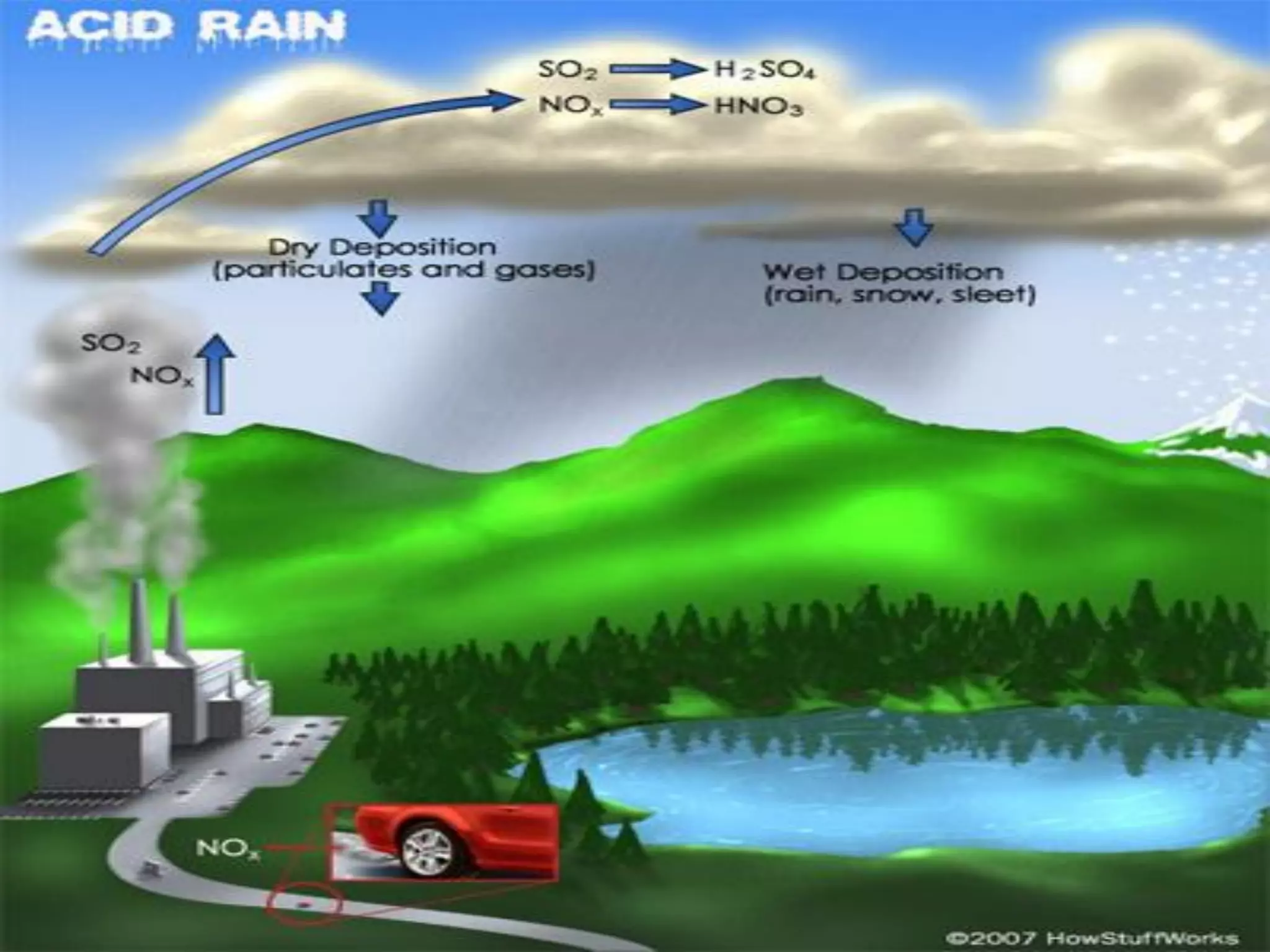
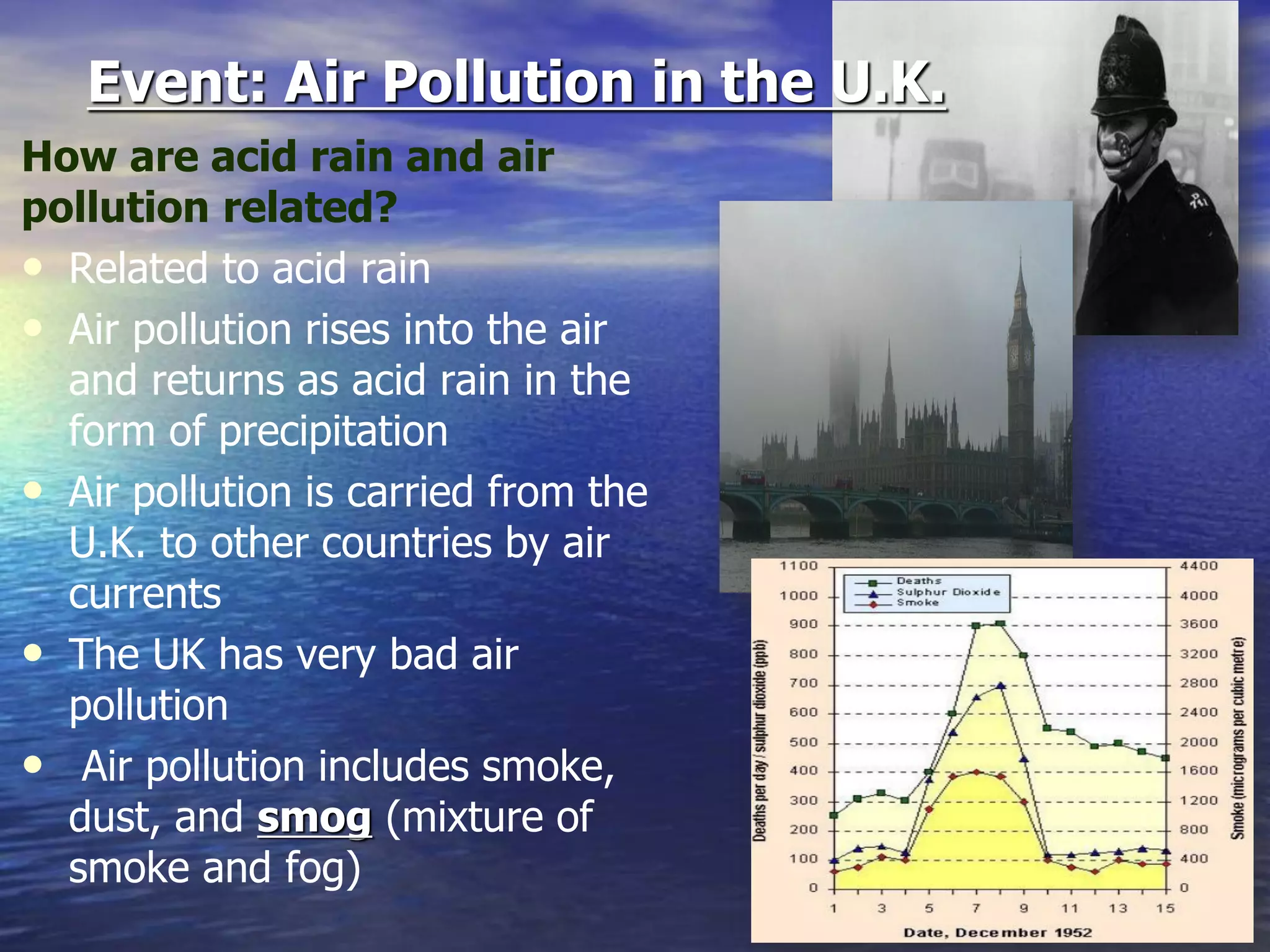
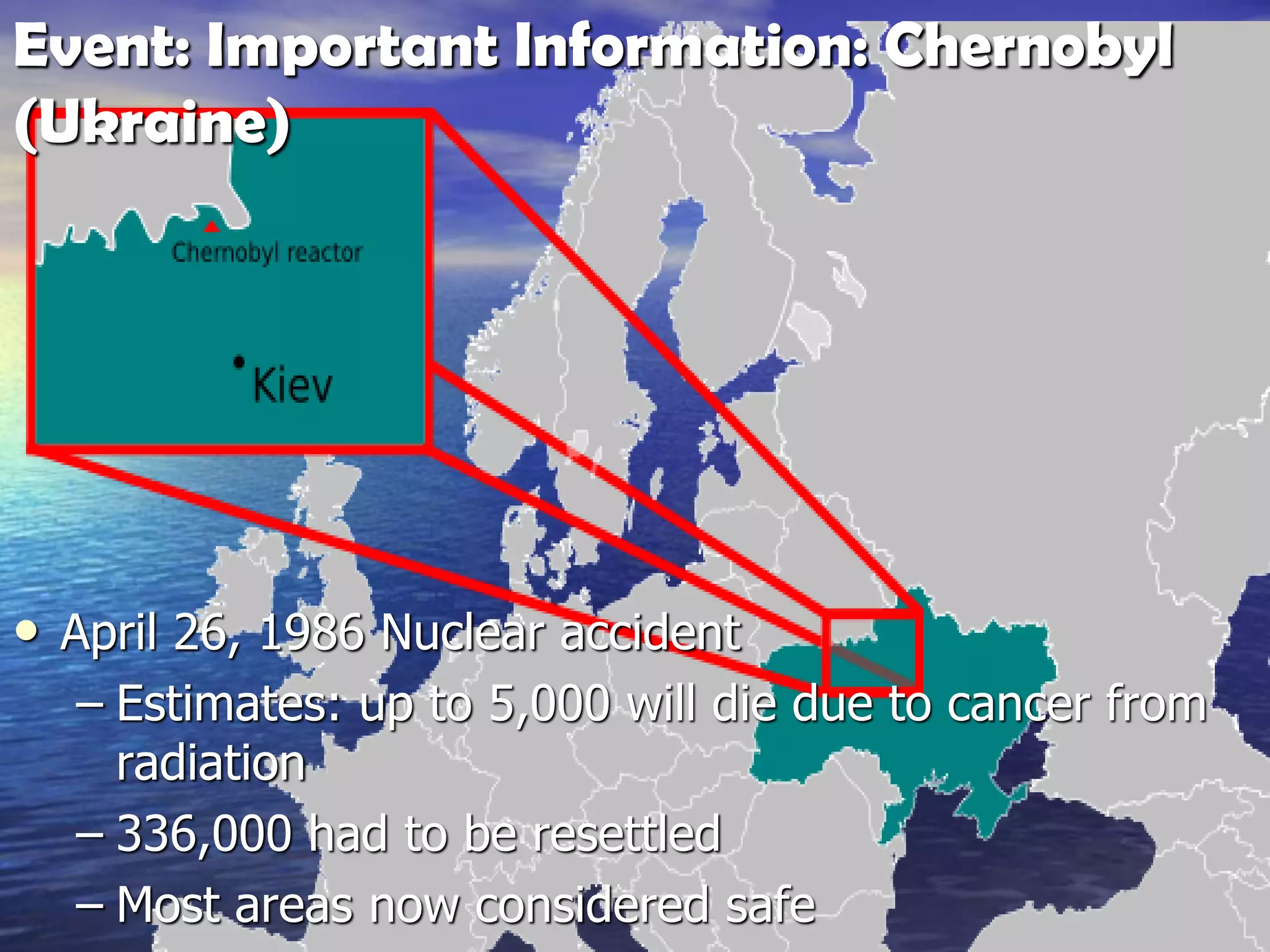
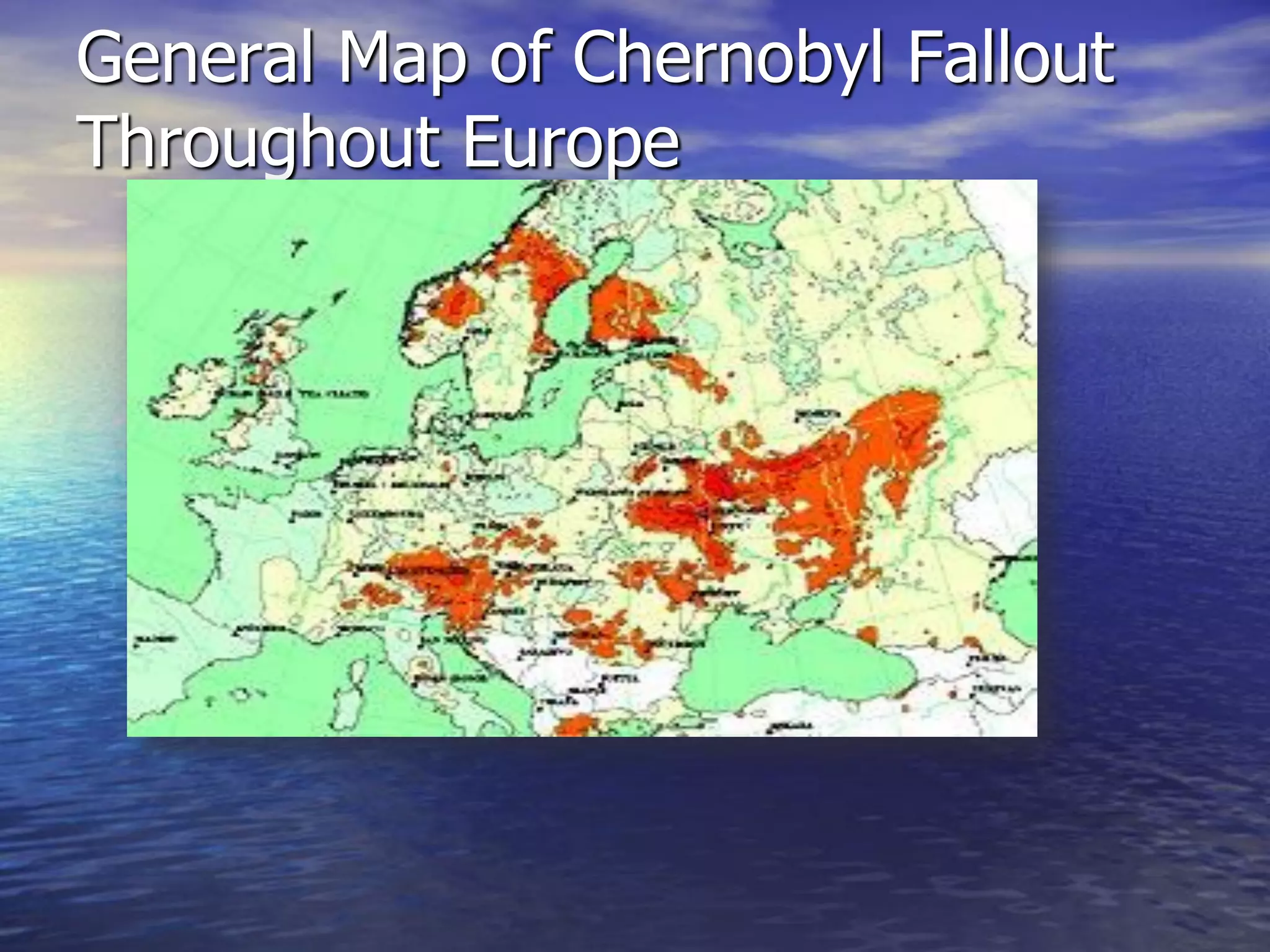
The document discusses three major environmental issues in Europe: acid rain in Germany, air pollution in the United Kingdom, and the Chernobyl nuclear disaster in Ukraine. Acid rain in Germany was caused by vehicle and factory emissions releasing sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides into the atmosphere. This resulted in acid rain that damaged forests and buildings and killed wildlife. Germany has taken strong action through emissions laws and alternative energy use to reduce acid rain. Air pollution in the UK was caused by coal burning and vehicle emissions, releasing smoke and smog that damaged plants, wildlife, and human health. Solutions included monitoring air quality and reducing vehicle use. Finally, the Chernobyl nuclear disaster occurred due to reactor defects and poor safety practices, contamin