traditional media to digital media. It discusses shifts from audiences to users, from media to content, and from editor-mediated information to non-mediated user-generated content. It also notes shifts from scarcity to abundance of information, from linear structures to hypertext, and from receiving data to actively generating knowledge. The key shifts have been driven by the rise of the Internet and new technologies that allow for increased interactivity, personalization, and access to information on demand.