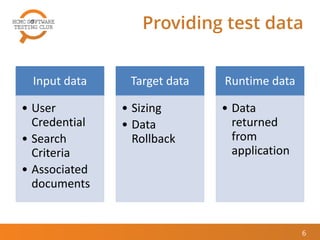
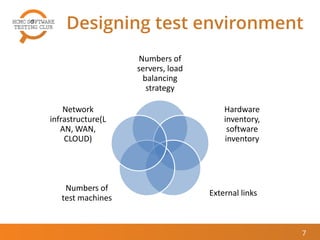
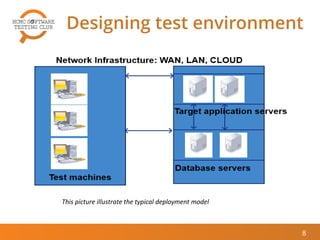
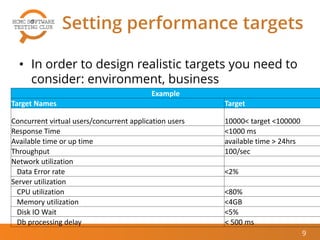
The document outlines best practices for performance testing, covering objectives, the identification of performance requirements, and designing test environments. It emphasizes the importance of establishing realistic performance targets, selecting appropriate testing tools, and executing various types of tests, including baseline and stress tests. The conclusion highlights that while performance testing can be challenging, it is also rewarding and beneficial for real-world applications.