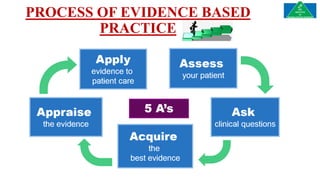
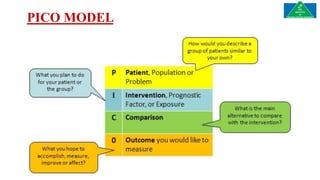
This document discusses the importance and process of evidence-based practice in the field of prosthetics and orthotics. It defines evidence-based practice as making clinical decisions based on the best available scientific evidence combined with clinical expertise and patient values. The process involves formulating a clinical question, locating relevant evidence, critically appraising the evidence, and applying it to patient care. Barriers to evidence-based practice in prosthetics and orthotics include lack of time, knowledge and administrative support. Overcoming these barriers requires educating practitioners, prioritizing evidence-based practice, and encouraging research in the field.