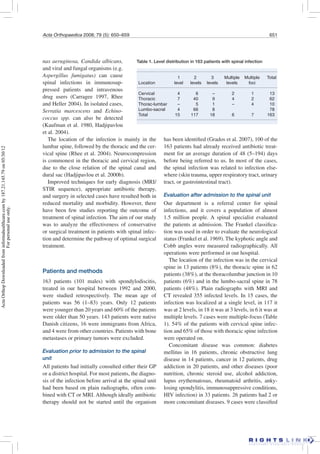
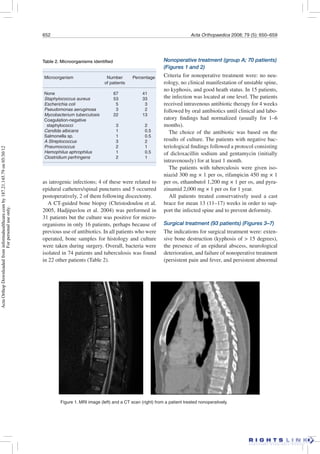
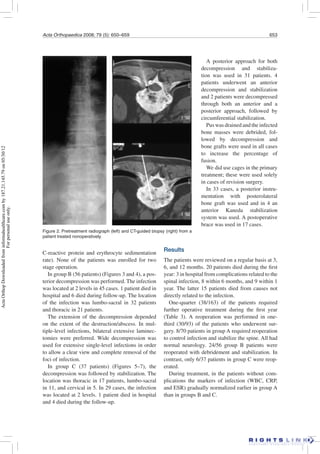
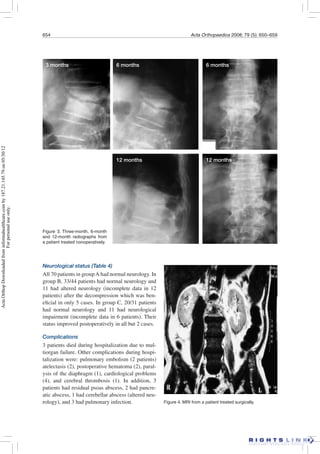
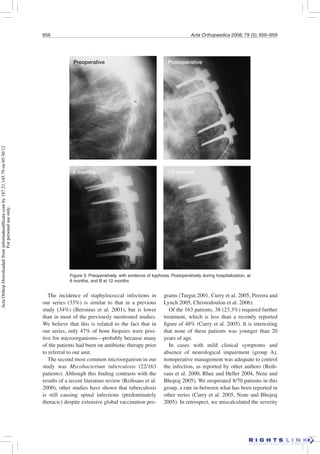
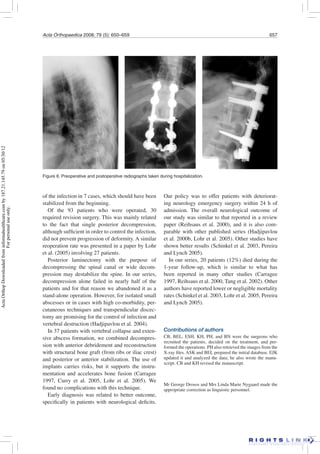
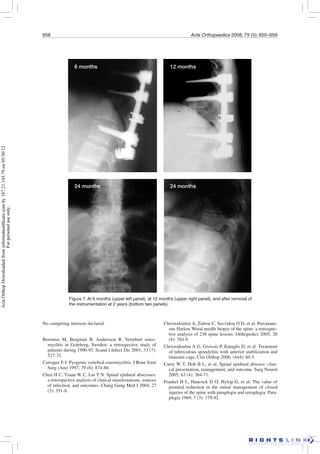
This study retrospectively analyzed 163 patients treated for spondylodiscitis (spinal infection) between 1992-2000. Patients were divided into 3 treatment groups:
Group A (70 patients) received non-operative treatment including antibiotics and bracing. 8 later required surgery.
Group B (56 patients) underwent posterior decompression alone. 24 later required additional surgery for debridement and stabilization.
Group C (37 patients) received decompression and internal stabilization. Only 6 later required re-operation.
Non-operative treatment was effective for most patients. Decompression alone had a higher re-operation rate compared to decompression with internal stabilization. Overall, surgical treatment improved neurological outcomes compared to non-