1. The document discusses the nursing process and its key steps: assessment, nursing diagnosis, planning, implementation, and evaluation. It emphasizes that critical thinking is essential for each step.
2. Key aspects of critical thinking discussed include reflection, intuition, problem-solving, decision-making, and developing critical thinking skills and attitudes.
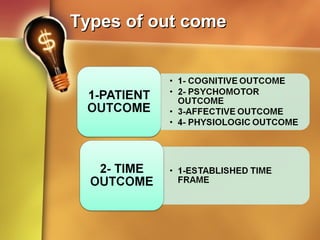
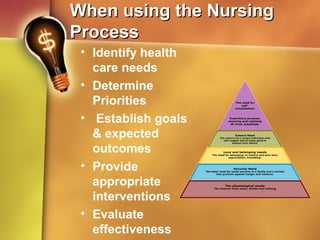
3. The nursing process provides a systematic framework for nurses to gather data, analyze it, identify issues, design goals and interventions, take action, and evaluate outcomes. It requires ongoing assessment, modification of the care plan as needed, and reevaluation until goals are met.