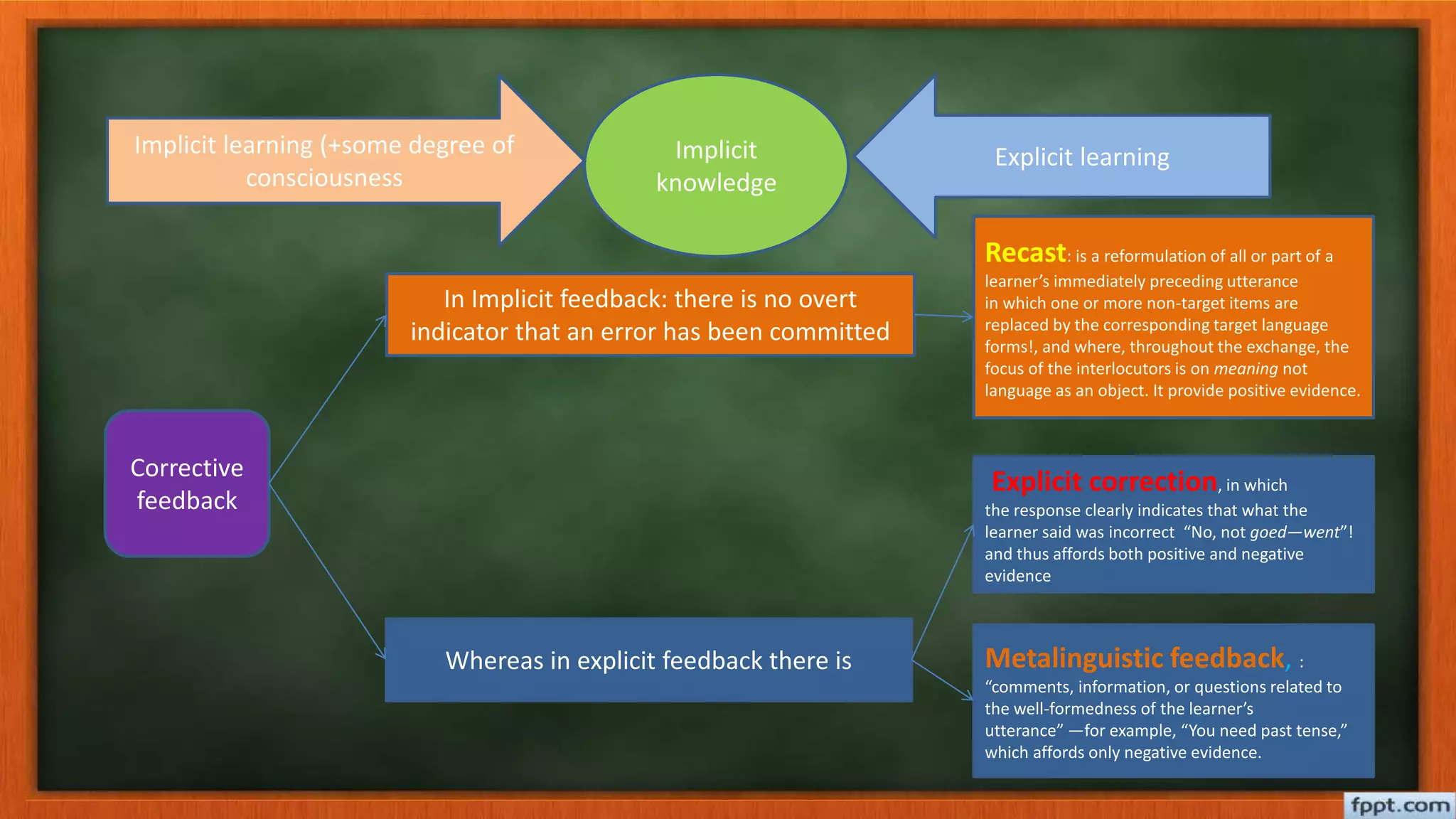
The document discusses error correction in language learning, outlining different types of errors and the distinction between implicit and explicit feedback methods. It details various techniques for correcting errors, such as recasts and metalinguistic feedback, while also critiquing a sample writing assignment for length and accuracy. The conclusion highlights the importance of knowing what, when, and how to correct errors in order to improve language skills effectively.