Embed presentation
Download to read offline


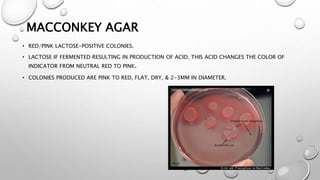


Eschericia coli (E. coli) is a rod-shaped bacterium commonly found in the intestines of warm-blooded organisms. E. coli strains are classified based on serological characteristics and virulence properties including enterotoxigenic E. coli, enteropathogenic E. coli, enteroinvasive E. coli, enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and enteroaggregative E. coli. On MacConkey agar, E. coli forms red or pink lactose-positive colonies due to acid production from lactose fermentation. On blood agar, E. coli colonies show no hemolysis but some pathogenic strains are beta-hemolytic, appearing smooth and gray, around




