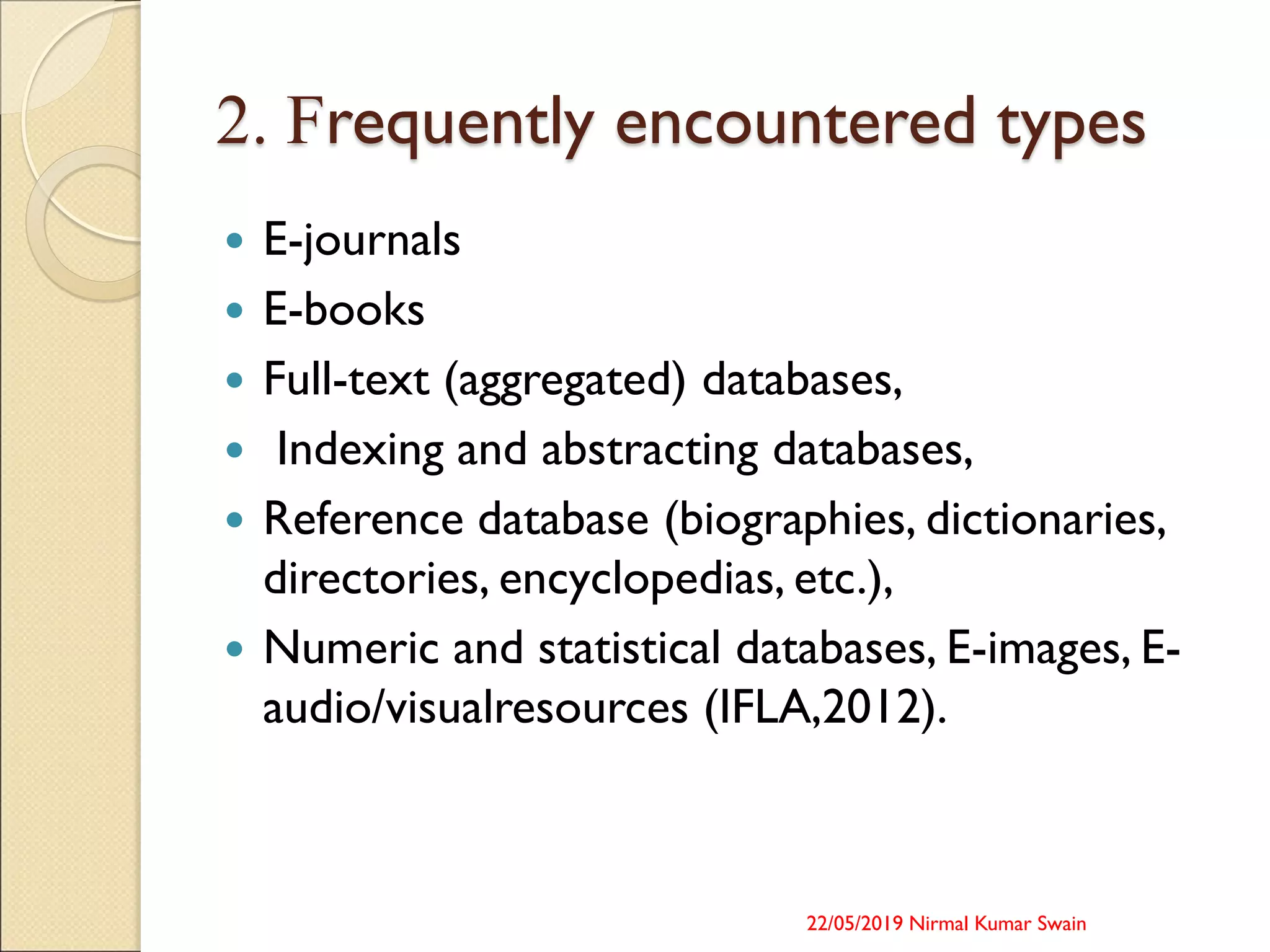
The lecture by Dr. Nirmal Kumar Swain at the refresher course addresses the digitalization of education in India, focusing on e-resources, their definitions, types, and technical configurations. It highlights the importance of open access resources and initiatives in India, while also discussing concerns like the digital divide and accessibility issues. The session emphasizes the need for inclusive policies and resources across various universities.