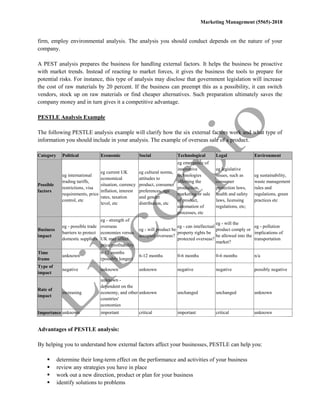
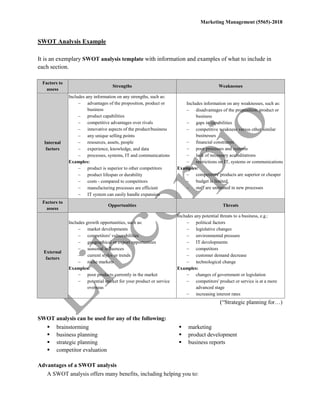
The document discusses the importance of environmental and SWOT analyses in marketing management, highlighting their roles in understanding both external and internal factors affecting businesses. Environmental analysis focuses on external influences using tools like PESTLE, while SWOT analysis examines strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats by integrating both internal and external components. Together, these analyses aid companies in strategic planning and decision-making to navigate market challenges effectively.