The document provides an overview of equity investments and security markets. It discusses various topics including types of capital markets, structure of securities exchanges, types of orders and margin transactions. It also summarizes key concepts related to stock market indices, market efficiency, security valuation techniques, industry and company analysis factors that affect stock valuation. The document is aimed to educate readers on fundamentals of equity investments and security analysis.







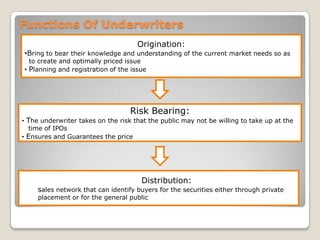







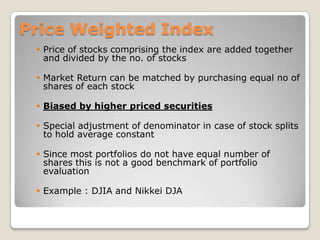
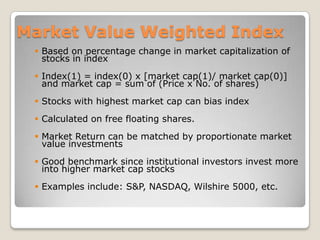















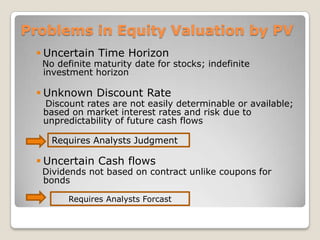











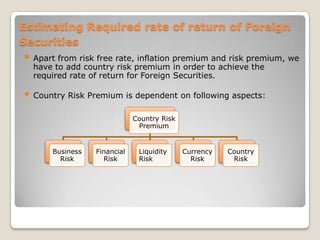

















![Index(1) = index(0) x [market cap(1)/ market cap(0)] and market cap = sum of (Price x No. of shares)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/newequity-110529145807-phpapp01/85/Equity-Investments-63-320.jpg)









