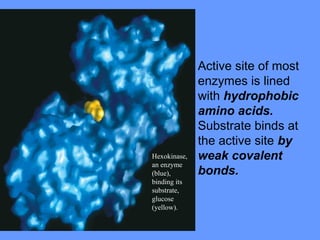
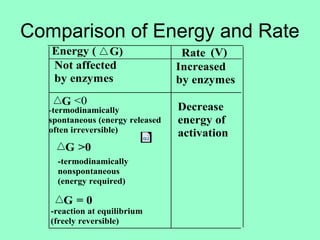
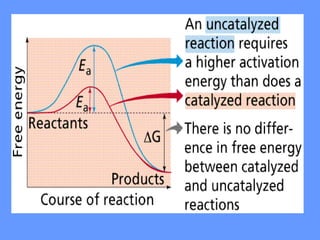
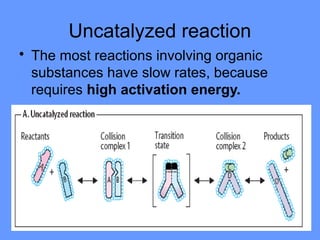
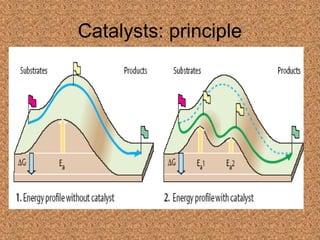
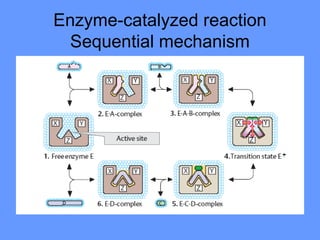
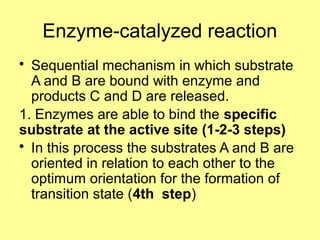
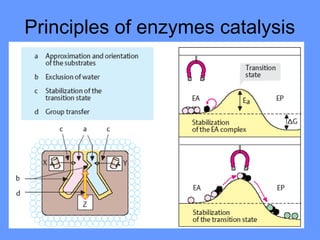
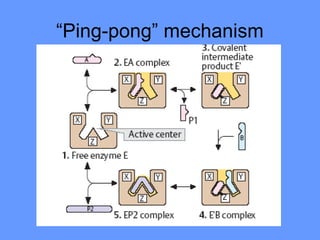
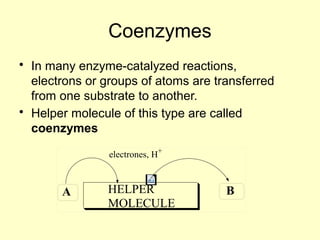
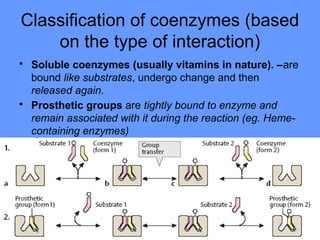
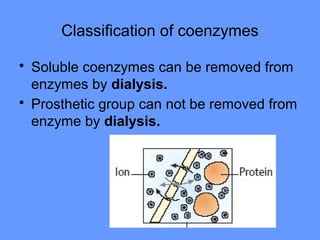
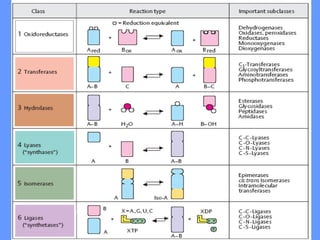
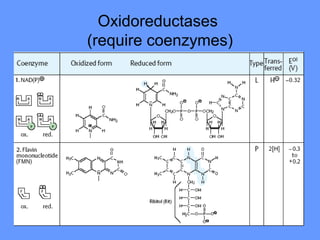
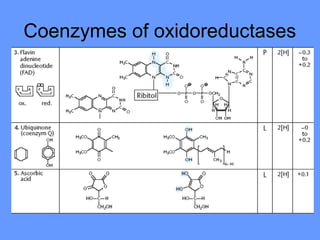
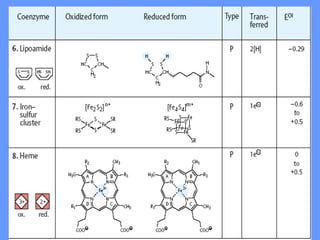
This document discusses enzymes and their mechanisms of action. It defines enzymes as protein catalysts that speed up chemical reactions. All enzymes have an active site where substrates bind. Enzymes decrease the activation energy needed for reactions to occur by properly orienting substrates. This allows reactions to proceed more rapidly. The document contrasts uncatalyzed reactions, which require high activation energies due to hydrated substrates, with enzyme-catalyzed reactions. It describes several mechanisms by which enzymes catalyze reactions, such as sequentially binding substrates and releasing products or forming covalent intermediates. Coenzymes, which transfer atoms or electrons, are also discussed. Coenzymes can be either soluble vitamins that dissociate from enzymes or prosthetic