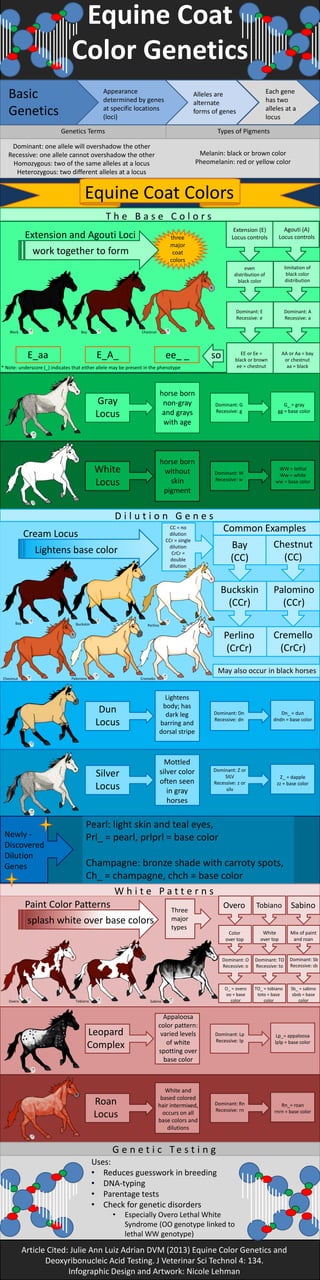
This document summarizes equine coat color genetics. It defines key genetics terms and describes the loci and alleles that determine the major base coat colors like black, bay, chestnut and gray. It also explains the dilution genes that produce colors like buckskin, palomino and cremello. Finally, it outlines the genetics behind white patterns like overo, tobiano and sabino as well as other coat patterns like leopard complex, roan and dun. Genetic testing can be used to identify an horse's coat color and pattern genes to aid in selective breeding and check for potential genetic disorders.