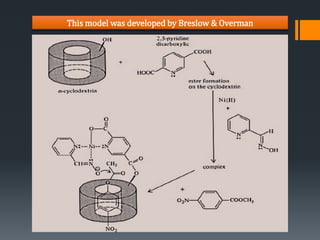
The document presents information on enzyme models. It discusses how enzyme models are synthetic molecules that contain features of enzymatic systems and mimic biological reactions. Examples of molecules used to create models include crown ethers, micelles, ionophores, and cyclodextrins. Cyclodextrins are particularly effective models as their cavity can facilitate reactions like selective substitution and ester hydrolysis in a similar way to enzymes. The document concludes that effective enzyme models exhibit hydrophobic interactions for substrate binding, provide a medium effect through proper polarity, and induce orientation effects through conformational restriction.