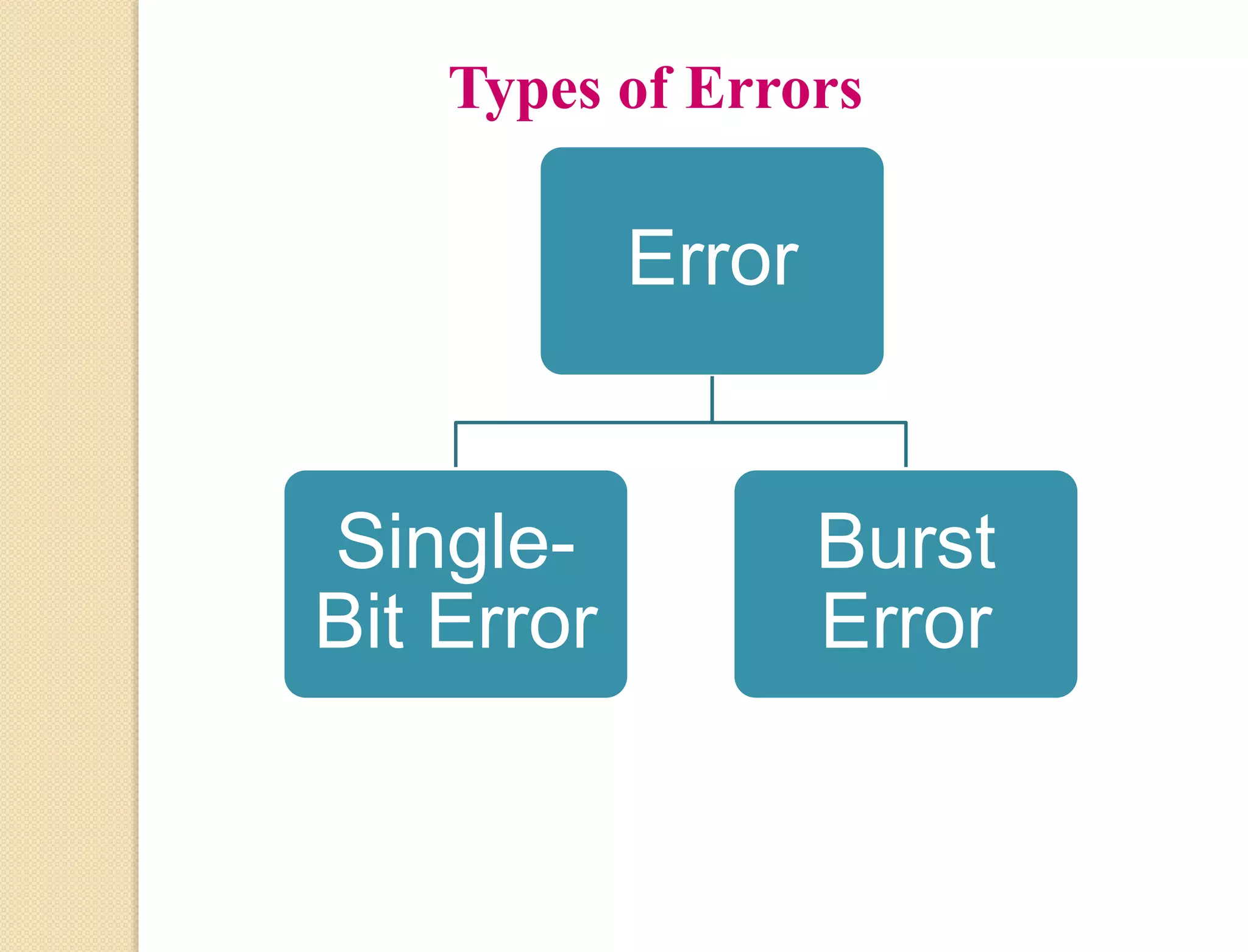
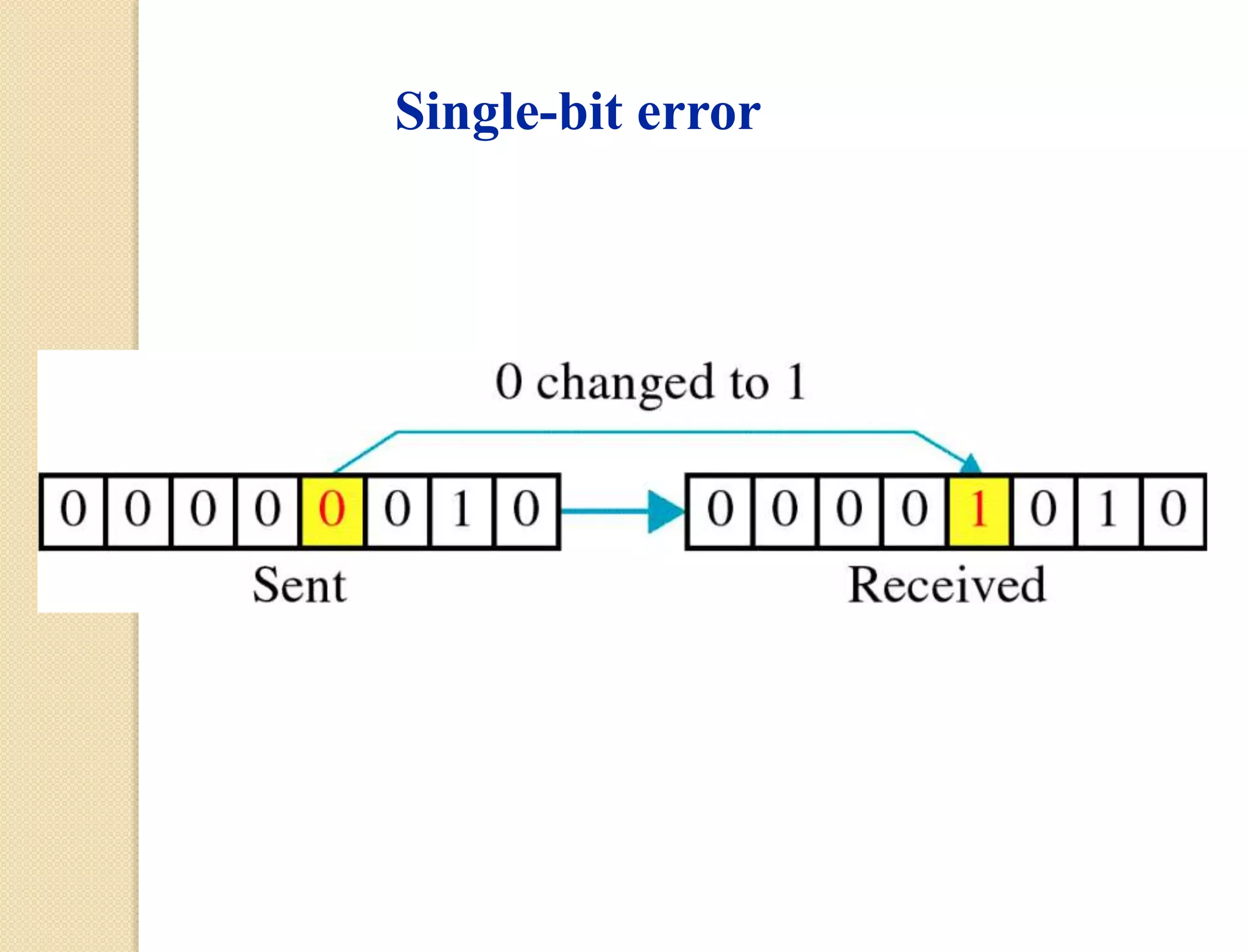
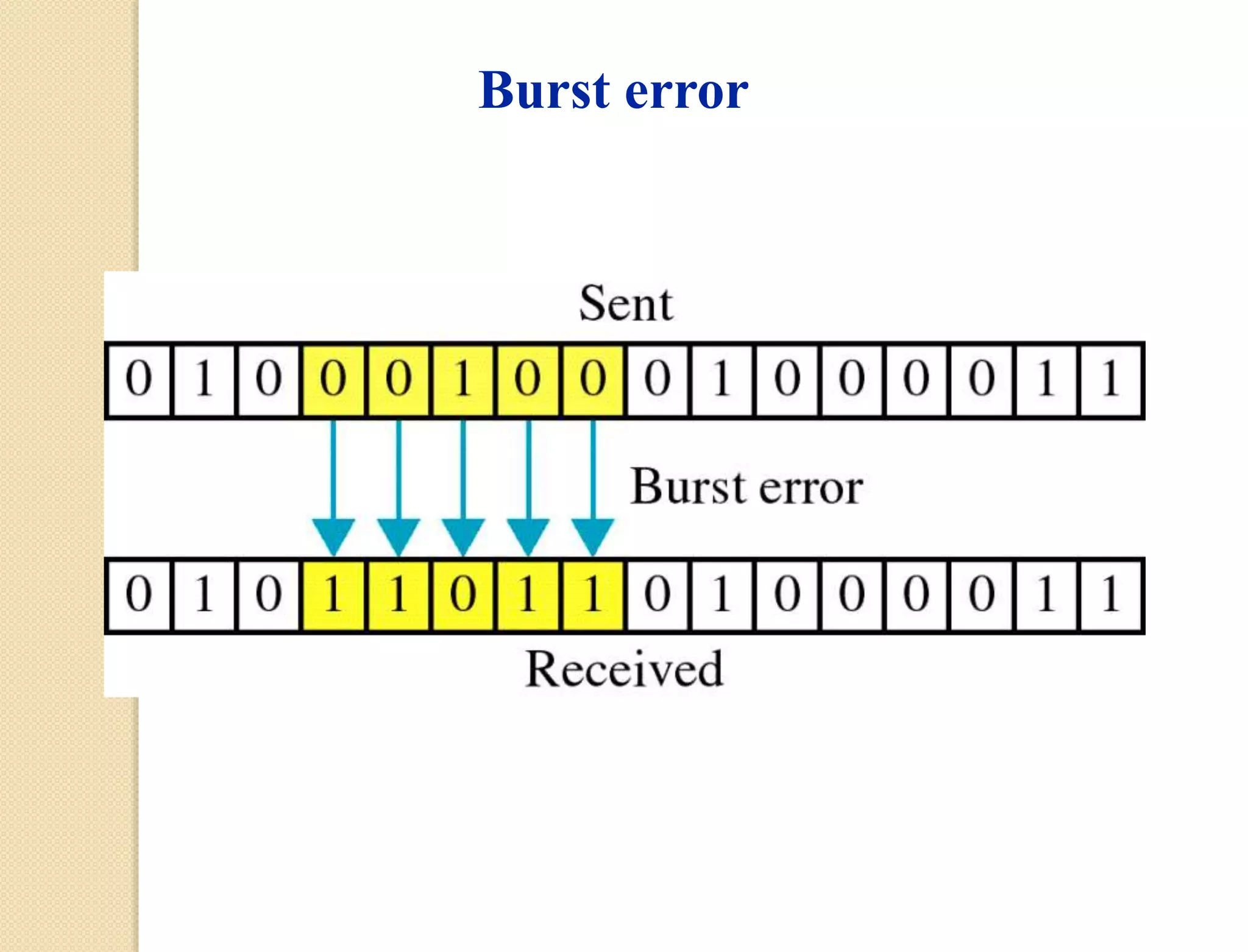
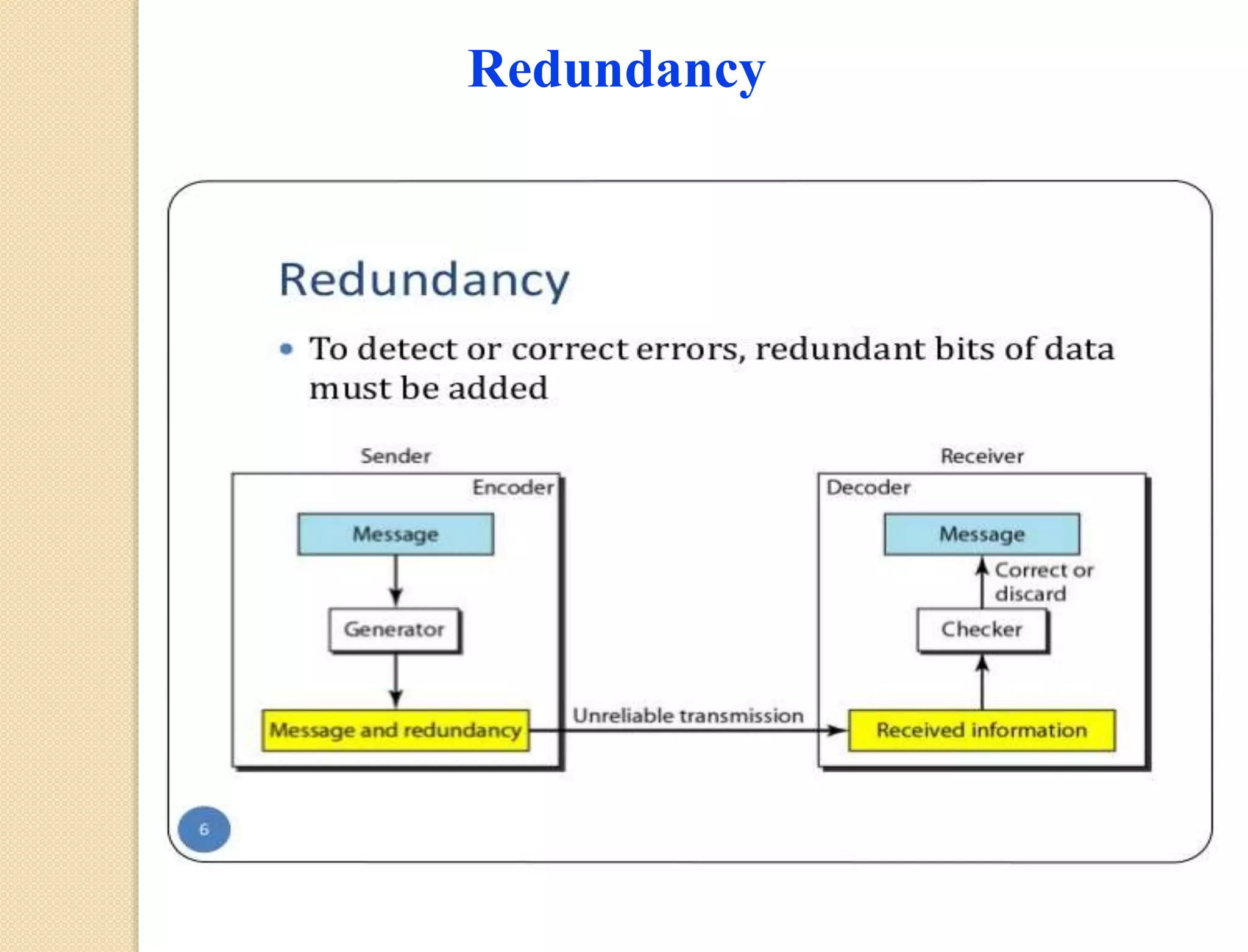
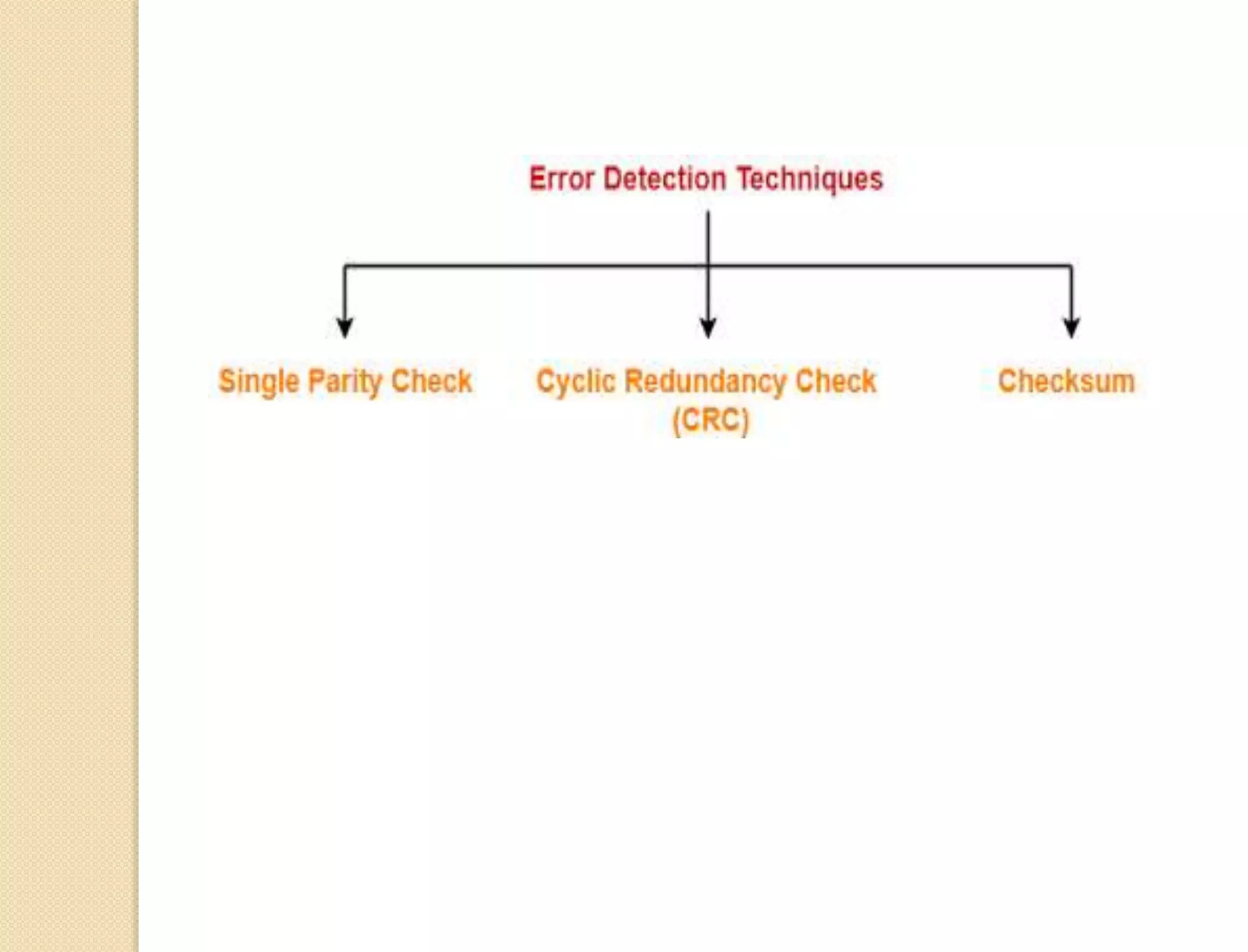
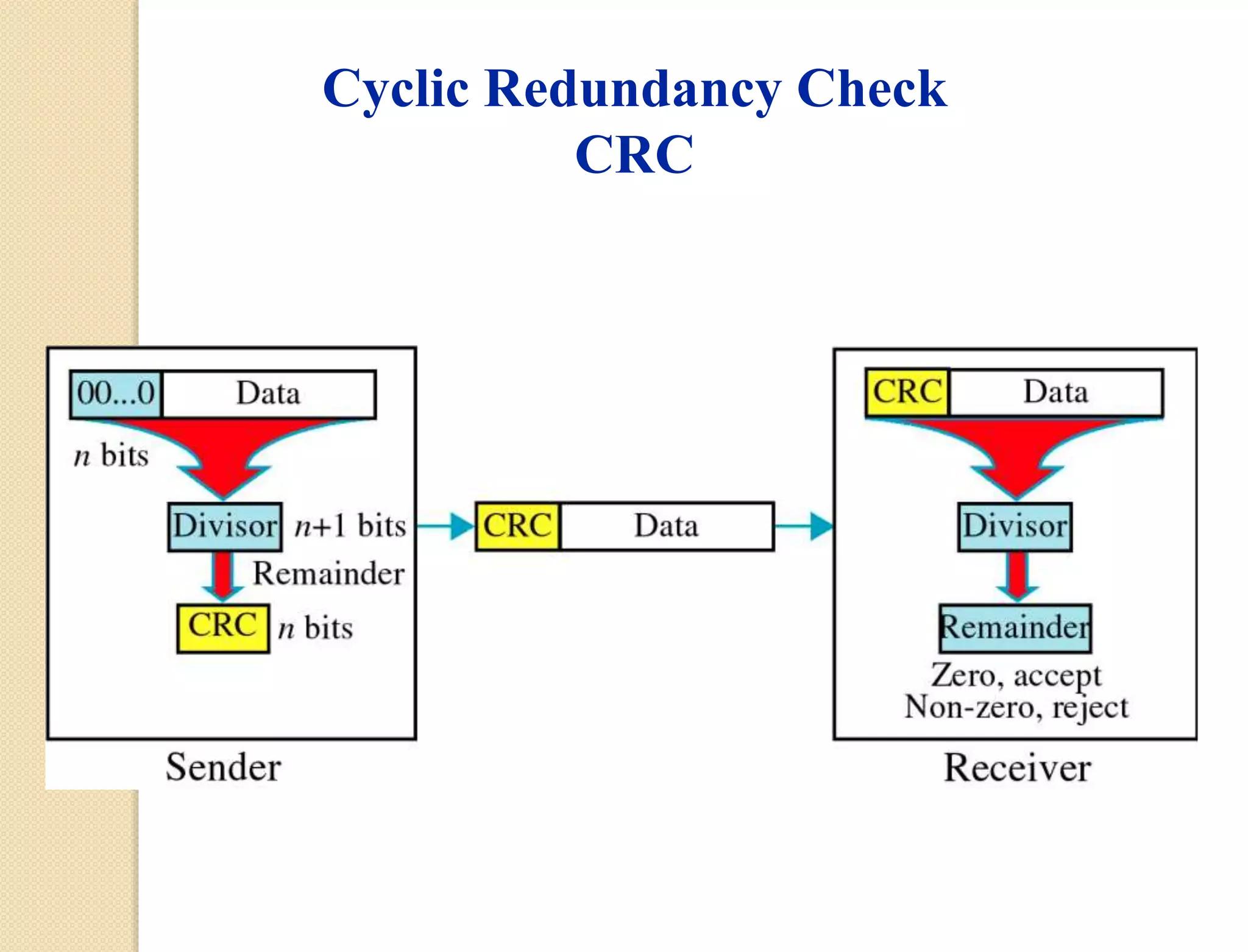
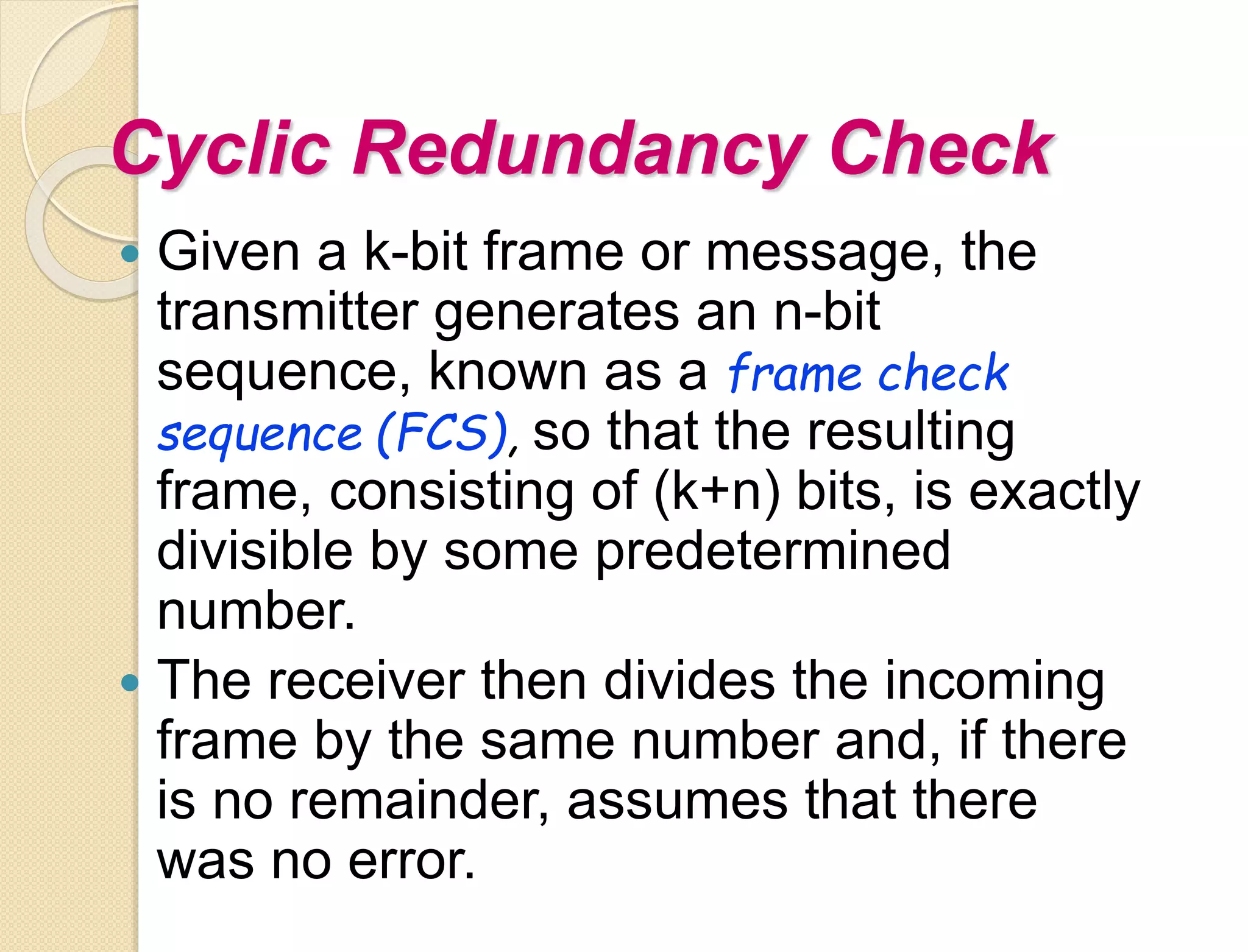
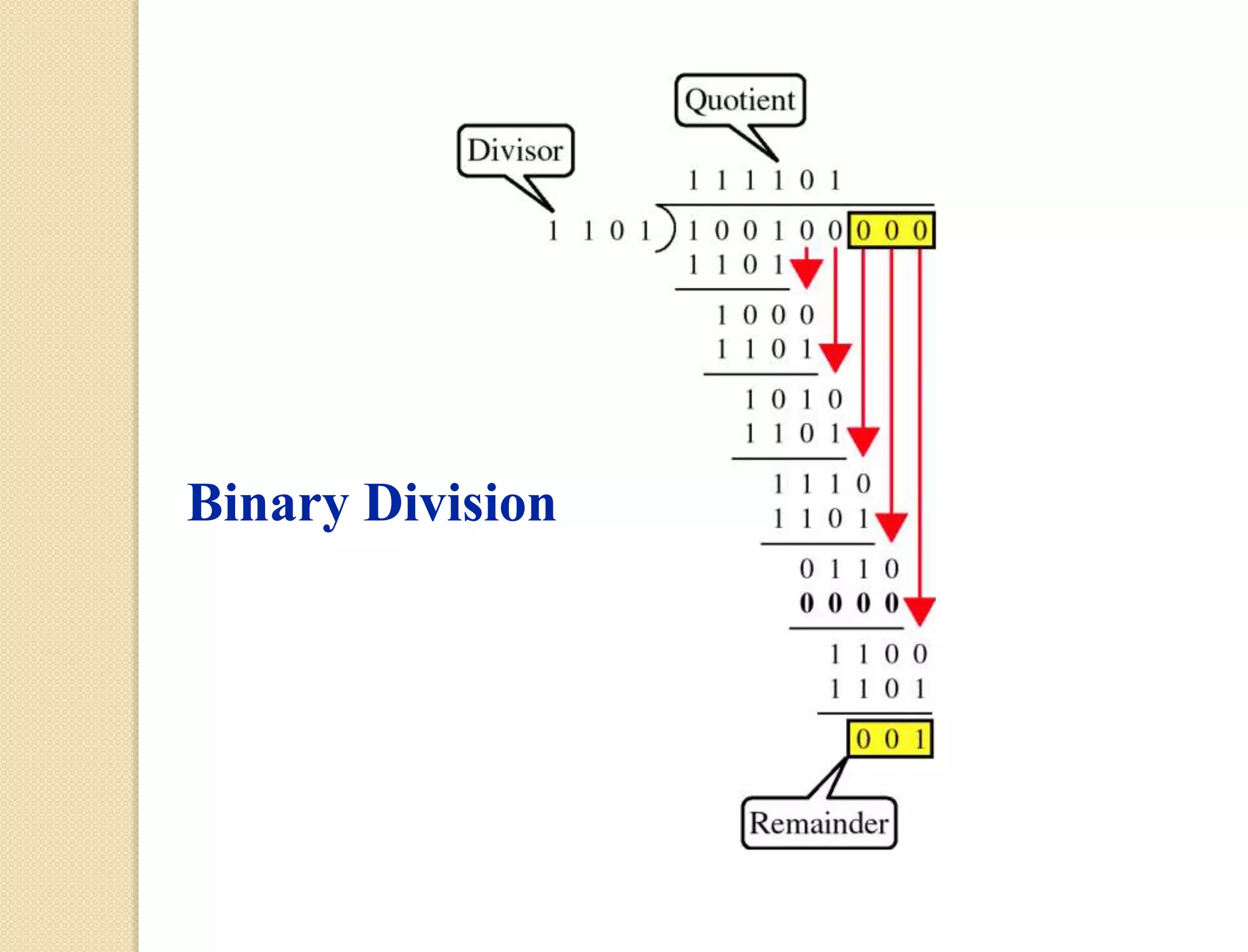
This document discusses error detection techniques used in data transmission. It describes two types of errors: single-bit errors and burst errors. It then explains error detection, which determines if received data is correct without having the original message. Error detection uses redundancy by adding extra bits. Common error detection techniques discussed include cyclic redundancy check (CRC), which generates a frame check sequence so the frame is divisible by a number, and checksums, where sections of data are added together and complemented to check for errors.