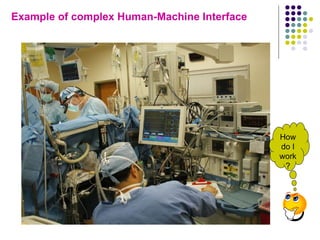
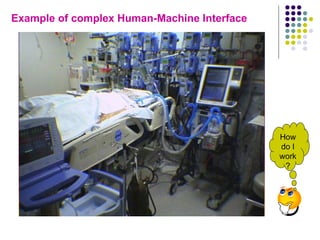
The document provides an overview of human factors engineering (HFE) and its importance, particularly in the field of biomedical engineering. It covers definitions, applications, and types of ergonomics, alongside the benefits of implementing ergonomic principles in design processes. It emphasizes the role of ergonomics in improving productivity, safety, and health, ultimately leading to cost savings and enhanced user satisfaction.