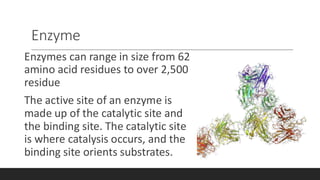
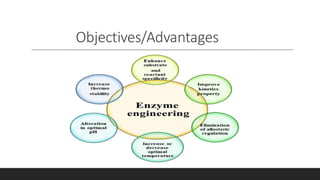
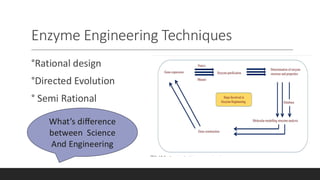
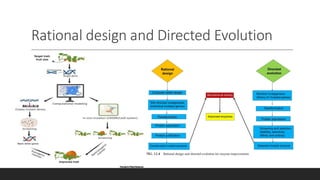
Enzyme engineering involves modifying enzymes to enhance their activity and utility by changing their amino acid sequences. This field has significant industrial applications, optimizing processes in pharmaceuticals, biofuels, and fine chemicals by increasing enzyme stability, specificity, and catalytic efficiency. Recent advancements include directed evolution techniques, which have led to notable increases in production yields and enzyme performance.