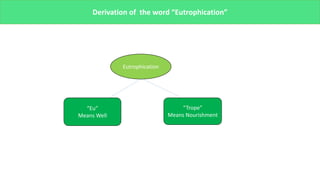
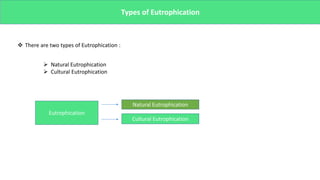
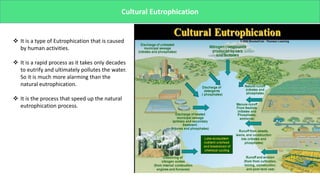
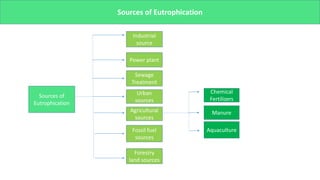
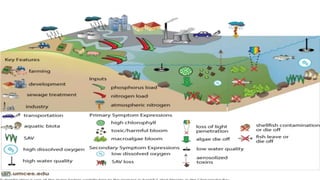
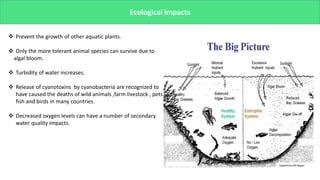
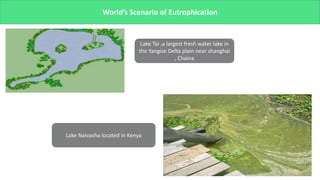
The presentation discusses microbial dynamics in eutrophication, which is primarily the result of excess nitrogen, phosphorus, and carbon in water bodies. It differentiates between natural eutrophication, a slow natural process, and cultural eutrophication, a rapid human-induced phenomenon that leads to water pollution. The document also addresses sources, ecological impacts, and scenarios of eutrophication globally and in specific regions, along with potential preventive measures.