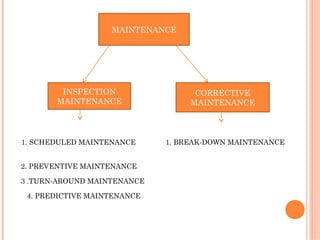
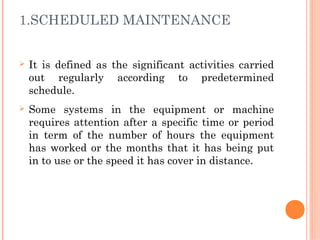
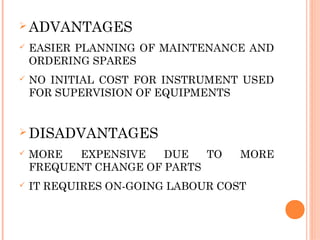
This document defines and describes various types of equipment maintenance. It discusses scheduled maintenance, preventative maintenance, turn-around maintenance, predictive maintenance, inspection maintenance, corrective maintenance, and breakdown maintenance. The objectives of maintenance are listed as optimizing utilization, cost effectiveness, prolonging equipment life, and ensuring safety. Maintenance scopes include operational efficiency, updated equipment records, and anticipating spare part needs.