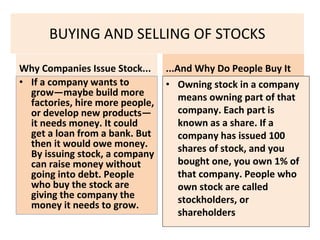
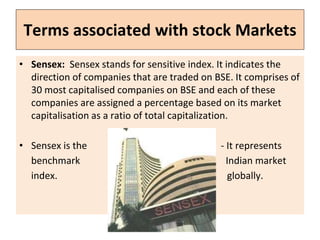
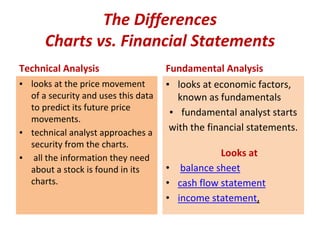
The document provides an overview of the stock market and key concepts related to technical analysis. It defines the stock market as the business of buying and selling shares of companies and explains why companies issue stock and why people buy it. It then discusses key technical analysis concepts like bulls and bears, trends in prices, and the three assumptions of technical analysis - that the market discounts everything, price moves in trends, and history tends to repeat itself. It also compares technical analysis to fundamental analysis and their differences in terms of time horizon and goals.