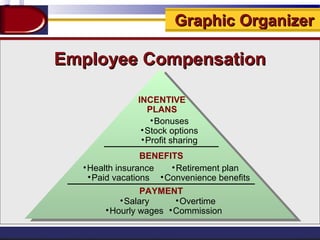
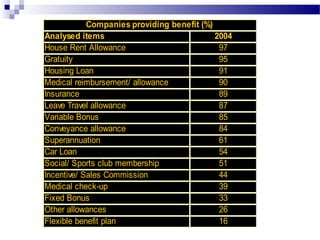
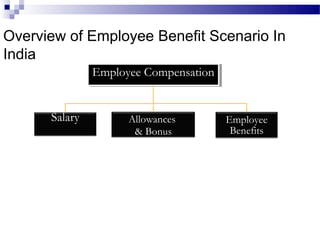
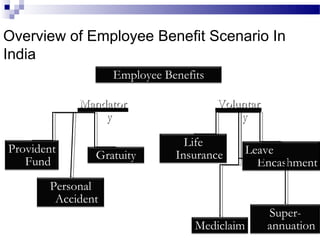
This document discusses equal employment opportunity (EEO) and issues related to compensation policies. It begins by defining EEO and outlining major anti-discrimination laws like Title VII and the Equal Pay Act. It then defines different types of discrimination and discusses workplace harassment. The document provides an overview of compensation, including direct, indirect, and non-monetary compensation. It also discusses legally required benefits like workers' compensation and social security as well as security and retirement benefits and health coverage. Finally, it analyzes India's employee benefit scenario and compensation structure at Pipavav shipyard.