Embed presentation
Download to read offline

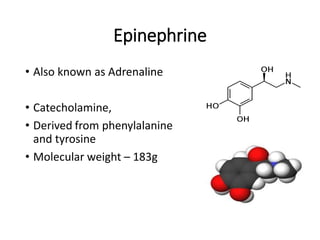
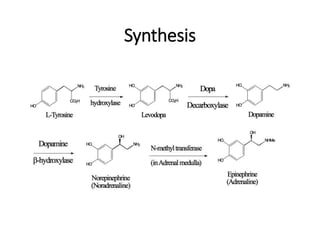
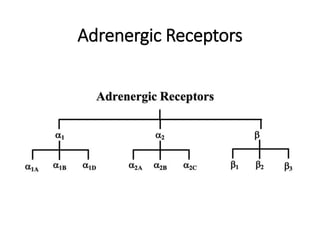
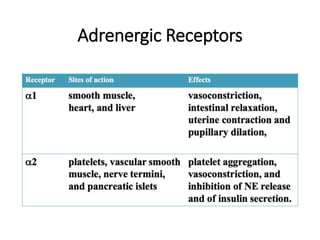
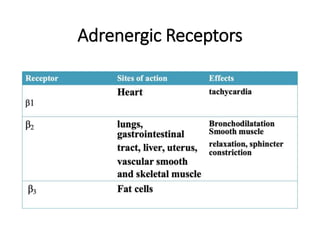
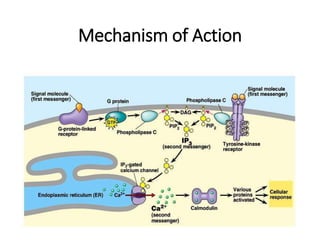
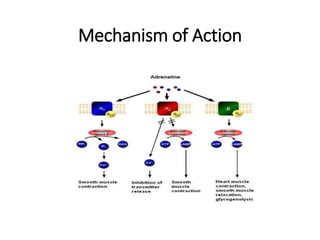







The document discusses two catecholamine neurotransmitters, epinephrine and norepinephrine. Epinephrine, also known as adrenaline, is synthesized from phenylalanine and tyrosine and has a molecular weight of 183g. It is used to treat resuscitation, anaphylaxis, hypotension, shock, and asthma. Norepinephrine also acts as both a hormone and neurotransmitter and is involved in the stress response and fight-or-flight response by increasing heart rate, releasing glucose, and increasing blood flow to muscles. It has potent actions on both alpha-1 and beta-1 receptors.














