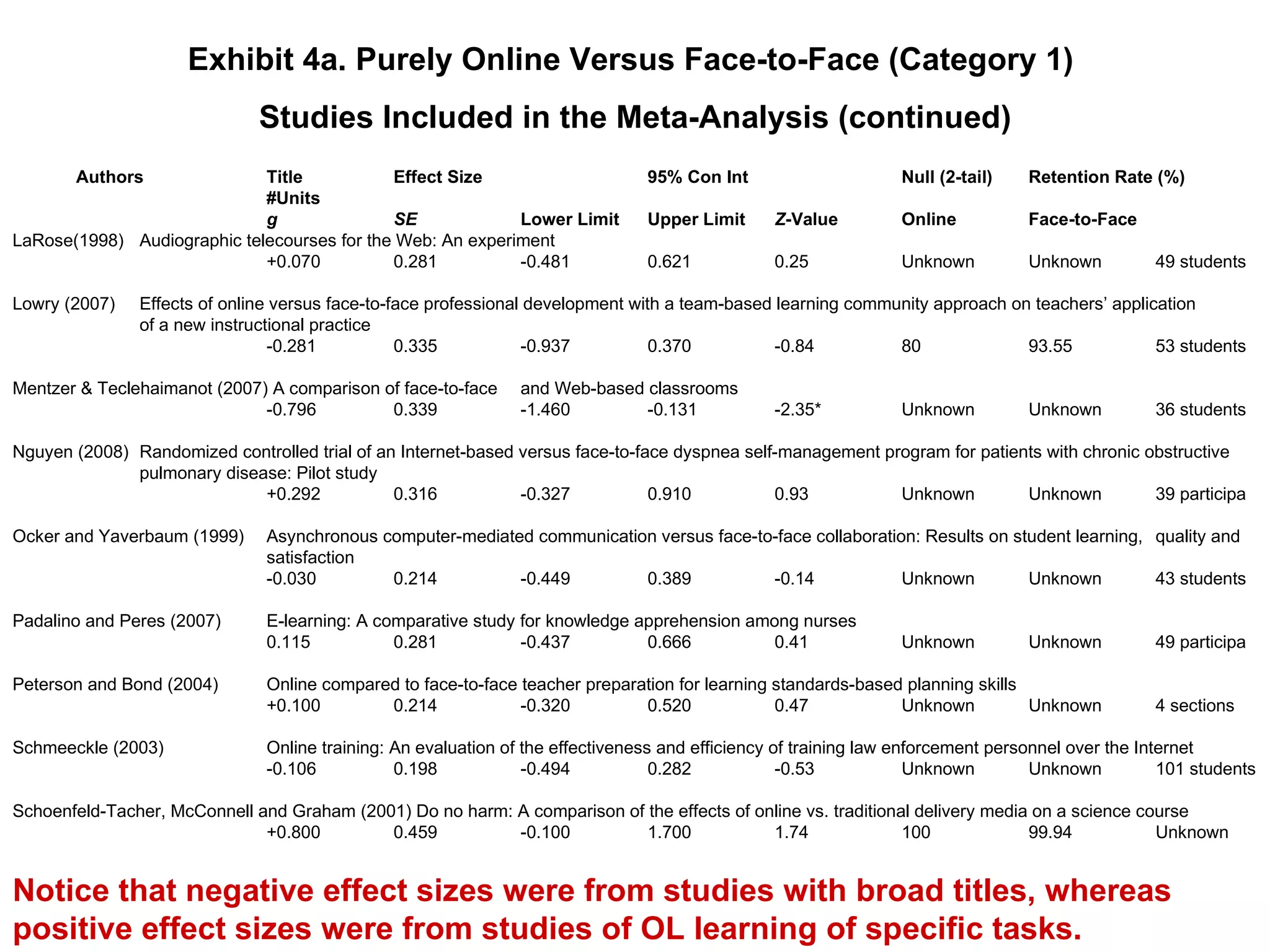
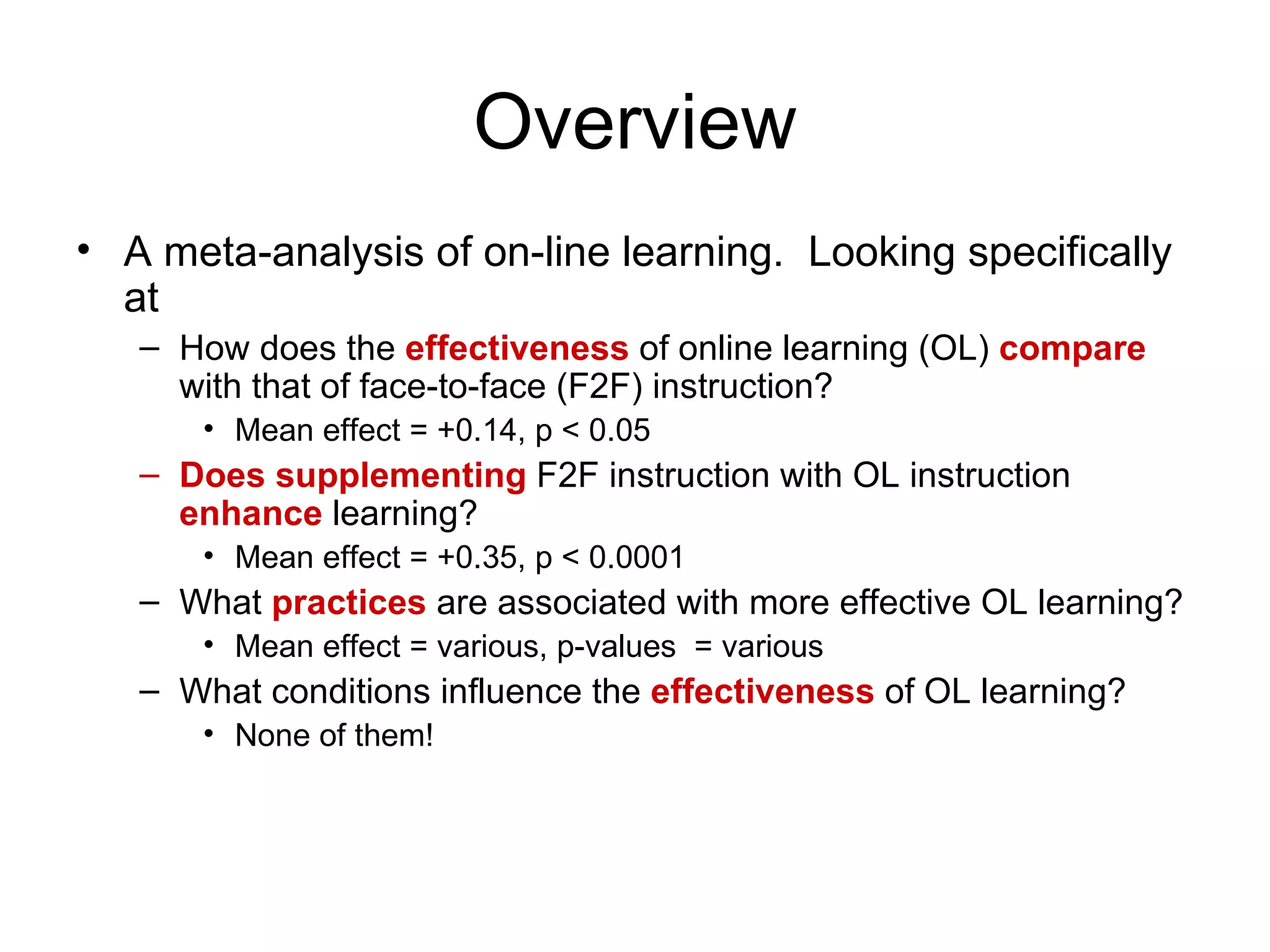
This meta-analysis reviewed research on online learning and compared its effectiveness to face-to-face instruction. It found that online learning was slightly more effective than face-to-face (average effect size of +0.14). Blended approaches with both online and face-to-face instruction were more effective than either alone (average effect size of +0.35). Certain practices like more time on task and learner reflection were associated with more effective online learning. The findings were limited by not being able to control for variables across studies.

![Observations The really want to find results for K-12, but alas-- (See caveats, page xii) Greatest effect for undergraduate and older students, but not K-12, secondary or graduate students. Weird. Hard to measure since time spent, pedagogy and curriculum are by definition different. “ [T]he studies . . . do not demonstrate that online learning is superior as a medium.” Page xvii “ Studies in which learners in the online condition spent more time on task than to students in the F2F condition found a greater benefit for online.” Duh. I’m seeing a creepy amount of p-values of 0.05. Trying too hard? Buried deeply is the definition of their effect sizes. Most as “smallish”.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/evaluationofevidence-basedpracticesinonlinelearning-100708123332-phpapp01/75/Evaluation-Of-Evidence-Based-Practices-In-Online-Learning-3-2048.jpg)