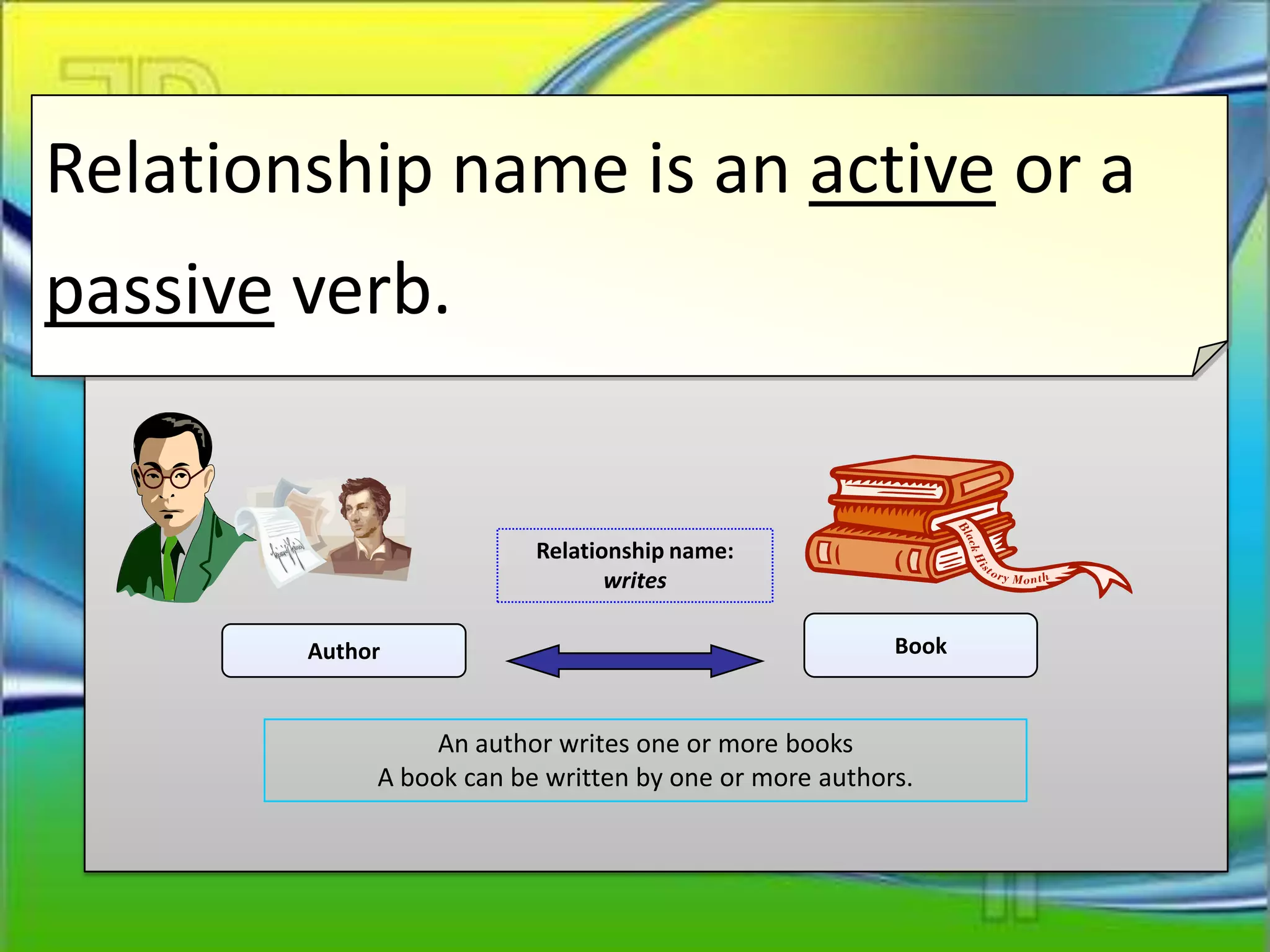
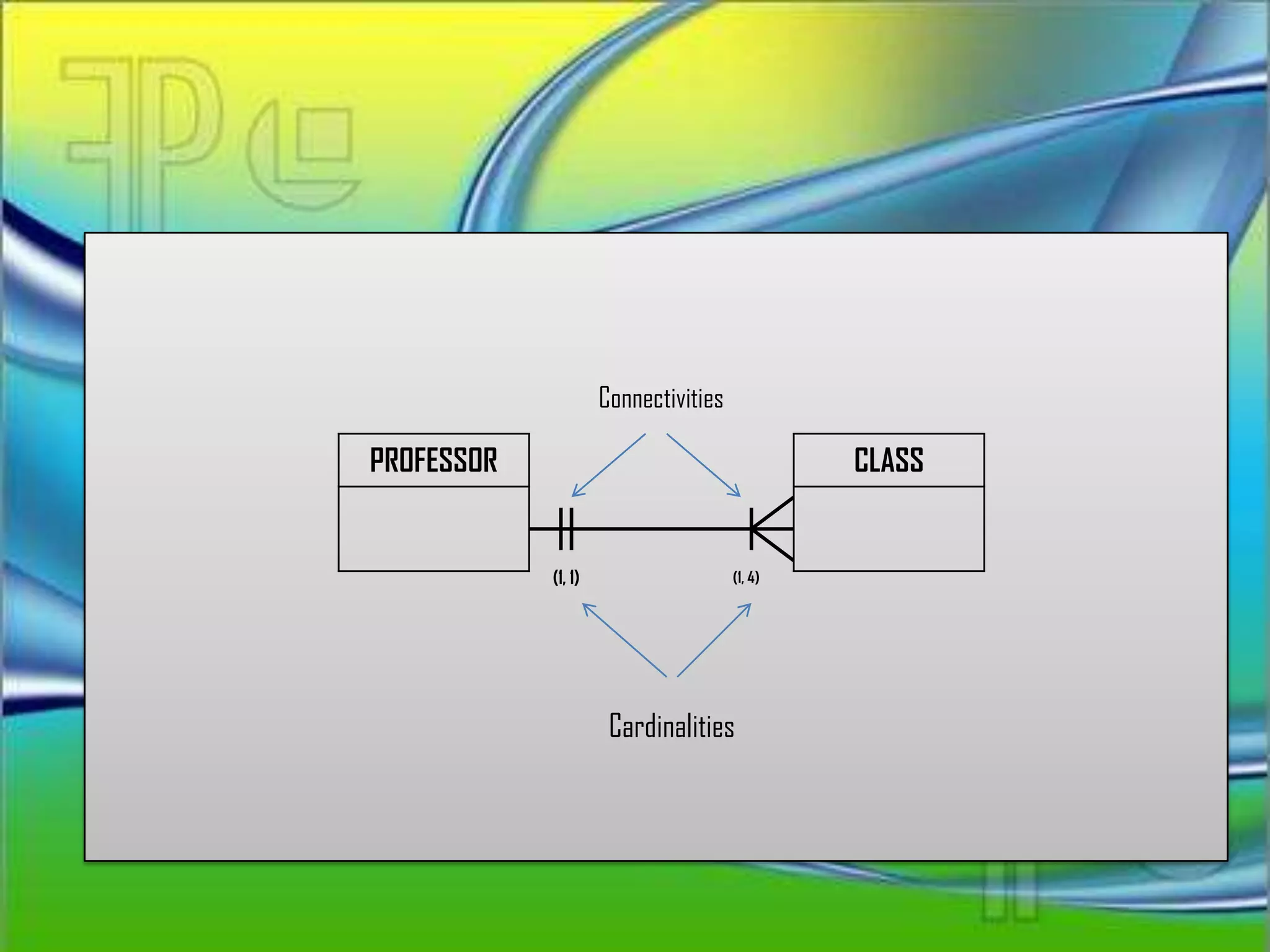
The Entity Relationship Model document defines key concepts in entity relationship modeling including:
Entities correspond to tables in a relational database. Attributes can be required, optional, single-valued, or multi-valued. Domains define possible attribute values. Primary keys uniquely identify entities. Relationships connect entities and have names, connectivity, and cardinality defining the minimum and maximum associated entities. Relationships, attributes, and entities are essential components of entity relationship modeling.