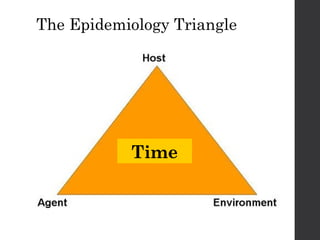
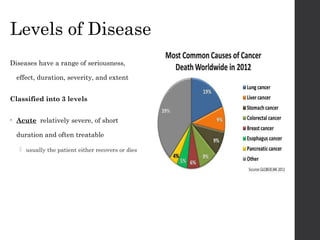
Epidemiology is the study of diseases within populations and the factors that influence their distribution. It involves investigating disease outbreaks and characterizing diseases based on affected groups. The major purpose is to study the root causes of diseases to provide a basis for prevention and control. A key concept is the epidemiology triangle, which shows the interrelationship between an agent, host, environment, and time in causing disease outbreaks. Breaking one leg of the triangle can help stop epidemics. Diseases are transmitted directly from person to person or indirectly through vectors or environments. Epidemics can be propagated or mixed. Diseases vary in severity from acute to chronic. Vaccines exist to prevent many infectious diseases.